Common Causes of Foot Discomfort in Children and How to Address Them
This comprehensive article discusses common causes of foot discomfort in children, including Sever's disease, Achilles tendonitis, and fractures. It emphasizes early diagnosis, conservative treatments, and preventive measures. Perfect for parents and caregivers aiming to understand and manage children's foot health effectively.

Understanding and Managing Foot Discomfort in Children
Foot discomfort is a common concern among parents and caregivers when it comes to children's health. Many children experience heel pain or general foot soreness at some point during their active years. While most causes are benign and resolve with minimal intervention, understanding the underlying reasons for foot pain is crucial for timely treatment and preventing potential complications. Recognizing symptoms early and seeking appropriate medical guidance can make a significant difference in a child's comfort and mobility.
Children's foot pain can stem from various causes, ranging from overuse injuries to accidental trauma. If your child exhibits persistent pain, tenderness, swelling, or limping, it’s essential to determine the cause to guide proper treatment. Neglecting foot injuries or discomfort can lead to prolonged pain and, in some cases, lasting damage to growing bones and tissues.
Foot injuries, particularly heel-related issues, tend to develop gradually if overlooked. Therefore, vigilant observation and timely intervention are vital. Children who participate in competitive sports, especially those involving jumping, running, or rapid directional changes, face higher risks of foot injuries. Parents should be attentive to changes in their child's activity levels, gait, or complaints of discomfort, as these can be early indicators of underlying problems.
In this article, we explore the most common causes of foot discomfort in children, including their symptoms, causes, and recommended treatments:
Calcaneal Apophysitis (Sever's Disease): The leading cause of heel pain in active children aged 5 to 11, resulting from overuse and repetitive stress.
Achilles Tendonitis: A condition arising from sudden increases in physical activity, causing heel and rear-foot pain.
Heel and Foot Fractures: Traumatic injuries caused by high-impact sports, presenting with severe pain and swelling.
Calcaneal Apophysitis (Sever's Disease)
One of the most prevalent causes of heel pain in children is Calcaneal Apophysitis, popularly known as Sever's disease. This condition predominantly affects active children between the ages of 5 and 11, particularly those engaged in sports that involve running, jumping, or repetitive impact. The disease results from repetitive stress on the growth plate located at the back of the heel bone (calcaneus). Essentially, the Achilles tendon exerts repeated pulling on the immature heel growth plate, leading to inflammation and pain.
This overuse injury can cause significant discomfort, especially during physical activities or even while walking. Children involved in sports like basketball, soccer, tennis, and gymnastics are at higher risk. Symptoms typically include heel pain that worsens with activity and eases with rest, tenderness, swelling, and stiffness around the heel. Proper diagnosis involves a healthcare provider examining the child's foot and possibly using imaging if needed.
Treatment usually involves conservative measures such as rest, ice application, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), and limiting activities that exacerbate symptoms. Proper footwear with adequate cushioning can help reduce stress on the heel. Physical therapy and stretching exercises targeting the Achilles tendon and calf muscles are often recommended. With appropriate management, Sever's disease tends to resolve as the child's growth progresses.
Achilles Tendonitis
Another common cause of heel discomfort in children is Achilles Tendonitis. This condition emerges when children suddenly increase their physical activity levels or resume sports after a period of rest, leading to inflammation of the Achilles tendon—the thick cord connecting calf muscles to the heel bone. This tendon plays a crucial role in walking, running, and jumping, and overloading it can lead to irritation and pain.
Symptoms of Achilles Tendonitis include pain at the back of the heel or along the tendon, swelling, warmth, and difficulty walking or pushing off the foot during movement. Children engaged in activities that involve repetitive jumping, sprinting, or abrupt directional changes—such as basketball players, dancers, and runners—are particularly susceptible.
Initial management involves rest and avoiding activities that cause pain. Applying ice to reduce inflammation, using compression bandages, and elevating the foot can provide relief. Over-the-counter NSAIDs are also effective in decreasing pain and swelling. In some cases, physical therapy focusing on stretching and strengthening exercises can promote healing. Proper footwear with good arch support and cushioned soles can help prevent recurrence. Most cases resolve with conservative care, and a gradual return to activity is advised once symptoms subside.
Heel and Foot Fractures
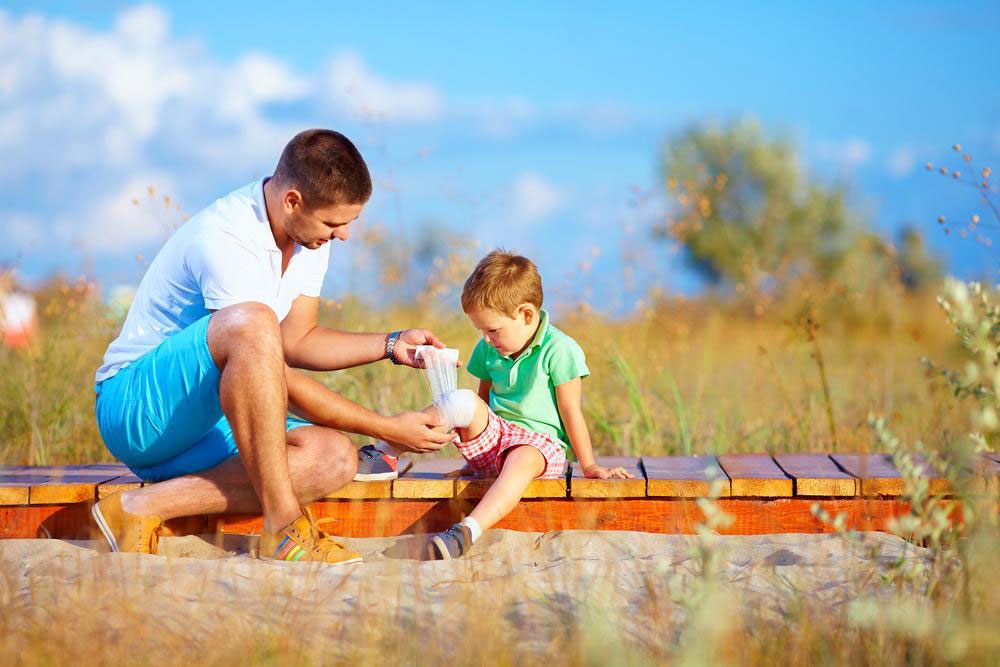
Trauma from high-impact sports or accidents is a common cause of fractures in the heel or other foot bones in children. Such injuries often result from falls, direct blows, or abrupt impacts during sports like football, basketball, or skateboarding. The symptoms are typically severe and sudden, including intense pain, swelling, bruising, and an inability to put weight on the affected foot.
Prompt treatment is essential to ensure proper healing. The initial approach involves immobilization using splints or casts, application of ice to reduce swelling, and administration of pain medications. Rest is critical, and children should avoid putting weight on the injury until a healthcare provider evaluates the injury thoroughly. Imaging studies like X-rays are necessary to confirm fractures and assess their severity.
Management varies depending on the type and location of the fracture. Minor fractures may heal with immobilization over several weeks, while complex fractures might require surgical intervention. Following a fracture, physical therapy and gradual reintroduction to activity are vital to restore function and prevent future injuries. Complete recovery often takes several weeks, emphasizing the importance of proper initial treatment and adherence to medical advice.
In conclusion, foot discomfort in children is a common concern with various causes, most of which respond well to conservative treatment. Recognizing symptoms early and seeking professional care can prevent complications and ensure children return to their normal activities quickly and safely. Maintaining proper footwear, encouraging appropriate physical activity, and monitoring for signs of overuse or injury are essential parts of preventing foot problems in children.