Comprehensive Guide to Managing High LDL Cholesterol: Causes, Risks, and Effective Solutions
This comprehensive article explores high LDL cholesterol, its causes, health risks, and effective strategies for management. It emphasizes lifestyle modifications, dietary changes, and medical options to help reduce cholesterol levels and prevent heart disease and stroke. Suitable for those seeking to improve cardiovascular health through informed choices and proactive management.

Comprehensive Guide to Managing High LDL Cholesterol: Causes, Risks, and Effective Solutions
Cholesterol is a waxy, fat-like substance vital for several bodily functions, including building cell membranes, synthesizing hormones such as estrogen and testosterone, and aiding in the production of digestive fluids like bile. It is naturally produced by the liver, and it also enters the body through dietary sources. While cholesterol is essential for health, having too much of certain types can pose serious health risks. Understanding the nuances of cholesterol types, their functions, and how to manage levels effectively is crucial for maintaining cardiovascular and overall health.
Elevations in cholesterol, especially high levels of low-density lipoprotein (LDL), can significantly impact health by promoting the buildup of plaque within arteries—a condition known as atherosclerosis. This plaque buildup results in the narrowing of blood vessels, decreasing blood flow, and increasing the risk of heart and brain-related conditions. When arteries supplying the heart become blocked, it can lead to a heart attack. Similarly, blockages in arteries supplying the brain can cause strokes, which may result in lasting neurological damage or death. Consequently, managing cholesterol levels is a cornerstone of preventing cardiovascular diseases and cerebrovascular events.
High LDL cholesterol, often termed the "bad" cholesterol, does not usually produce noticeable symptoms, making regular check-ups vital. Elevated LDL levels increase the risk of developing atherosclerosis, which can lead to heart attacks, strokes, and other cardiovascular complications. Conversely, high-density lipoprotein (HDL), known as the "good" cholesterol, helps remove excess cholesterol from the bloodstream, transporting it back to the liver for processing and excretion. Maintaining a healthy balance between LDL and HDL is essential for cardiovascular health.
Understanding what causes high LDL cholesterol can help you take targeted actions to reduce your risk. Several factors contribute to elevated LDL levels, and many of these are modifiable through lifestyle changes or medical intervention. Knowing these factors enables individuals to make informed decisions about their health and work proactively to maintain optimal cholesterol levels.
Factors Leading to Elevated LDL Cholesterol
The primary contributors to increased LDL cholesterol include dietary habits, physical activity levels, genetics, body weight, and other health conditions. Diets high in saturated fats found in red meats, full-fat dairy products, and trans fats present in many processed foods significantly elevate LDL levels. Consuming cholesterol-rich foods can also contribute, though their impact may vary among individuals.
Being overweight or obese is strongly associated with higher LDL and lower HDL levels. Excess weight, especially around the abdomen, increases the likelihood of cardiovascular issues. Sedentary lifestyles further exacerbate this problem by reducing HDL levels and impairing overall lipid profiles.
As people age, particularly past 20, cholesterol levels tend to rise gradually. Genetics also play a crucial role; familial hypercholesterolemia is a hereditary condition characterized by high cholesterol levels that often require medical management. Additionally, having a large waist circumference—40 inches or more for men, and 35 inches or more for women—correlates with higher LDL and increased cardiovascular risk.
Health conditions, such as type 2 diabetes, also influence cholesterol levels. Diabetes often causes an imbalance, with increased LDL and decreased HDL. Smoking is another significant risk factor, as it reduces HDL levels and promotes oxidative damage to blood vessels, accelerating plaque formation.
Effective Strategies to Lower LDL Cholesterol
Fortunately, many of the modifiable causes of high LDL cholesterol can be addressed through lifestyle modifications and medical interventions. Adopting a heart-healthy diet is fundamental. Emphasizing foods rich in soluble fiber, such as oats, beans, lentils, fruits, and vegetables, can help lower LDL levels. Incorporating fatty fish like salmon, mackerel, and sardines provides omega-3 fatty acids that support heart health and improve lipid profiles.
Limiting intake of saturated fats and trans fats is vital. These unhealthy fats are prevalent in fried foods, baked goods, and processed snacks. Choosing lean meats, low-fat dairy, and cooking methods like baking, steaming, or grilling can significantly reduce lipid intake.
Regular physical activity is equally important. Engaging in aerobic exercises, such as brisk walking, cycling, swimming, or jogging, improves HDL levels and lowers LDL cholesterol. The American Heart Association recommends at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise or 75 minutes of vigorous activity weekly, combined with muscle-strengthening activities on two or more days.
Maintaining a healthy weight through diet and exercise not only reduces LDL cholesterol but also improves overall cardiovascular health. Quitting smoking dramatically increases HDL levels and reduces the risk of heart disease and stroke.
For individuals with persistently high or dangerously elevated LDL levels, pharmacological treatments may be necessary. Statins are the most commonly prescribed medications, effectively lowering LDL cholesterol. Other options include bile acid sequestrants, ezetimibe, and PCSK9 inhibitors. These medications should always be taken under strict medical supervision, as they can have side effects and require monitoring.
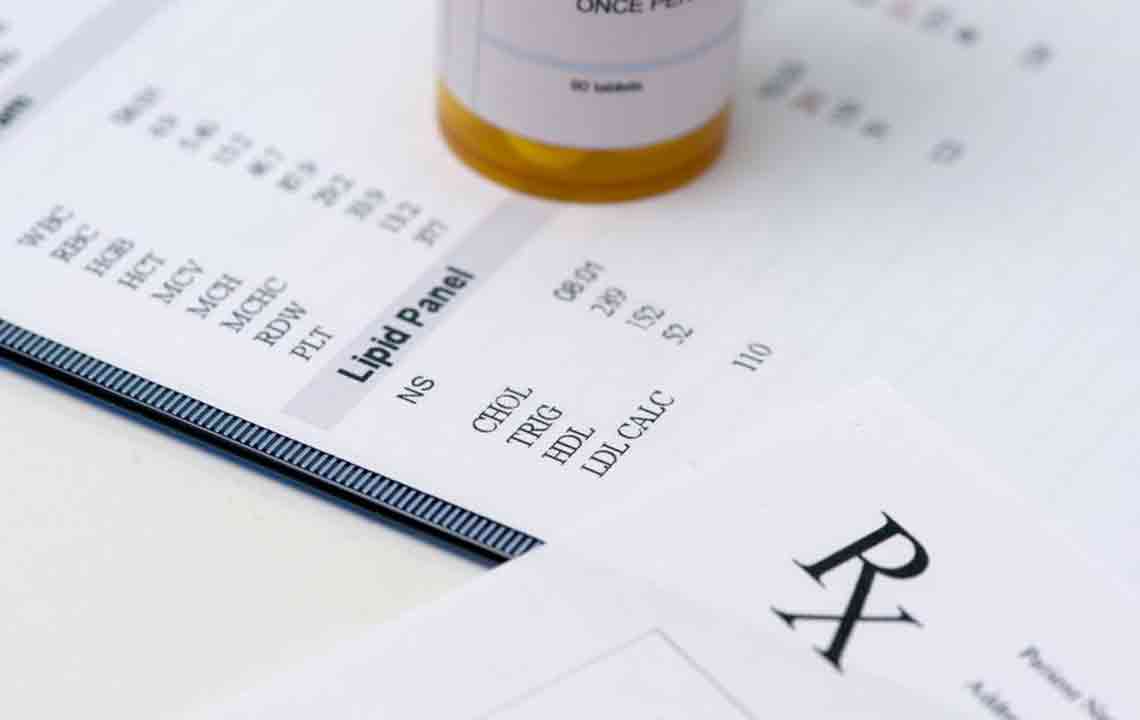
In addition to lifestyle and medication, routine health check-ups and lipid panel testing are essential. Regular testing enables early detection of cholesterol abnormalities, allowing for timely intervention before serious complications develop. It is recommended that adults have their cholesterol checked at least once every five years, or more frequently if risk factors are present.
To achieve lasting health benefits, a comprehensive approach combining diet, exercise, weight management, and medical guidance is essential. By understanding the causes and implementing effective strategies, individuals can significantly reduce their risk of cardiovascular disease and enhance their overall well-being.