Comprehensive Medical Approaches for Neurofibromatosis Management
This extensive guide explores effective management strategies for neurofibromatosis, including FDA-approved medications like selumetinib, surgical solutions, advanced radiation therapies, and hearing restoration options. It emphasizes the importance of personalized treatment plans, early detection, and ongoing research to improve patient outcomes in this complex genetic disorder.

Comprehensive Medical Approaches for Neurofibromatosis Management
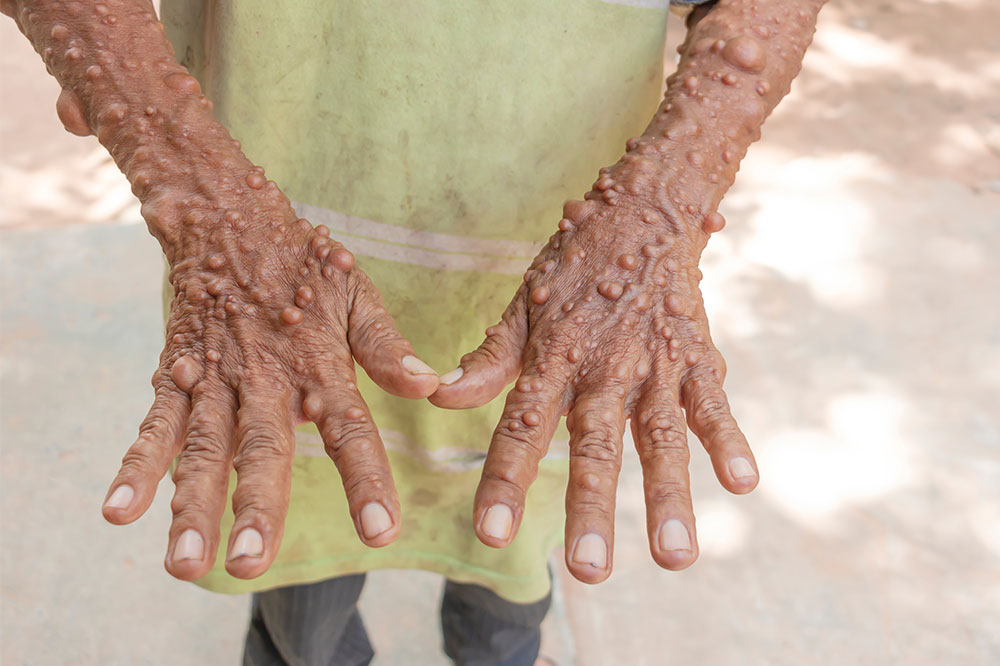
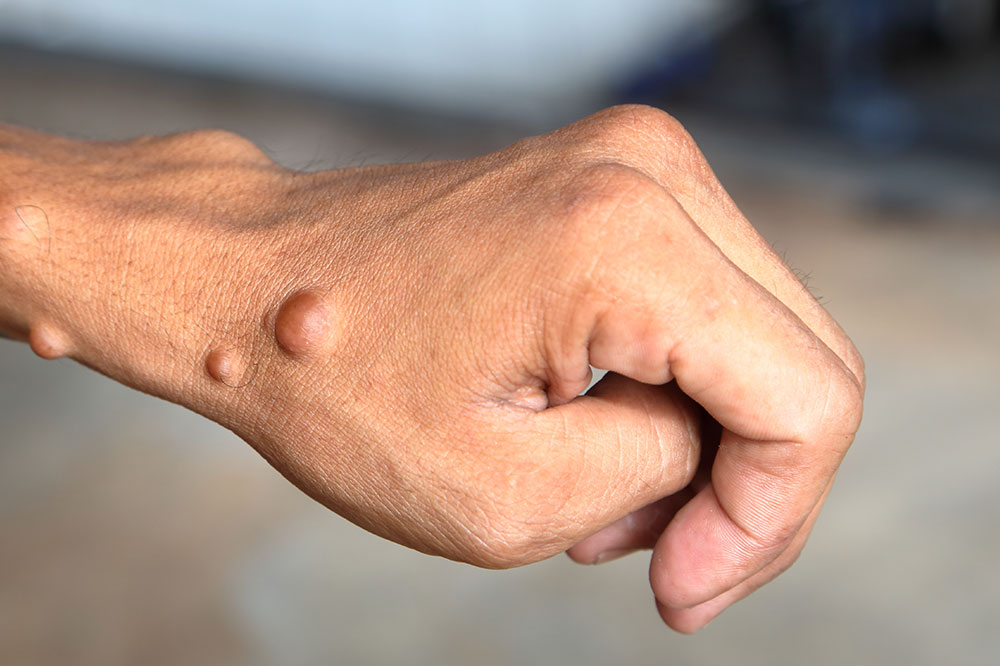
Neurofibromatosis (NF) is a complex genetic disorder that principally affects the nervous system, leading to the growth of non-cancerous tumors along nerve tissues throughout the body. This condition manifests primarily in two main types: Neurofibromatosis type 1 (NF1), which is more common, and Neurofibromatosis type 2 (NF2), each characterized by distinct clinical features and challenges. Managing neurofibromatosis requires a multifaceted approach tailored to the specific type and individual symptoms. Advances in medicine have led to innovative treatment options, including targeted medications, surgical interventions, and supportive therapies that significantly improve patient quality of life. This article provides an in-depth overview of the current effective medical strategies for managing neurofibromatosis, offering hope and guidance for patients and healthcare providers alike.
FDA-Approved Targeted Therapy: KOSELUGO® (selumetinib)
One of the most significant breakthroughs in neurofibromatosis treatment in recent years has been the FDA approval of KOSELUGO® (selumetinib). This medication is specifically indicated for pediatric patients with plexiform neurofibromas, a type of tumor that can grow along nerves and cause substantial functional impairments. Selumetinib belongs to a class of drugs known as MEK inhibitors, which target specific pathways involved in tumor growth. Ongoing clinical trials are exploring the potential benefits of selumetinib and similar agents for adult populations and other tumor types associated with neurofibromatosis, aiming to expand therapeutic options and improve long-term outcomes.
Pain Management in Neurofibromatosis
Chronic pain is a prevalent and debilitating symptom in neurofibromatosis, especially with conditions like Schwannomatosis, which involves nerve sheath tumors. Effective pain control is essential for maintaining patient quality of life. Physicians often recommend a combination of medications to alleviate nerve pain and discomfort. These include:
Amitriptyline: A tricyclic antidepressant that has been used for neuropathic pain management.
Gabapentin (such as Neurontin, Gralise, Horizant) and pregabalin (Lyrica): These medications are frequently prescribed for nerve-related pain and are effective in reducing neuropathy symptoms.
Antiepileptic drugs: Such as topiramate (Topamax, Qudexy XR, Trokendi XR) and carbamazepine (Carbatrol, Tegretol), which help stabilize nerve activity and decrease pain.
Duloxetine (Cymbalta, Drizalma Sprinkle): An SNRI that provides relief from chronic neuropathic pain while also improving mood and overall well-being.
Surgical Options for Tumor Removal
For patients with NF2 experiencing significant tumor growth, especially in critical areas like the brainstem, surgical intervention remains a mainstay of treatment. Removing tumors such as acoustic neuromas—benign tumors that can impair hearing and affect adjacent structures—can help reduce pressure symptoms and preserve neurological function. Complete resection of schwannomas in Schwannomatosis cases can significantly decrease persistent pain. However, surgery must be carefully planned to minimize risks and optimize functional outcomes.
Stereotactic Radiosurgery: A Precision Approach
Non-invasive techniques like stereotactic radiosurgery (such as Gamma Knife or CyberKnife) have gained popularity for their ability to deliver targeted radiation to tumors, sparing surrounding healthy tissue. This approach is particularly beneficial for NF2 patients with vestibular schwannomas or other tumors near vital structures. Precise radiation minimizes collateral damage, reduces side effects, and often helps in maintaining hearing and balance functions.
Hearing Restoration Technologies
Hearing impairment is a common complication in NF2 due to tumor growth affecting the auditory nerve. Advanced implantable devices offer hope for restoring hearing capabilities. Auditory brainstem implants (ABIs) and cochlear implants are two primary options that have demonstrated significant improvements in auditory function for patients with NF2-related deafness. These devices bypass damaged nerves or cochlear structures to transmit sound signals directly to the brain, greatly enhancing communication and quality of life.
Monitoring and Managing Malignant Transformations
While neurofibromatosis primarily involves benign tumors, there is an increased risk for malignant transformation, particularly into malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumors (MPNST). Early detection is crucial. Regular imaging, clinical evaluations, and awareness of warning signs such as rapid tumor growth, pain, or neurological deficits are essential. When malignancies are identified, treatment options typically include chemotherapy, radiation therapy, or surgical resection, based on tumor staging and patient health. Multidisciplinary care is vital for effective management of these complex cases.
In conclusion, managing neurofibromatosis requires a comprehensive approach that includes targeted pharmacotherapy, surgical procedures, radiation therapy, and supportive devices. The latest advancements, especially FDA-approved drugs like selumetinib, have transformed the treatment landscape by offering options beyond symptomatic relief, aiming at tumor control and functional preservation. Continued research and clinical trials are essential for expanding therapeutic possibilities, ultimately improving outcomes and quality of life for individuals living with this challenging genetic disorder.