Early Warning Signs of Testicular Cancer: What Men Need to Know
This article provides an in-depth guide to recognizing the early signs of testicular cancer, emphasizing the importance of prompt detection for effective treatment. It discusses key symptoms such as lumps, swelling, pain, and hormonal changes, along with risk factors and diagnostic methods. Early diagnosis significantly improves prognosis and survival rates, making awareness crucial for men's health. Regular self-examinations and medical check-ups are vital strategies to catch symptoms early and ensure timely intervention, ultimately saving lives and improving quality of life.

Identifying Critical Symptoms of Testicular Cancer at the Onset
Testicular cancer is a significant health concern for men worldwide, but early detection can make a substantial difference in treatment success and survival rates. Being aware of the key symptoms allows for timely medical intervention, potentially saving lives. In this comprehensive guide, we explore the main signs you should watch for and when to seek consultation with healthcare professionals.
Testicular cancer involves the abnormal growth of cells within the testes, which are crucial components of the male reproductive system. When cancer spreads via the bloodstream to other parts of the body, it is classified as metastatic testicular cancer. The good news is that even in advanced stages, many forms of testicular cancer respond well to treatment, highlighting the importance of early detection.
Most testicular cancers originate from germ cells, which are responsible for producing immature sperm. There are various types of testicular tumors, including seminomas, non-seminomas, and stromal tumors such as Leydig cell and Sertoli cell tumors. Recognizing signs early plays a vital role in effective management, as late diagnosis can lead to more complicated treatments and increased mortality, despite the overall treatability of the disease.
Noticeable Testicular Lump or Swelling
One of the hallmark early signs of testicular cancer is the appearance of a small, often pea-sized lump or swelling in one of the testes. This lump, sometimes referred to as a spermatocele, develops near the epididymis—the tube that stores sperm—and might not be painful initially. However, as the lump enlarges or if additional swelling occurs, it can become uncomfortable or tender. Detecting this painless swelling early is crucial for prompt diagnosis and better prognosis.
Persistent Lower Abdominal or Groin Discomfort
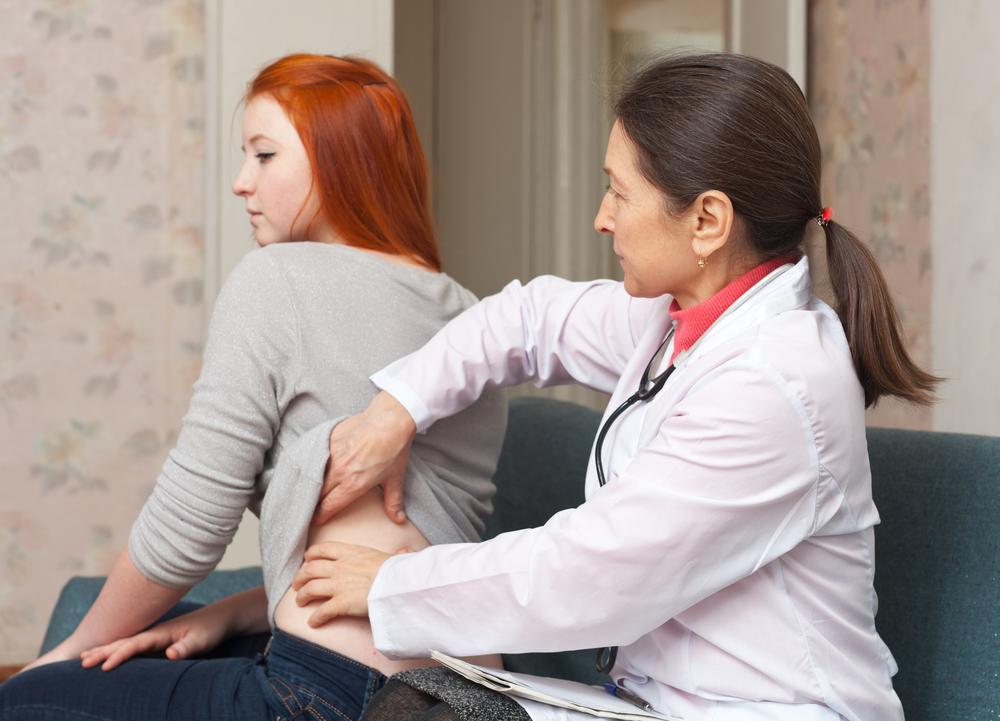
Men with early-stage testicular cancer often experience a dull ache, heaviness, or discomfort in the lower abdomen, groin, or scrotal region. These symptoms can be subtle and easy to overlook but should not be ignored. Swelling or palpable lumps in these areas are signals that require medical assessment to rule out malignancy.
Respiratory Issues and Chest Pain Signaling Metastasis
As the cancer progresses and spreads to the lungs, individuals may develop symptoms such as shortness of breath, a persistent cough, chest pain, or even coughing up blood. These are serious signs indicating lung metastasis, which demands urgent medical attention. Early detection of metastatic spread can substantially improve treatment outcomes and quality of life.
Enlarged or Swollen Lymph Nodes
Swelling of lymph nodes in the abdomen or neck can be a sign that cancer has spread beyond the testes. While less common than lung metastasis, enlarged lymph nodes are an important symptom to recognize, as they indicate systemic involvement and may necessitate comprehensive diagnostic procedures.
Scrotal Swelling Due to Fluid Build-Up (Hydrocele)
Fluid accumulation in the scrotum, known medically as hydrocele, may cause noticeable swelling. Although hydroceles can arise from injuries or infections, persistent or increasing swelling should always prompt medical evaluation to determine if it is related to underlying malignancy.
Male Breast Enlargement (Gynecomastia)
In rare cases, testicular tumors secrete hormones that disrupt normal balance, leading to gynecomastia—growth and tenderness of male breast tissue. Elevated levels of human chorionic gonadotropin (HCG), often produced by certain tumors, are the cause. Recognizing this unusual symptom can lead to earlier diagnosis of testicular cancer.
Heaviness or Changes in Testicular Size and Shape
Feeling of heaviness, firmness differences, or noticeable changes in the size or shape of the testes can be early warning signs of cancer progression. Such alterations should prompt immediate medical consultation for evaluation and diagnosis.
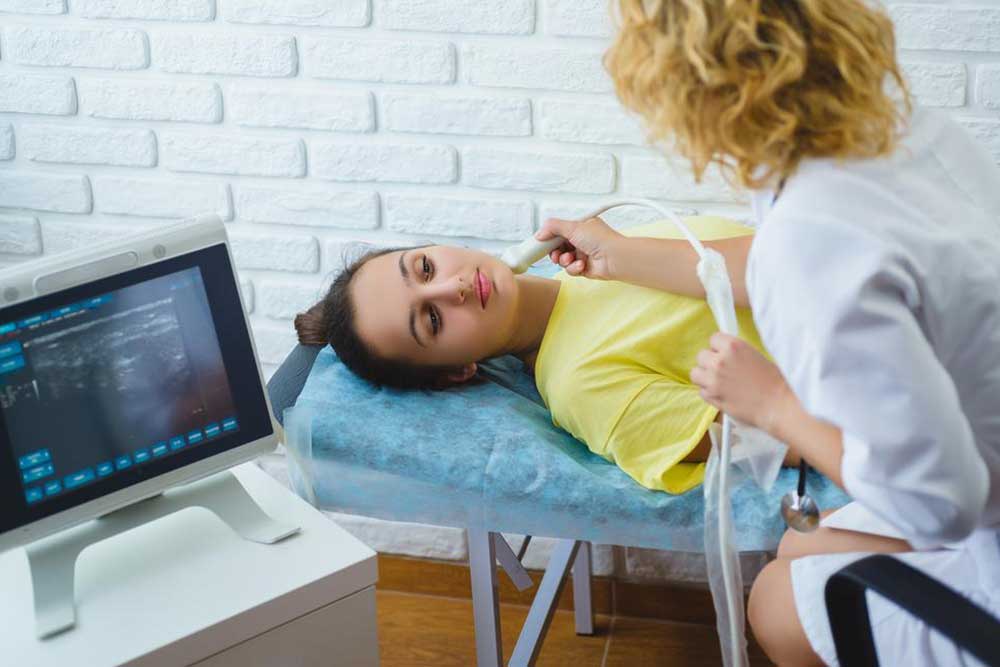
While the exact cause of testicular cancer remains uncertain, risk factors include undescended testes, familial genetic history, and certain congenital abnormalities. Regular self-examination is vital: men should learn how to check their testes and seek medical advice if they detect any unusual lumps, swelling, or discomfort. Diagnostic tools such as ultrasound imaging, blood tests for tumor markers, and biopsy are essential for confirmation.
Treatment options vary depending on the stage and type of cancer but typically include surgery (orchiectomy), radiation therapy, and chemotherapy. Though these treatments are effective, side effects like infertility are possible, making early diagnosis even more important to preserve health and reproductive function. Continuous monitoring and follow-up care are critical components of comprehensive management.