A Comprehensive Guide to Contact Dermatitis: Recognizing Symptoms, Understanding Causes, and Exploring Effective Treatments
This comprehensive article explores contact dermatitis, detailing its symptoms, causes, types, and effective treatments. It emphasizes early recognition and proper management to prevent complications, providing valuable insights for individuals suffering from skin irritation and inflammation. Learn how to identify triggers and seek appropriate care to maintain healthy skin and reduce discomfort.
All You Need to Know About Contact Dermatitis: Symptoms, Causes, and Proven Treatment Options
Have you recently experienced sudden redness, swelling, or irritation on your skin? These symptoms, especially when accompanied by intense itching, burning sensations, or blisters, could be signs of contact dermatitis. While mild cases may resolve naturally over time, more persistent or severe reactions require prompt diagnosis and targeted treatment to avoid complications. Contact dermatitis often appears localized to the area of contact, but its effects can be uncomfortable and disruptive. Recognizing early symptoms and understanding the underlying causes are critical steps in managing this condition effectively.
Understanding the distinct types and triggers of contact dermatitis empowers individuals to prevent flare-ups and seek appropriate treatment. There are mainly two primary forms: irritant and allergic contact dermatitis, each with unique causes and symptoms.
Recognizing the Signs and Symptoms of Contact Dermatitis
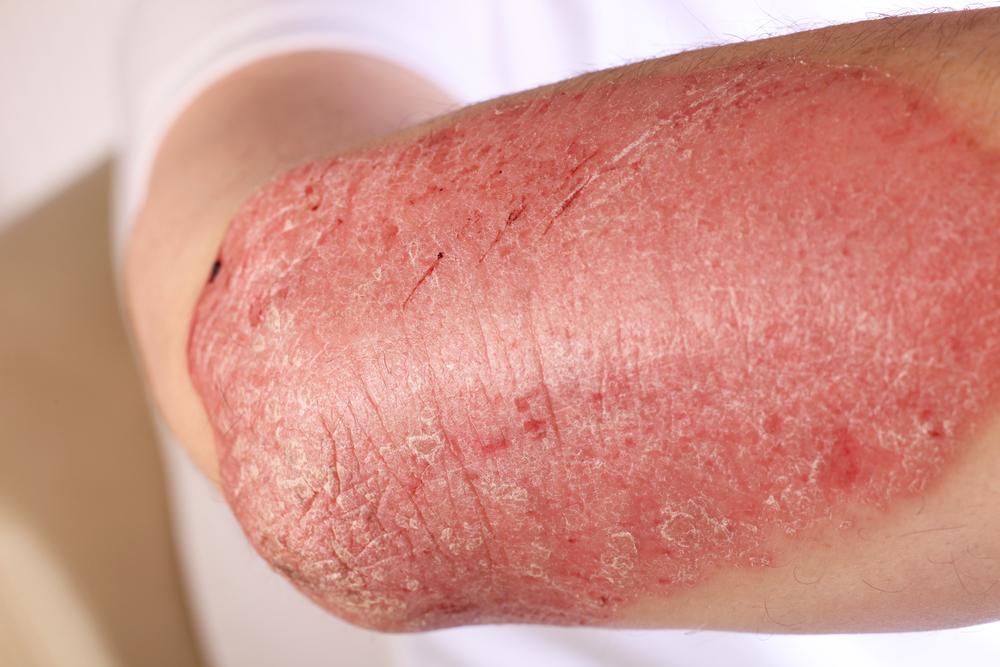
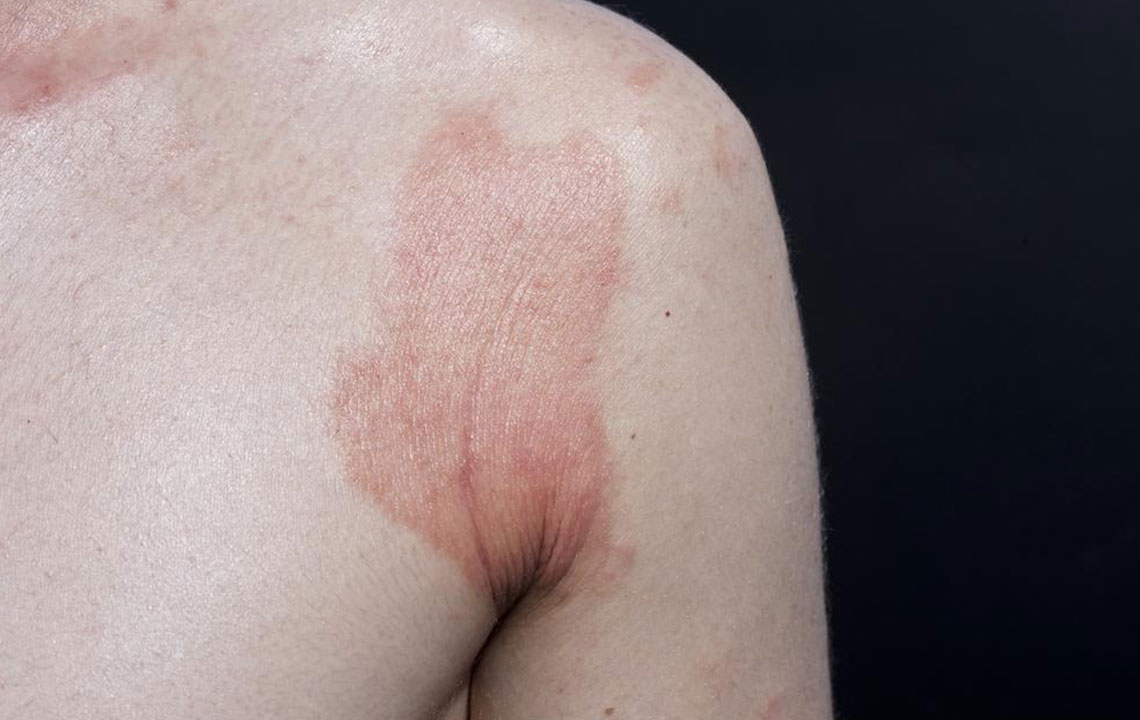
Contact dermatitis manifests with redness, swelling, and itching at the site of contact. Allergic contact dermatitis might also present with dry, flaky skin, blisters, hives, and heightened sensitivity to sunlight, which can worsen the skin's appearance and comfort. Persistent redness may lead to skin thickening or hyperpigmentation over time. Swelling around the eyes, lips, or groin region is often noted in allergic cases. The severity can vary from mild irritation to intense inflammation that significantly impacts daily life.
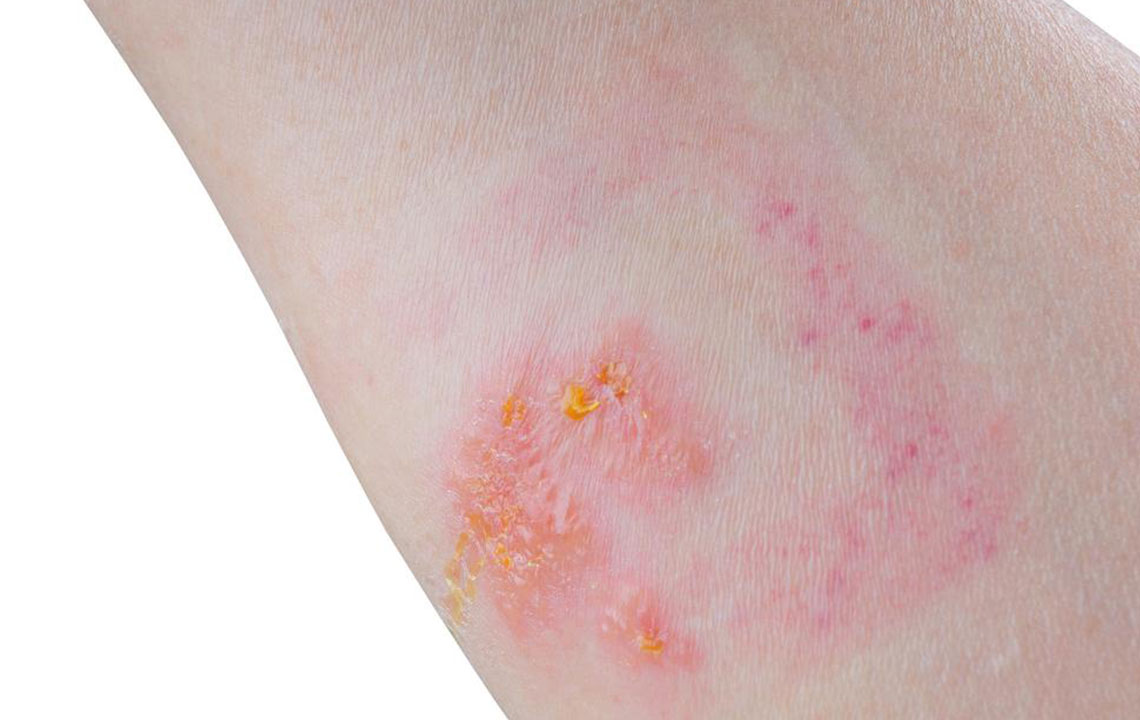
In contrast, irritant contact dermatitis often causes cracking, blistering, swelling, and sometimes open sores that may crust over. The skin reaction depends heavily on the irritant's concentration, duration of exposure, and individual sensitivity.
Causes of contact dermatitis are generally classified into three categories: irritating agents, allergens, and photo-reactive substances. Understanding these can help prevent future episodes and guide safe product selection.
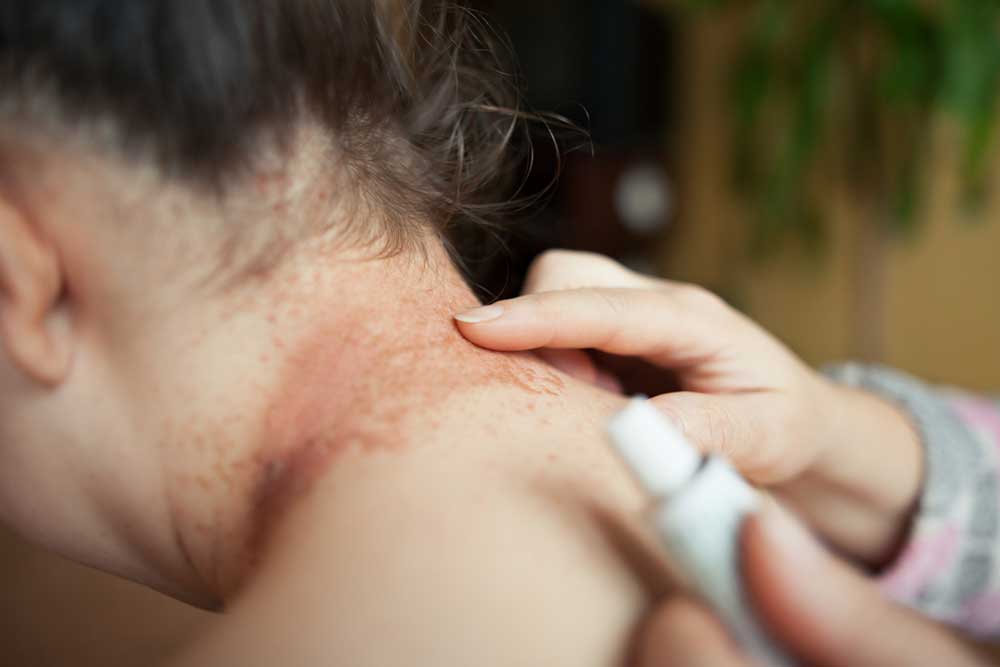
Allergic contact dermatitis is triggered when specific substances activate an immune response in the skin. Common allergens include metals like nickel and gold found in jewelry, certain chemicals in cosmetics and cleaning products, perfumes, latex gloves, and plants like poison ivy, oak, and sumac. When the immune system recognizes these as foreign threats, it causes inflammation, redness, and swelling.
Photo-contact dermatitis is less widespread but important to recognize. It occurs when chemicals applied to the skin react under exposure to sunlight, creating an inflammatory response hours after application. Substances like certain medications, fragrances, or chemicals in skincare products can cause this reaction.
By far the most common form, irritant contact dermatitis results from direct damage to the skin by harsh substances such as detergents, cleaning agents, solvents, pepper spray, kerosene, bleach, or even soap and water. Repeated exposure to these agents weakens the skin's natural barrier, leading to inflammation, cracking, and pain.
Effective Strategies for Treating Contact Dermatitis
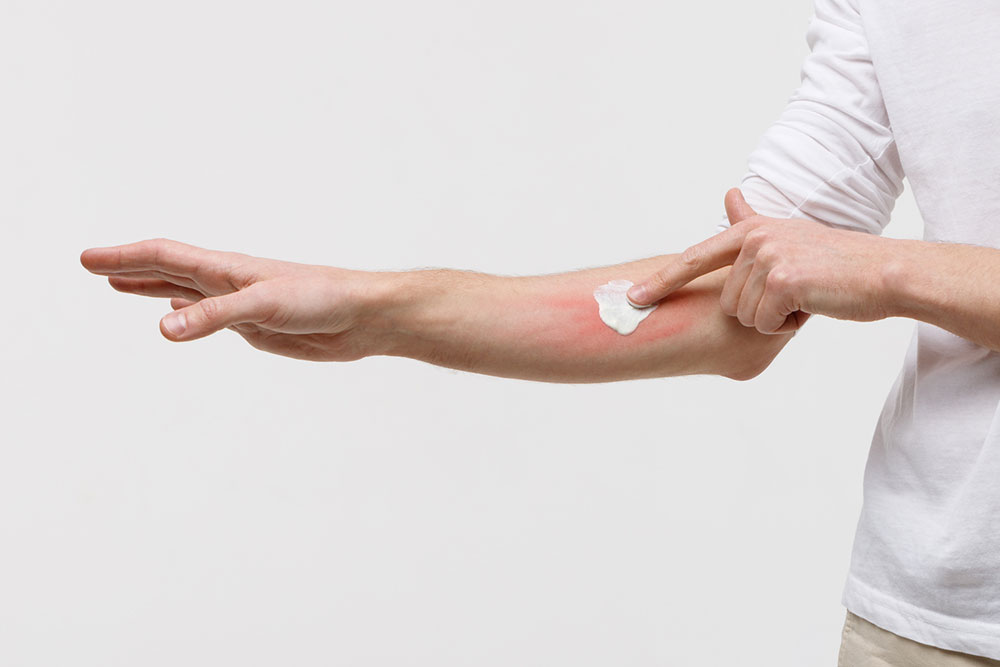
To manage contact dermatitis effectively, avoiding known triggers is essential. The first step is identifying and eliminating contact with suspected irritants or allergens. Gentle cleansing of the affected area with lukewarm water and mild, fragrance-free cleansers can help remove residual irritants. Applying soothing, unscented moisturizers such as petroleum jelly, coconut oil, or natural aloe vera gel reduces inflammation and promotes healing.Home remedies can be helpful in alleviating symptoms, but persistent or severe cases require professional medical intervention. If symptoms linger beyond three weeks, worsen, or include blisters, oozing, spreading redness, or significant discomfort, consult a healthcare provider promptly. Medical treatments may include topical corticosteroids, antihistamines, or other prescribed medications.
Particularly in cases involving the face, genitals, or large areas of the body, medical guidance is crucial to prevent complications. Additionally, recurrent exposure to allergens increases the risk of chronic dermatitis, emphasizing the importance of cautious product use and patch testing to identify sensitivities.
It's vital to distinguish contact dermatitis from other skin conditions that produce similar symptoms. Conditions like eczema, viral or bacterial infections, flea bites, shingles, or fungal infections such as candidiasis can mimic contact dermatitis. Diaper rash and other dermatological conditions also share overlapping signs. Accurate diagnosis by a healthcare professional ensures appropriate treatment and helps avoid unnecessary interventions. Properly managing contact dermatitis not only relieves discomfort but also prevents long-term skin damage and improves overall skin health.