Comprehensive Nutritional Strategies for Managing Fatty Liver Disease Effectively
This comprehensive article explores effective dietary strategies for managing fatty liver disease. It emphasizes the importance of nutrient-rich foods, including vegetables, lean proteins, and healthy fats, while advising on the reduction of sugars and unhealthy fats. The piece highlights the liver's regenerative capacity and offers practical tips on lifestyle modifications to reverse fatty liver. Readers will understand how proper diet, supplements, and healthy cooking methods can significantly improve liver health and prevent progression to serious liver conditions. An essential guide for those seeking to manage fatty liver through nutrition.

Laid-Out Dietary Approaches to Combat and Manage Fatty Liver Disease
Fatty liver disease, scientifically termed steatosis, is a condition characterized by excessive fat buildup within liver cells. Under normal circumstances, the human liver contains up to approximately 10% fat, which is essential for various metabolic processes. However, when fat accumulation exceeds this threshold, it leads to fatty liver, a condition increasingly diagnosed worldwide. Recognizing and managing this condition early is crucial because it can progress into more severe liver issues if left unaddressed.
The liver, being the body's second-largest organ, plays a pivotal role in metabolizing nutrients, synthesizing proteins, and detoxifying harmful substances. An overload of fat hampers these vital functions, resulting in systemic health consequences, including metabolic disturbances and increased risk of cardiovascular disease. The good news is that fatty liver disease is often reversible with appropriate lifestyle and dietary changes. The liver possesses an extraordinary regenerative capacity, capable of healing and regenerating new healthy cells to replace those damaged. Nevertheless, persistent injury and ongoing fat accumulation can lead to irreversible scarring, a condition known as cirrhosis, which significantly impairs liver function and can have life-threatening implications.
Multiple factors contribute to the development of fatty liver disease, with poor dietary choices and sedentary lifestyles being among the primary causes. It is most commonly diagnosed in individuals between 40 and 60 years of age, although it can affect anyone regardless of age. The cornerstone of managing fatty liver involves targeted dietary modifications aimed at reducing liver fat levels and supporting overall metabolic health.
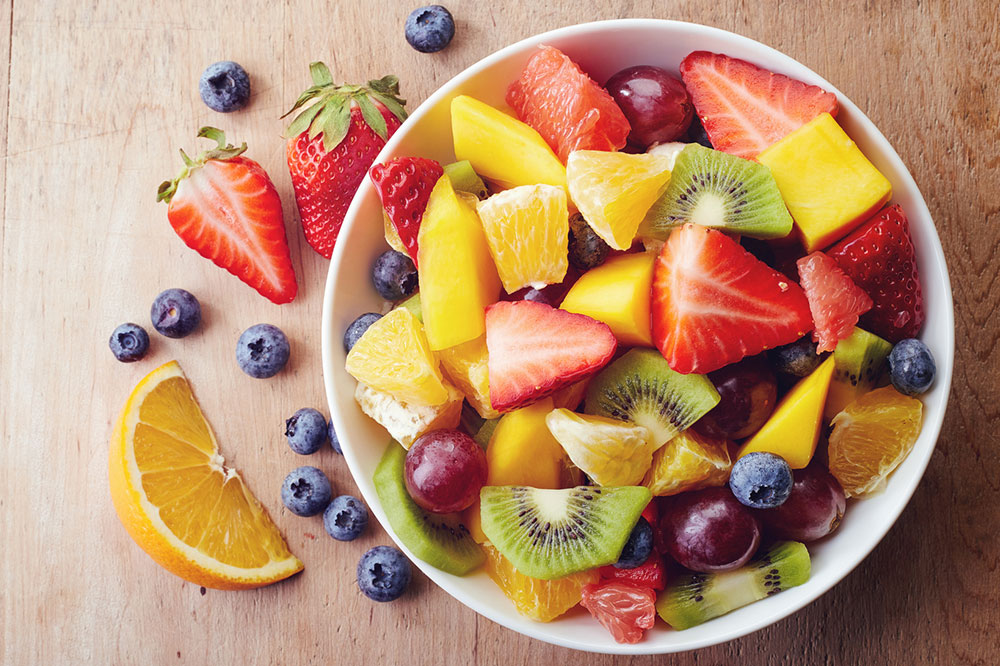
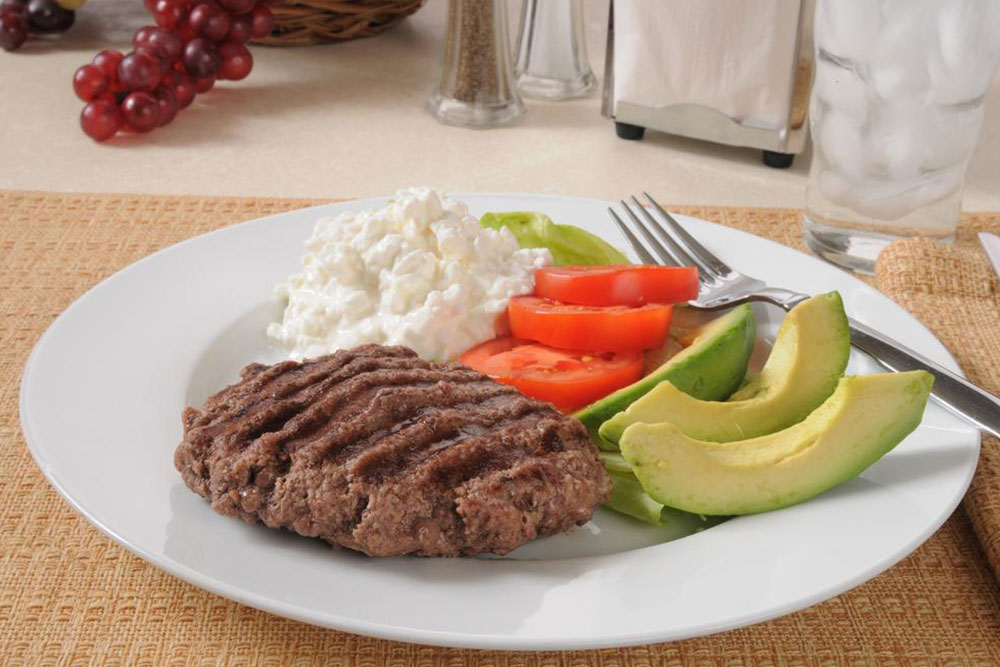
One fundamental approach involves increasing the intake of raw vegetables, which are naturally low in sugars and calories, thereby aiding in weight control and fat reduction. Limiting high-sugar fruits such as grapes, bananas, and tropical fruits is also recommended since excess sugars can contribute to fat deposition in the liver. Dietary focus should be on composite meals rich in vegetables, lean proteins, and healthy fats.
Vegetables are an excellent food choice because they possess low sugar content and are abundant in fiber, vitamins, and antioxidants. Including a diverse range of cooked vegetables in meals not only enhances nutrient intake but also helps maintain a balanced diet. It is advisable to avoid starchy vegetables like potatoes, which can contribute to carbohydrate load, and instead opt for non-starchy options such as leafy greens, zucchini, and peppers.
To prevent nutrient deficiencies, especially of essential proteins, incorporate lean protein sources such as seafood, poultry, lean cuts of red meat, eggs, and plant-based options like legumes and beans. These proteins are vital for cellular repair and regeneration in the liver.
Supplementation can also support liver health. Liver tonics and detoxifying supplements supply necessary nutrients that aid in liver cleansing and repair. Glutathione, a potent antioxidant produced naturally in the body, plays a significant role in detoxification processes; thus, increasing glutathione levels through diet or supplements is beneficial. Consuming sulfur-rich foods—such as eggs, cabbage, broccoli, and garlic—enhances the body's ability to produce glutathione and supports overall hepatic detoxification.
In addition, reducing intake of fried foods, especially those cooked in unhealthy vegetable oils, can decrease oxidative stress and further fat accumulation in the liver. Switching to healthier cooking methods, such as baking, steaming, or frying in olive oil, helps protect liver cells and supports metabolic health. Emphasizing a balanced, nutrient-rich diet coupled with regular physical activity forms the foundation of effective fatty liver disease management.