Effective Nutritional Strategies to Manage Hypothyroidism and Support Thyroid Health
This comprehensive guide offers effective nutritional strategies and lifestyle modifications to manage hypothyroidism. From understanding causes and symptoms to implementing diet plans including rich nutrients like selenium and vitamin D, it emphasizes the importance of a holistic approach. Supported by medical treatment, these strategies aim to improve thyroid health, reduce symptoms, and enhance overall well-being for those living with hypothyroidism. Learn how tailored nutrition and lifestyle changes can significantly impact disease management and quality of life.

Effective Nutritional Strategies to Manage Hypothyroidism and Support Thyroid Health
Maintaining optimal thyroid function is a significant aspect of overall health. While some individuals enjoy naturally balanced thyroid activity, many others face challenges like hypothyroidism, a condition characterized by insufficient thyroid hormone production. This article explores comprehensive dietary strategies, lifestyle adjustments, and treatment options to effectively manage hypothyroidism. Understanding the underlying causes, recognizing symptoms early, and adopting tailored nutrition plans can significantly improve quality of life for those affected. Whether newly diagnosed or seeking ways to optimize thyroid health, this guide provides valuable insights into managing hypothyroidism through informed dietary choices.
Hypothyroidism is a condition where the thyroid gland fails to produce enough hormones, which can disrupt numerous bodily functions and lead to various health issues. Addressing this condition comprehensively involves not only medications but also targeted nutritional interventions designed to support thyroid function and alleviate symptoms.
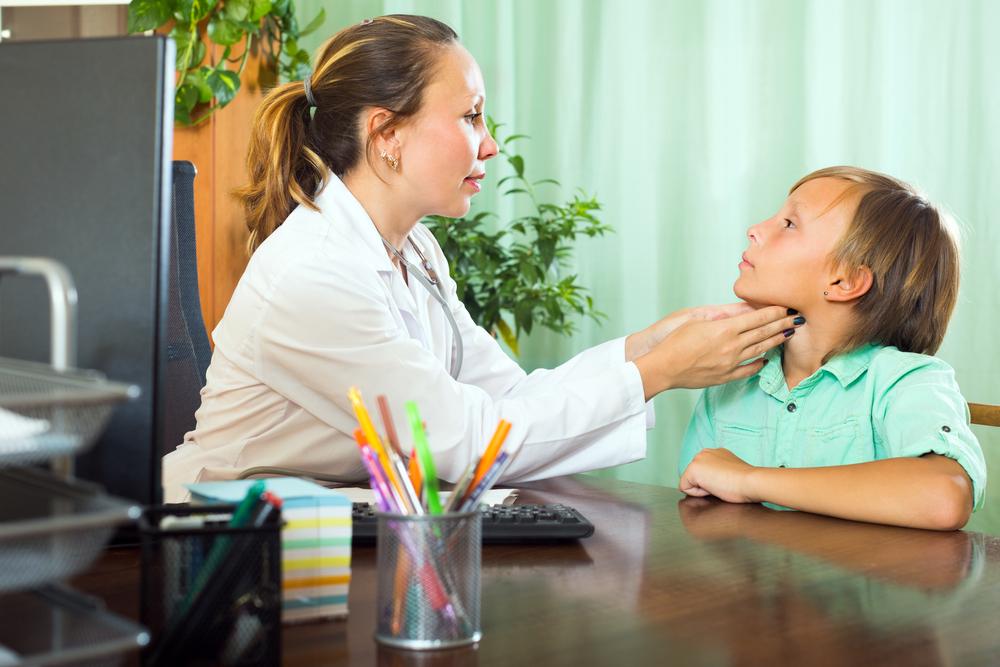
Many individuals are unaware that inadequate production of thyroid hormones, particularly thyroxine, underpins many common symptoms such as unexplained weight gain, persistent fatigue, feelings of depression, and more subtle signs like dry skin and cold intolerance. Early detection through blood tests is crucial since symptoms can often be mistaken for other health issues. Recognizing the signs early can lead to prompt management, significantly improving outcomes.
Understanding the Causes and Risk Factors of Hypothyroidism
Autoimmune Disorders: The most common cause, especially Hashimoto's thyroiditis, involves the immune system mistakenly attacking the thyroid gland, leading to decreased hormone production. Women are disproportionately affected by this autoimmune condition.
Surgical and Medication-Related Factors: Treatments such as thyroidectomy (surgical removal of the thyroid) or radioactive iodine therapy for hyperthyroidism can result in permanent hypothyroidism. Medications like lithium and certain anti-inflammatory drugs may also interfere with thyroid hormone synthesis.
Strategies for Managing Hypothyroidism through Diet and Medical Treatment
While medication remains the cornerstone of hypothyroidism treatment—typically involving thyroid hormone replacement therapy—certain dietary modifications can support medication efficacy and help manage symptoms. It’s essential to work with healthcare professionals to develop a personalized treatment plan that includes dietary, lifestyle, and medical components.
Key dietary elements supportive of thyroid health include staying well-hydrated, increasing intake of fiber-rich foods to combat constipation, and ensuring adequate nutrients vital for thyroid function. Foods high in vitamin D, such as fatty fish (salmon, mackerel), eggs, and fortified products, are beneficial. Selenium, obtained from foods like Brazil nuts, eggs, and sunflower seeds, plays a crucial role in thyroid hormone synthesis. Moderate caffeine consumption can boost alertness without impairing absorption of thyroid medications, whereas excessive caffeine may interfere with mineral absorption.
Including gluten-containing grains may be beneficial for some individuals, aiding in medication absorption and reducing autoimmune reactions. However, these dietary adjustments should be tailored to individual tolerance and medical advice. Regular screening, adherence to prescribed medications, and lifestyle modifications form the backbone of effective hypothyroidism management.
In addition to nutrition, engaging in regular, gentle exercise helps boost metabolism, enhance mood, and improve overall health. Stress management techniques such as yoga, meditation, or deep-breathing exercises can mitigate autoimmune triggers and hormonal imbalances. Avoiding environmental toxins and limiting exposure to endocrine disruptors in plastics and pesticides can also support thyroid health.
Ignoring the importance of diet and lifestyle modifications may lead to complications like goiter, cardiovascular problems, reproductive challenges, and increased risk of congenital disabilities if pregnancy occurs. Early diagnosis, ongoing medical supervision, and a holistic approach to treatment are essential for maintaining a stable, healthy thyroid function and improving long-term health outcomes.