Comprehensive Guide to Cholesterol: Detection, Risks, and Prevention Strategies
This comprehensive article explores the importance of understanding cholesterol, its detection methods, and effective prevention strategies. It emphasizes the role of lifestyle choices, diet, regular testing, and medical advice in maintaining healthy cholesterol levels to prevent heart disease and related conditions. With detailed insights, readers are empowered to take proactive steps towards cardiovascular health and reduce their risk of life-threatening complications.

Comprehensive Guide to Cholesterol: Detection, Risks, and Prevention Strategies
Cholesterol is a waxy, fat-like substance that circulates throughout our bloodstream, playing a crucial role in maintaining healthy cell membranes and facilitating hormone production. Despite its importance, having too much cholesterol in your blood can lead to considerable health issues, especially related to the heart and blood vessels. Elevated cholesterol levels contribute to the development of fatty deposits within arteries, known as atherosclerosis, which can significantly impede blood flow and lead to severe cardiovascular events such as heart attacks and strokes. Understanding how cholesterol builds up, how to detect abnormal levels, and ways to prevent its dangerous accumulation are essential for maintaining long-term heart health.
The Process of Cholesterol Accumulation
The process of cholesterol accumulation in arteries, often called atherosclerosis, is generally gradual and can progress without obvious symptoms in its initial stages. Typically, high cholesterol levels are asymptomatic for many years, making routine checkups vital. Over time, excess low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol, often referred to as 'bad cholesterol,' deposits within arterial walls, forming plaques—a build-up of fats, cholesterol, calcium, and other cellular debris. These plaques cause arteries to narrow, reducing blood flow to vital organs such as the heart and brain.
If these plaques rupture, blood clots can form at the site, further blocking blood flow. Such events may lead to heart attacks, strokes, or other serious cardiovascular complications. The severity of cholesterol buildup depends on various factors, including genetics, lifestyle, diet, and overall health, emphasizing the need for early detection and proactive prevention measures.
Methods for Detecting High Cholesterol Levels
Detecting elevated levels of cholesterol typically does not involve symptoms in the early stages, which makes regular screening important. A simple blood test called a lipoprotein profile, or lipid panel, is the standard diagnostic tool used to assess cholesterol levels. This test measures total cholesterol, LDL cholesterol, high-density lipoprotein (HDL or ‘good’ cholesterol), and triglycerides—another type of fat found in the blood.
For most adults, health guidelines recommend getting a lipid profile at least once every five years, starting from age 20. Individuals with a family history of heart disease, high cholesterol, or other risk factors such as obesity, smoking, or diabetes may need more frequent testing. In addition to blood tests, doctors may assess other cardiovascular risk factors, including blood pressure, body mass index, and personal medical history, to develop a comprehensive risk profile and tailor treatment options accordingly.
Effective Prevention Strategies for Managing Cholesterol Levels
While genetics influence cholesterol levels, lifestyle habits play a crucial role in preventing and managing high cholesterol. Making informed choices about diet, exercise, stress management, and habits can significantly reduce your risk of developing hazardous cholesterol levels. Implementing these strategies can improve overall vascular health and prevent cardiovascular diseases.
Understanding and Managing Personal Risks
If your family has a history of heart disease or cholesterol issues, you should be especially vigilant. Knowledge of personal risk factors enables you to take proactive steps and work closely with healthcare professionals to monitor your health and prevent complications.
Setting Clear, Achievable Health Goals
Establishing realistic targets for cholesterol levels helps direct your lifestyle modifications and medical interventions. Knowing the accepted healthy range for total cholesterol, LDL, and HDL guides your efforts and motivates sustainable habits.
Adopting a Heart-Healthy Diet
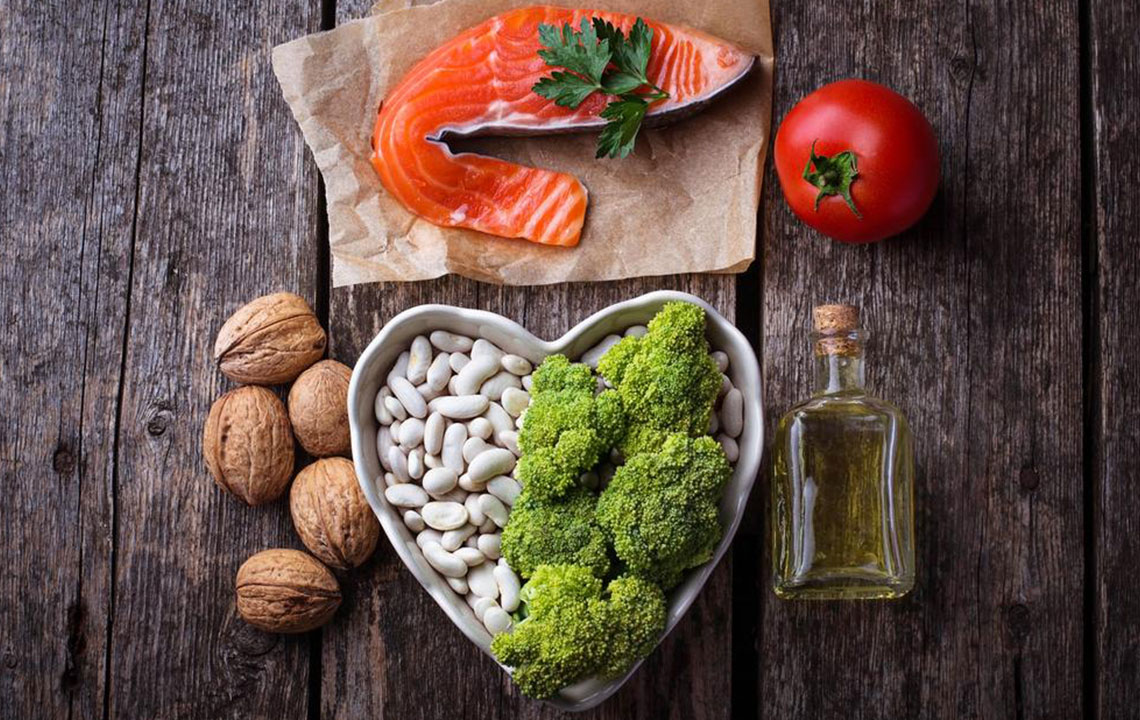
Diet plays an essential role in controlling cholesterol levels. Focus on reducing intake of saturated fats found in red meats, full-fat dairy, and processed foods, as well as trans fats present in many fried and commercially baked goods. Emphasize nutrient-rich foods such as vegetables, fruits, whole grains, nuts, seeds, and legumes, which help lower bad cholesterol while boosting good cholesterol levels.
Incorporate heart-healthy fats like those found in oily fish (salmon, mackerel, sardines), olive oil, and avocados. These fats contribute to improved lipid profiles and overall cardiovascular health.
Engaging in Regular Physical Activity
Exercise is a cornerstone of effective cholesterol management. Aim for at least three to four sessions of moderate to vigorous physical activity each week, such as brisk walking, cycling, swimming, or aerobic classes. Physical activity helps raise HDL cholesterol, lower LDL cholesterol, and improve blood circulation, reducing the risk of plaque buildup.
Quitting Smoking and Avoiding Excessive Alcohol
Smoking dramatically worsens cardiovascular health and accelerates fatty deposits in arteries, leading to higher risks of heart disease and stroke. Quitting smoking is one of the most impactful steps you can take to improve your cholesterol profile and overall health. Furthermore, limiting alcohol consumption can help prevent triglyceride elevation and other adverse effects on lipid levels.
In conclusion, managing cholesterol levels is vital for preventing life-threatening cardiovascular diseases. Through regular screening, lifestyle modifications, and medical interventions when necessary, individuals can significantly reduce their risk of developing serious health complications. Raising awareness, making informed choices, and collaborating with healthcare providers form the foundation of effective cholesterol management for a healthier future.