Essential Dietary Strategies to Support Thyroid Health in Hypothyroidism Management
This comprehensive guide explores the most effective dietary choices for managing hypothyroidism. It emphasizes nutrient-rich foods such as fatty fish, nuts, fruits, vegetables, and seaweeds that support thyroid function, reduce inflammation, and boost immunity. The article provides practical tips on incorporating essential nutrients like iodine and selenium into daily meals, along with lifestyle recommendations. Proper nutrition is a key element in effectively managing hypothyroidism, enhancing overall well-being through diet, exercise, and mindful habits.

Essential Dietary Strategies to Support Thyroid Health in Hypothyroidism Management
The thyroid gland, a vital butterfly-shaped organ situated at the base of your neck, plays a crucial role in regulating various bodily functions, including metabolism, temperature control, heart rate, and energy levels. When this gland becomes underactive—a condition known as hypothyroidism—its reduced hormone production can lead to a wide range of symptoms, from weight gain and persistent fatigue to mood disturbances and heightened cold sensitivity. Managing hypothyroidism effectively requires a holistic approach that addresses inflammation, nutrient deficiencies, gut health, and hormonal balance. One of the most impactful strategies is adopting a proper, nutrient-rich diet tailored to support thyroid function. This comprehensive guide explores the most beneficial foods and dietary practices to help maintain and enhance thyroid health, offering practical insights for those managing hypothyroidism.
Optimizing nutrition for hypothyroidism involves selecting foods that promote healthy thyroid activity, reduce inflammation, and supply essential nutrients like iodine, selenium, and omega-3 fatty acids. An informed dietary approach can significantly improve quality of life and complement existing treatment plans.
Fatty Fish and Seafood
Incorporating omega-3 rich fish such as salmon, mackerel, sardines, and tuna can greatly benefit individuals with hypothyroidism. These fish are rich in omega-3 fatty acids, which are essential for reducing systemic inflammation, supporting cardiovascular health, and boosting immune function. Additionally, shellfish like shrimp and crab provide vital minerals such as iodine and zinc, which are fundamental for thyroid hormone production and regulation. Regular consumption of these healthy fats and nutrients helps reinforce the body's metabolic processes and encourages a healthy inflammatory response.
Nuts, Seeds, and Selenium Sources
Nuts such as Brazil nuts, hazelnuts, and macadamia nuts are excellent sources of selenium, a trace mineral that plays a crucial role in thyroid hormone synthesis and conversion. Adequate selenium intake helps prevent damage to thyroid tissue and supports the regulation of hormones in autoimmune conditions like Hashimoto's thyroiditis and Graves' disease. It's recommended to consume selenium within safe limits—roughly 50 to 400 micrograms per day—to avoid toxicity. Seeds like chia, flax, and sunflower also provide essential nutrients and healthy fats that support overall metabolic health.
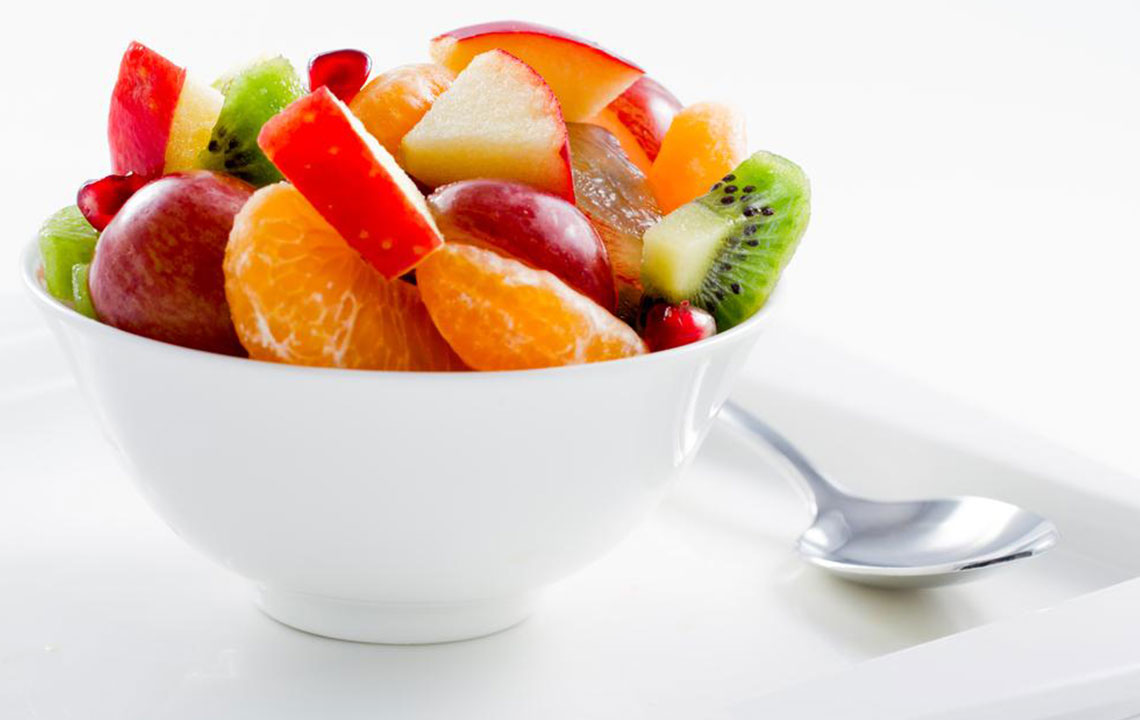
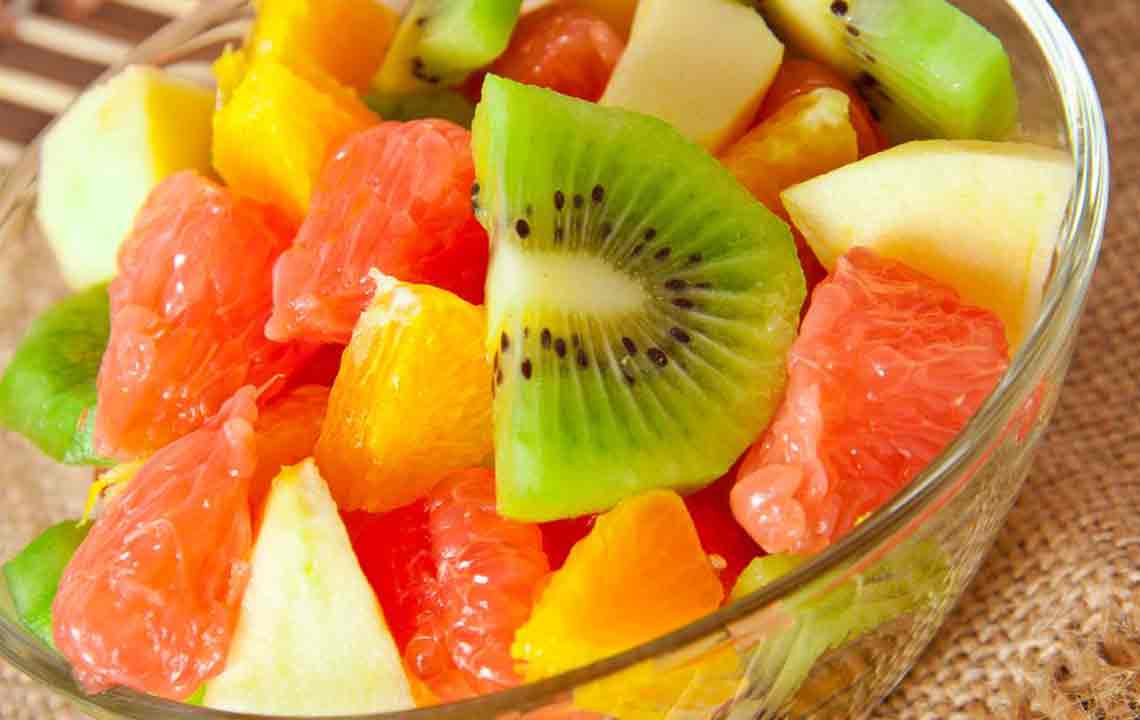
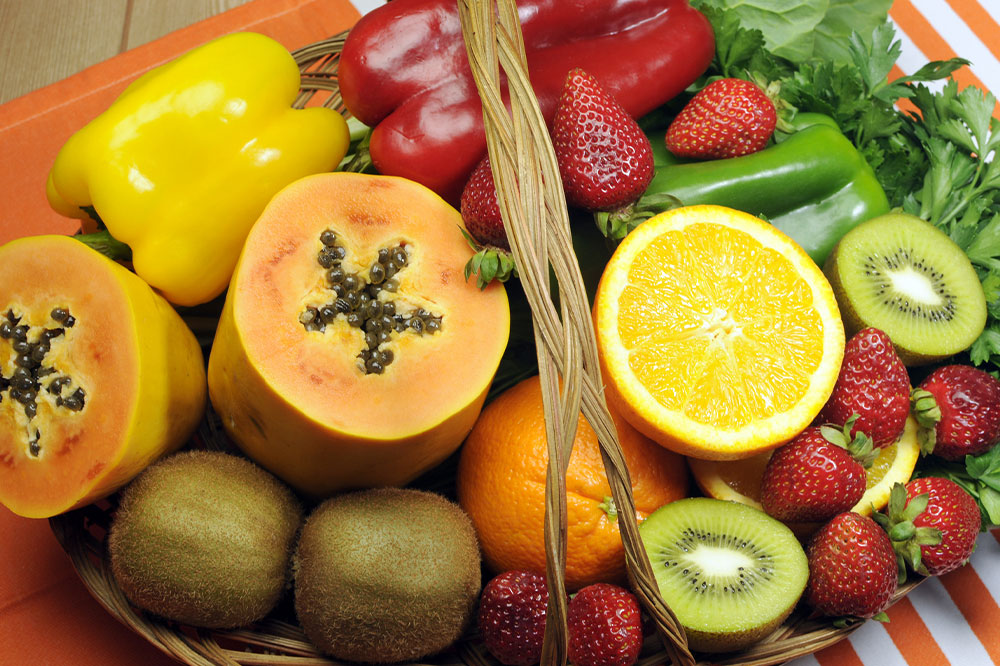
Fruits and Vegetables Rich in Antioxidants
Incorporating a variety of colorful fruits and vegetables such as berries, cherries, spinach, and sweet potatoes can significantly reduce inflammation and oxidative stress in the body. These foods are rich in antioxidants, vitamins, and minerals that promote heart health, support detoxification, and stabilize immune responses. For hypothyroidism management, emphasizing antioxidant-rich produce can help mitigate inflammation-related symptoms and contribute to a balanced immune system.
Iodine-Rich Seaweeds and Marine Products
Seaweeds like nori, wakame, and kelp are natural sources of iodine—an essential element for the synthesis of thyroid hormones. Including moderate amounts of seaweed in meals can support healthy hormone production, but it's vital to avoid excessive intake, as too much iodine can exacerbate thyroid issues. Besides iodine, seaweed provides calcium, fiber, and a spectrum of important vitamins, making it a nutritious addition to a hypothyroid-friendly diet.
Eggs as a Nutrient Powerhouse
Eggs, particularly the yolk, contain high levels of iodine, selenium, and B vitamins—all of which play roles in thyroid function and energy metabolism. They are an affordable, versatile protein source that can be easily incorporated into daily meals, supporting overall nutritional needs for hypothyroid individuals.
Legumes and Plant-Based Proteins
Beans, lentils, chickpeas, and other pulses provide complex carbohydrates, fiber, and vital vitamins and minerals. These foods help sustain energy levels, improve gut health, and support muscle function. Their inclusion in a balanced diet can promote stable blood sugar levels and aid digestion, both of which are beneficial for managing hypothyroidism symptoms.
Dairy Products for Iodine and Probiotics
Milk, yogurt, and cheese are rich in iodine and contain beneficial probiotics that support gut health and immune function. Choosing organic or fortified dairy options can enhance nutrient intake and reduce exposure to unwanted additives or hormones, further bolstering thyroid health.
Coconut Oil and Healthy Fats
Medium-chain triglycerides (MCTs) found in coconut oil support energy production and metabolism. Additionally, coconut oil possesses antibacterial, antifungal, and antioxidant properties that may help reduce inflammation and support immune function, making it a valuable addition to the hypothyroid diet.
Bone Broth for Digestive and Immune Support
Rich in amino acids such as glycine and proline, bone broth promotes digestive health, enhances immune response, and provides vital minerals including calcium, magnesium, and phosphorus. Regular consumption can support tissue repair, reduce inflammation, and boost overall vitality.
High-Fiber Foods for Digestion and Heart Health
Incorporating plenty of vegetables, berries, seeds, and pulses helps improve digestion, lower cholesterol, and stabilize blood sugar levels. These foods contribute to cardiovascular health and overall well-being, especially important as hypothyroidism can influence metabolic processes.
In addition to emphasizing these nutrient-dense foods, it’s equally important to limit intake of processed foods, refined grains, and added sugars, which can promote inflammation and disrupt thyroid function. For individuals with gluten sensitivities or celiac disease, reducing gluten consumption may be beneficial, as gluten can trigger autoimmune responses that impair thyroid health. Consulting with a healthcare provider about probiotic supplementation and potential food sensitivities is advisable for personalized management. Combining these dietary strategies with regular exercise and stress management can greatly enhance the effectiveness of hypothyroidism treatment, leading to improved energy, mood, and overall health.