Comprehensive Guide to Managing Fibromyalgia: Symptoms, Treatments, and Lifestyle Strategies
This comprehensive guide provides detailed insights into fibromyalgia, including its symptoms, possible causes, and effective relief methods. It emphasizes a multifaceted approach incorporating medication, diet, stress management, physical activity, and alternative therapies. Personalized care and ongoing management are vital for improving quality of life and alleviating chronic pain associated with fibromyalgia. Designed to inform and empower patients, the article highlights practical strategies for living well with this complex condition.

Understanding Fibromyalgia: Causes, Symptoms, and Practical Ways to Find Relief
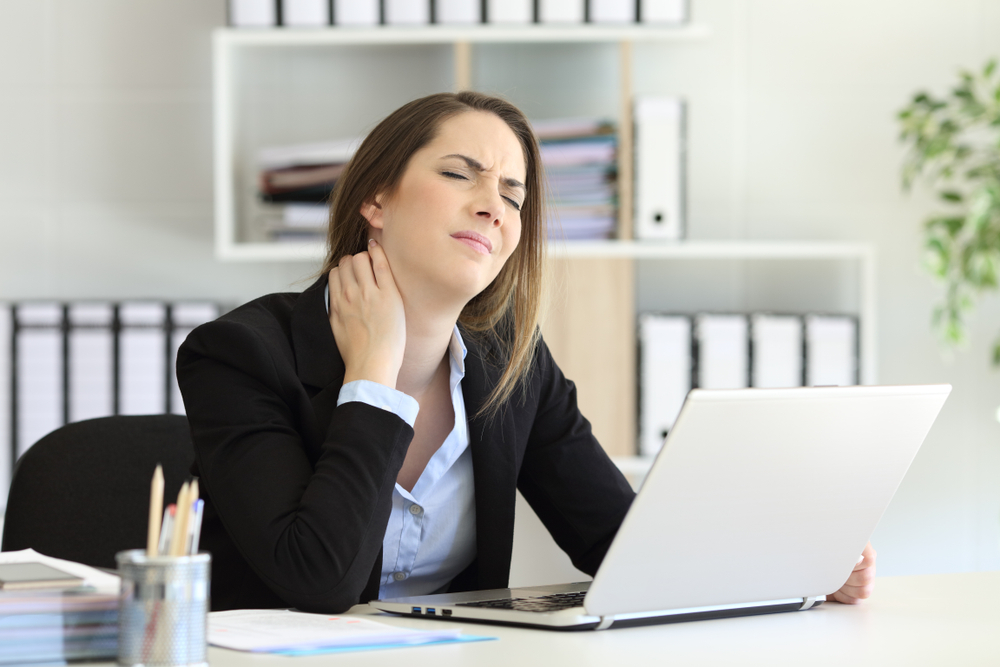
Fibromyalgia is a complex, chronic condition that affects millions of individuals worldwide. Characterized by widespread musculoskeletal pain, persistent fatigue, and heightened tenderness, this disorder often leaves sufferers seeking ways to alleviate discomfort and improve their quality of life. Despite being a challenging condition, advances in understanding and managing fibromyalgia have empowered many to take control of their symptoms through tailored treatments, lifestyle adjustments, and holistic therapies. In this comprehensive guide, we delve into the core aspects of fibromyalgia, including its symptoms, potential causes, and effective strategies for relief, helping you navigate this condition with informed confidence.
Recognizing the Signs and Symptoms of Fibromyalgia
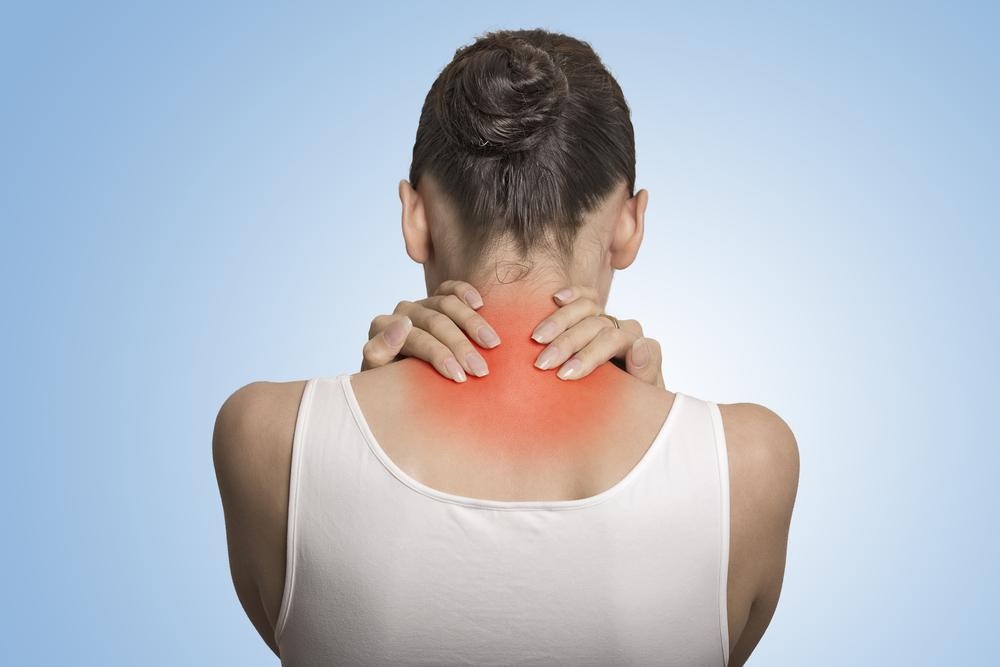
Persistent Musculoskeletal Pain and Tenderness
Chronic Fatigue That Affects Daily Activities
Sleep Disturbances Including Insomnia and Non-Restorative Sleep
Difficulty Concentrating or Brain Fog
Emotional Challenges Such as Anxiety and Depression
Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS) Symptoms
Frequent Headaches and Migraines
Morning Stiffness and Aching Joints
Feeling of Tingling or Numbness in Extremities
Painful Menstrual Cramps and Reproductive Discomfort
Unraveling the Causes and Triggers of Fibromyalgia
Although the precise origins of fibromyalgia remain unclear, evidence suggests a combination of genetic, environmental, and neurological factors. Some researchers believe that abnormal processing of pain signals in the brain and spinal cord plays a crucial role, leading to heightened sensitivity to pain stimuli. Triggers such as physical injury, infections, stressful life events, or emotional trauma can precipitate or worsen symptoms. Understanding these factors can help in crafting personalized management plans and identifying potential triggers that may exacerbate discomfort.
Effective Strategies to Relieve Fibromyalgia Symptoms
Managing fibromyalgia often requires a multifaceted approach encompassing medication, lifestyle changes, and complementary therapies. Here, we explore various scientifically supported methods to ease symptoms and enhance daily functioning.
Pharmacological Treatments for Pain and Fatigue
Over-the-counter medications such as aspirin, naproxen, and ibuprofen can provide temporary relief from muscular aches and reduce inflammation. However, these should be used judiciously, and long-term reliance is not advisable without medical supervision. For persistent pain and associated symptoms, prescription medications like certain antidepressants (e.g., duloxetine, milnacipran) are commonly prescribed. These drugs can modulate pain signals and improve sleep quality but may cause side effects, including nausea, dry mouth, or mood changes. In severe cases, physicians might consider opioids; however, due to the risk of dependency and tolerance, these are reserved for carefully selected patients and used under strict supervision.
Diet and Nutrition: Tailoring Your Diet to Combat Symptoms
Adopting an anti-inflammatory diet can significantly alleviate fibromyalgia symptoms. Focus on consuming foods rich in antioxidants, omega-3 fatty acids, and phytochemicals, such as berries, leafy greens, nuts, seeds, and fatty fish like salmon and mackerel. These foods may help reduce systemic inflammation and improve overall well-being. Conversely, minimizing processed foods, excessive salt, refined sugars, and artificial additives is crucial, as these can provoke inflammation and exacerbate symptoms. Limiting intake of monosodium glutamate (MSG), reducing fructose and lactose consumption, and staying away from artificial sweeteners are additional dietary considerations. Consulting a registered dietitian can help develop a personalized nutrition plan suited to specific needs.
Vitamins, Minerals, and Supplements to Support Health
Deficiencies in magnesium, vitamin D, and other nutrients have been linked to increased muscle pain and fatigue in fibromyalgia patients. Blood tests can determine specific deficiencies, and healthcare providers may recommend supplements to correct these imbalances. Incorporating magnesium supplements, vitamin D capsules, or calcium can support musculoskeletal health and reduce symptom severity. However, self-medicating without professional advice is discouraged, as excess intake may have adverse effects.
Stress Management and Psychological Support
Stress exacerbates fibromyalgia symptoms by affecting the nervous system and hormonal balance. Adopting relaxation techniques such as meditation, deep breathing exercises, biofeedback, or guided imagery can help manage stress levels effectively. Engaging in hobbies, spending quality time with loved ones, and practicing mindfulness can foster emotional resilience. For many, psychological counseling or cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) offers valuable tools to cope with chronic pain, depression, and anxiety. Support groups also provide a platform for sharing experiences and gaining encouragement from others facing similar challenges.
Complementary and Alternative Therapies
Many individuals find relief through alternative therapies integrated alongside conventional medicine. Acupuncture has shown promise in reducing pain intensity and improving sleep quality for some patients. Massage therapy can relax tense muscles and decrease pain, while biofeedback teaches control over physiological functions linked to stress and pain perception. Guided imagery and relaxation techniques can also help in managing discomfort and promoting mental calmness. It’s essential to discuss these options with healthcare providers to ensure safety and appropriateness.
Physical Activity and Exercise: Building Strength and Endurance
Although fatigue can make exercise seem daunting, regular physical activity is vital in managing fibromyalgia. Low-impact activities such as walking, swimming, yoga, and cycling can stimulate the release of endorphins—natural painkillers—while simultaneously reducing depression and anxiety symptoms. Consistent, moderate exercise improves sleep patterns, enhances flexibility, and boosts overall energy levels. Starting slow and gradually increasing activity intensity under professional guidance can prevent overexertion and injury.
Implementing Lifestyle Changes for Symptom Management
Simple adjustments in daily routines can make a significant difference. Ergonomic furniture supports proper posture, reducing musculoskeletal strain. Establishing a consistent sleep schedule and creating a calming bedtime routine promote restorative sleep. Pacing activities throughout the day helps prevent overexertion, while stress reduction practices foster emotional well-being. Maintaining a balanced diet, staying hydrated, and avoiding caffeine later in the day complement these lifestyle modifications.
Psychological Support and Counseling
Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) is highly effective in helping individuals develop coping strategies for dealing with persistent pain and emotional challenges. Therapy sessions focus on changing negative thought patterns, managing stress, and fostering resilience. Support groups and online communities serve as additional resources, providing encouragement, understanding, and practical advice from others living with fibromyalgia. Combining psychological support with physical therapies creates a holistic approach that addresses both mind and body, leading to improved quality of life.
In conclusion, fibromyalgia is a lifelong condition that requires ongoing management and personalized care. By exploring a combination of medication, dietary adjustments, physical activity, stress management, and complementary therapies, individuals can significantly reduce their symptoms and enhance their daily functioning. Working closely with healthcare professionals to develop a tailored plan is essential to achieving optimal results and living a comfortable, fulfilling life despite the challenges of fibromyalgia.