Comprehensive Dietary Strategies for Effective Gout Management and Prevention
Discover comprehensive dietary strategies for managing gout. Learn about low-purine foods, beneficial superfoods, and lifestyle tips to prevent flare-ups and promote joint health. This detailed guide helps you build an effective gout-friendly diet for long-term relief and improved quality of life.

Essential Guidelines for Maintaining a Gout-Friendly Diet
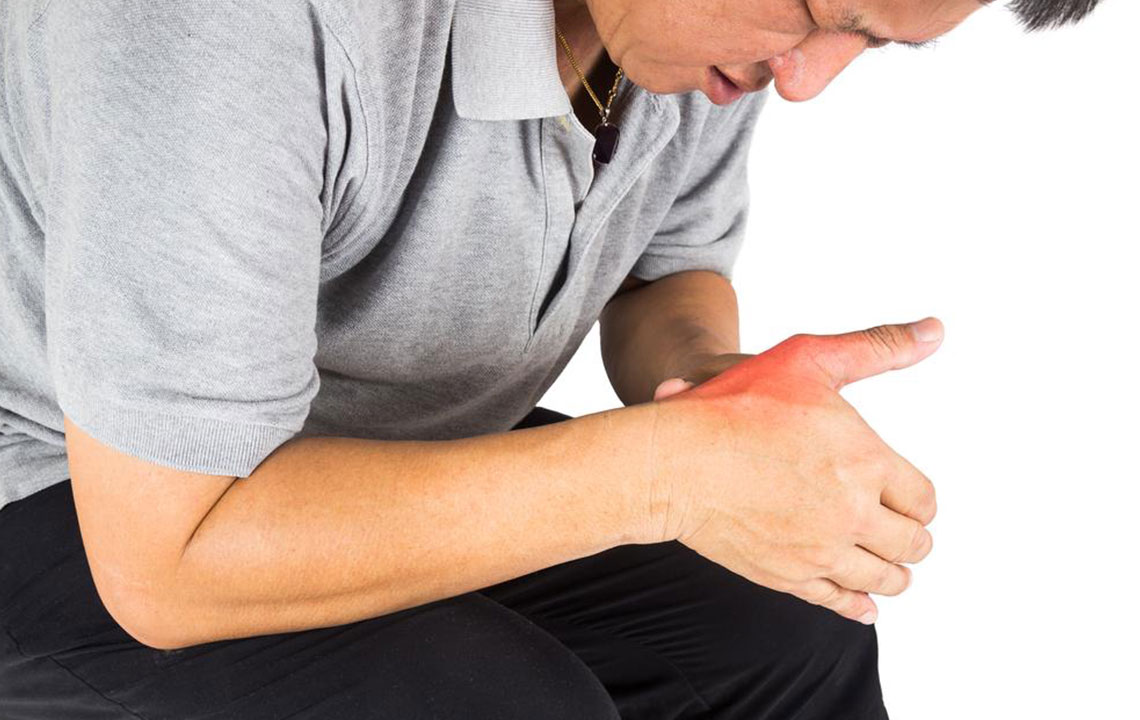
Gout is a prevalent form of inflammatory arthritis that affects a significant portion of the population worldwide. It is characterized by sudden, severe episodes of joint pain, swelling, redness, and warmth, often causing considerable discomfort and limiting mobility. While it can affect various joints, the big toe is frequently the most afflicted, though knees, elbows, fingers, and ankles can also be involved. The root cause of gout lies in the accumulation of excess uric acid in the bloodstream, which crystallizes and deposits in the joints, leading to inflammation and pain. Managing gout effectively involves a multifaceted approach, but dietary modification remains one of the most crucial elements in preventing flare-ups and maintaining long-term joint health.
Incorporating specific foods known as superfoods into your daily diet can significantly reduce the frequency, severity, and duration of gout episodes. The key to successful management lies in understanding which foods contribute to uric acid production and which ones help lower it, thereby easing joint inflammation and pain. Adopting a gout-friendly diet involves choosing low-purine foods, maintaining hydration, and avoiding high-risk foods that elevate uric acid levels. Here are detailed recommendations and insights on foods beneficial for gout management:
Essential Dietary Tips for Gout Control
Effective gout management starts with understanding the impact of various dietary components. Purines are natural substances found in many foods, and their breakdown in the body produces uric acid. When uric acid levels become excessively high, crystals form within joints, triggering gout attacks. Consequently, limiting high-purine foods and focusing on nutrient-dense, low-purine options can dramatically reduce flare-ups.
Top Superfoods for Managing Gout
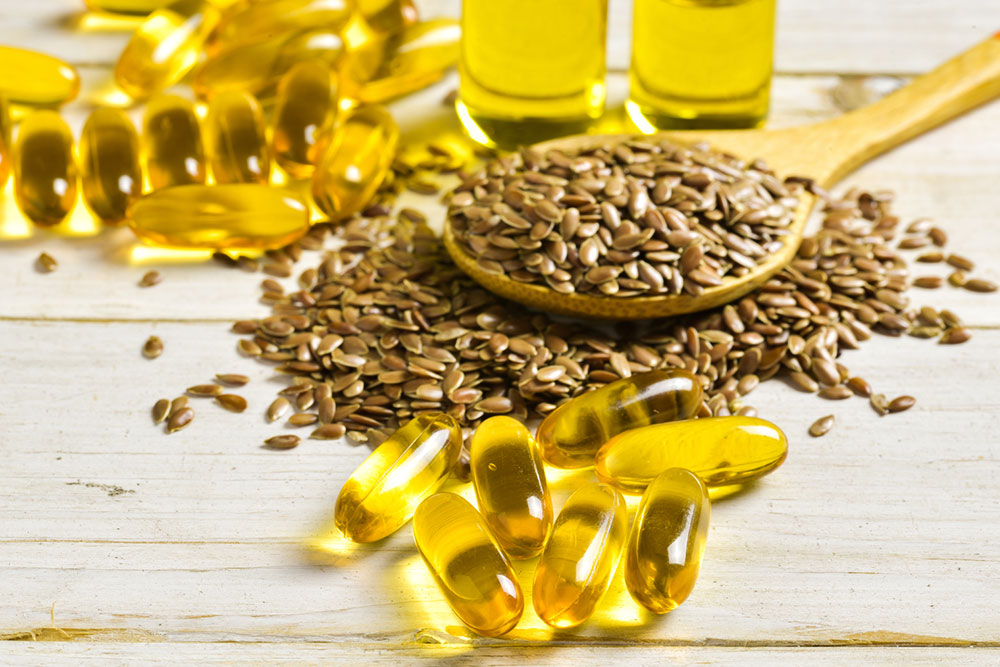
1. Nuts and Seeds
Many nuts, including almonds, walnuts, and pistachios, are excellent additions to a gout-friendly diet. They are packed with healthy fats, vitamins, and minerals that support joint health and reduce inflammation. Nuts can serve as nutritious snacks or ingredient additions, providing sustenance without contributing to uric acid buildup.
2. Whole Grains
Incorporate brown rice, oats, barley, and whole wheat products into your meals. These foods are rich in dietary fiber, which aids digestion, supports gut health, and helps eliminate excess uric acid more efficiently. Whole grains also provide essential nutrients that promote overall health and prevent nutritional deficiencies.
3. Legumes and Plant-Based Proteins
Foods such as lentils, chickpeas, tofu, and soybeans are nutrient-dense sources of protein that are lower in purines compared to animal meats. Regular consumption of legumes has been associated with decreased inflammation and pain in gout sufferers, making them a valuable part of a balanced diet.
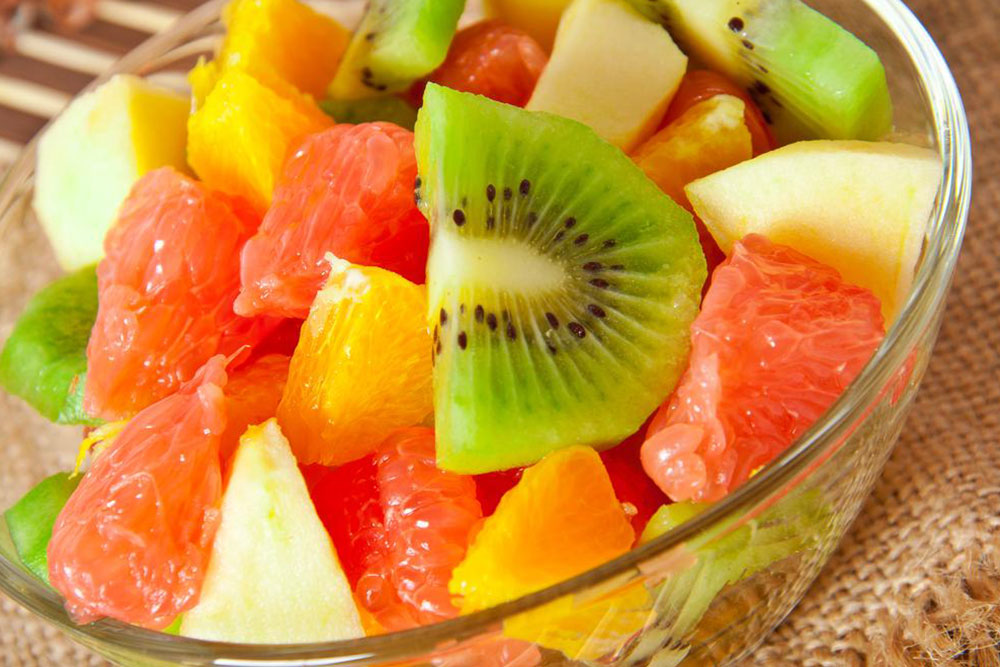
4. Fruits with Anti-Inflammatory Properties
Fruits are vital for all-round health, especially in managing inflammation associated with gout. Berries, citrus fruits, and particularly cherries have numerous studies supporting their ability to reduce uric acid levels and prevent attacks. Cherries contain anthocyanins—potent antioxidants that inhibit the enzymes responsible for uric acid production, making them a natural remedy for gout prevention.
5. Green Leafy Vegetables
Vegetables such as spinach, kale, broccoli, and collard greens supply vital minerals, antioxidants, and vitamins that help restore body strength, improve metabolism, and reduce uric acid deposits in joints. Including green vegetables in diets ensures adequate nutrient intake while helping to lower inflammation.
Foods to Avoid for Effective Gout Management
While emphasizing beneficial foods, it’s equally important to recognize items that exacerbate gout symptoms. High-purine foods and those rich in added sugars or fructose are known to elevate uric acid levels and should be restricted.
Examples include:
Organ meats such as liver, kidney, and sweetbreads
Certain fish like herring, sardines, trout, tuna, and anchovies, which are high in purines
Yeast and beer, which contain high levels of purines and additional compounds that can worsen symptoms
Additionally, foods and beverages high in added sugars, especially those containing high-fructose corn syrup such as sodas, candies, and sweetened cereals, should be limited. Refined carbohydrates like cakes, cookies, and white bread can also contribute to elevated uric acid levels and provide little nutritional benefit.
Additional Lifestyle and Dietary Recommendations
Beyond diet, staying well-hydrated helps dilute uric acid and facilitates its excretion. Aim to drink plenty of water throughout the day. Maintaining a healthy weight reduces the stress on joints and decreases uric acid levels, which can help in preventing recurrent gout attacks. Regular physical activity, combined with dietary management, constitutes a comprehensive approach for optimal gout control. Limiting alcohol consumption, especially beer and spirits, further supports reducing flare-up risk.
Conclusion: Building a Gout-Resistant Lifestyle
Managing gout effectively requires a holistic approach centered on diet, hydration, weight management, and lifestyle adjustments. Incorporating anti-inflammatory foods, avoiding known triggers, and cultivating healthy habits can help prevent painful flare-ups and improve overall quality of life. Consulting with healthcare professionals and dietitians ensures personalized strategies tailored to individual needs, maximizing the benefits of dietary modifications and supporting long-term joint health.