Comprehensive Guide to Reducing Bad Cholesterol (LDL) for Better Heart Health
This comprehensive guide explores effective lifestyle strategies to lower bad LDL cholesterol and enhance heart health. It emphasizes dietary adjustments, exercise, weight management, and supplements, offering detailed insights to help individuals reduce their cardiovascular risks naturally. Consistent implementation of these methods can lead to lasting improvements in cholesterol levels and overall well-being.

Comprehensive Strategies for Lowering Bad Cholesterol (LDL) and Improving Cardiovascular Health
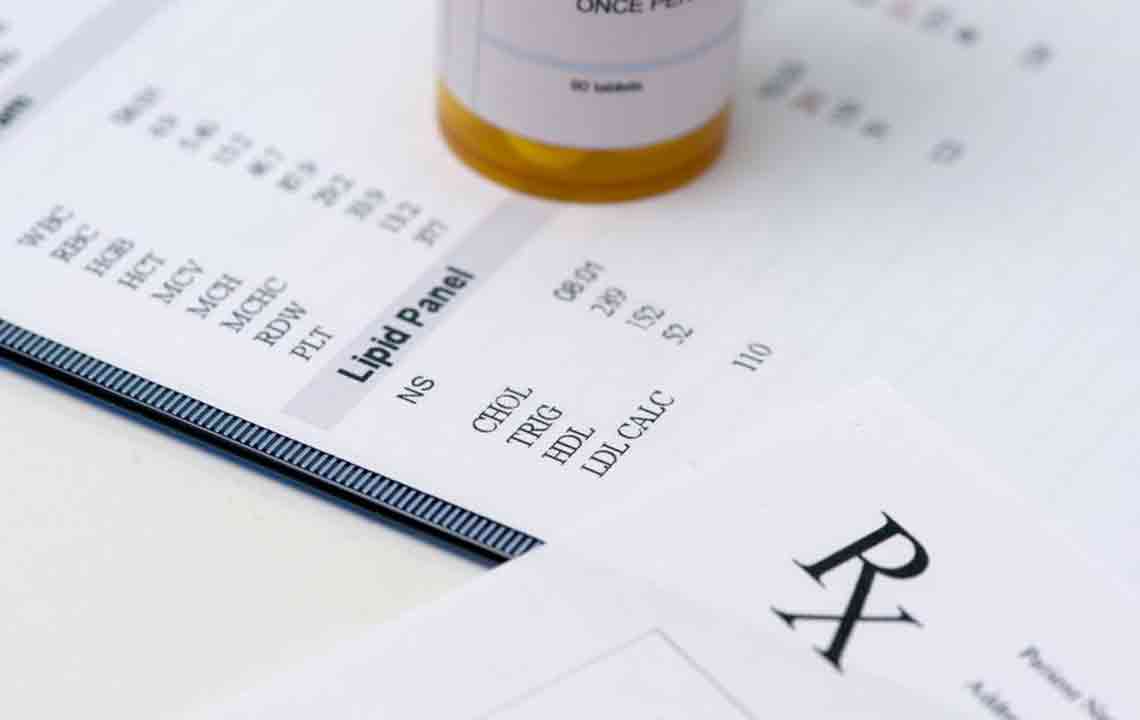
Maintaining optimal levels of low-density lipoprotein (LDL), commonly known as "bad cholesterol," is essential for safeguarding heart health. Elevated LDL levels are directly linked to the buildup of plaque in arteries, increasing the risk of cardiovascular diseases such as heart attacks and strokes. Scientific studies consistently emphasize that keeping LDL within a healthy range—preferably between 80 to 100 mg/dL—can dramatically reduce the likelihood of cardiovascular events.
While medications like statins are often prescribed to manage high LDL cholesterol, adopting sustainable lifestyle changes remains one of the most effective strategies for long-term control. These modifications not only help regulate cholesterol levels but also contribute to overall health enhancement.
The timeline for noticeable improvements varies among individuals, generally spanning six to eight weeks, provided there are no other underlying health issues. Consistency in healthy habits, however, is key to achieving and maintaining desirable LDL levels and reducing heart disease risk.
Several targeted lifestyle strategies can substantially lower LDL cholesterol levels. These include dietary modifications, increased physical activity, weight management, and supplement use. Implementing these steps can lead to significant health benefits and a reduction in cardiovascular risk factors.
Adopt a Heart-Healthy, Balanced Diet
Emphasize foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids, such as fatty fish (salmon, mackerel, sardines), which help increase HDL ('good' cholesterol) and reduce LDL ('bad' cholesterol). Focus on unsaturated fats found in olive oil, avocados, and nuts, while limiting saturated and trans fats present in processed foods and fried items. Incorporate a variety of fresh fruits and vegetables to provide essential nutrients and antioxidants that support heart health.
Enhance Fiber Intake with High-Fiber Foods
Soluble fiber plays a crucial role in lowering LDL cholesterol naturally. Integrate sources like oats, barley, legumes (beans, lentils), sweet potatoes, carrots, and eggplants into daily meals. Berries, citrus fruits such as oranges, and apples are also beneficial. These foods trap cholesterol in the digestive system, preventing its absorption into the bloodstream. Additionally, nuts and seeds like flaxseeds and chia seeds are excellent choices for cholesterol management.
Engage in Regular Cardiovascular Exercise
Physical activity plays a vital role in improving cholesterol profiles. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise, such as brisk walking, cycling, or swimming, per week. Consistent cardio workouts help raise HDL levels and lower LDL, while also enhancing overall cardiovascular function.
Maintain a Healthy Body Weight
Excess body weight elevates LDL cholesterol and increases the risk of heart disease. Prioritize weight loss through a combination of diet and exercise. Limiting intake of fatty, sugary, and high-calorie foods can prevent obesity and support weight management goals.
Incorporate Plant Sterol and Stanol Supplements
These natural compounds, found in fortified foods and supplements, can lower LDL cholesterol by competing with dietary cholesterol absorption. A daily intake of 1–2 grams of plant sterols or stanols has been proven effective without adding extra calories or sugars to your diet.
Utilize Psyllium Husks as a Dietary Supplement
Psyllium fiber, taken in doses of 9–10 grams per day, helps in reducing LDL cholesterol levels. It also promotes digestive health by improving bowel regularity. Incorporate psyllium into smoothies, water, or other beverages for ease of consumption.
Adopting these comprehensive strategies not only promotes lower LDL cholesterol but also contributes to improved overall cardiovascular health and well-being. Regular monitoring of cholesterol levels, along with lifestyle modifications, can lead to sustainable health benefits. Remember, making incremental changes and maintaining consistency are vital for long-term success in managing cholesterol levels effectively.