Comprehensive Guide to Identifying Causes and Detecting Swellings in the Armpit Area
This comprehensive guide details the causes, assessment, and diagnostic procedures for armpit swellings. Understanding when swelling signals a benign condition versus a serious health concern is essential. The article covers common causes such as infections, autoimmune diseases, and cancers, offering insights into diagnosis and treatment options. With thorough evaluations and proper medical attention, most armpit swellings can be effectively managed. Learn about the signs that warrant medical consultation and the diagnostic tests used to identify underlying health issues, ensuring prompt and accurate care.

Comprehensive Guide to Identifying Causes and Detecting Swellings in the Armpit Area
The presence of a swelling in the armpit, often characterized by an enlarged lymph node beneath the skin, can be a cause for concern or simply a benign occurrence. These lymph nodes are integral to your immune system, acting as filters that trap bacteria, viruses, and other harmful substances. Located throughout your body, particularly in regions like the neck, groin, and armpits, these small oval-shaped glands vary in size and can sometimes become swollen due to various factors.
In some instances, armpit swellings are minor, painless, and go unnoticed, vanishing on their own without treatment. However, at other times, such swellings can become more prominent, tender, or persistent, prompting individuals to seek medical advice. Recognizing the causes and understanding when to seek medical attention is crucial for early diagnosis and treatment, especially since some causes may be linked to more serious health conditions.
Below are comprehensive insights into the common reasons behind armpit swellings, assessment procedures, and diagnostic tests to help you better understand this condition:
Identifying the Common Causes of Armpit Swellings
Swollen lymph nodes in the armpit are generally benign and often temporary. They frequently occur due to minor tissue responses or infections, and many resolve without medical intervention. Nonetheless, some swellings may signal underlying health issues necessitating careful evaluation. Here are some prevalent and less common causes:
Immune System Reactions to Vaccines: Many individuals experience lymph node swelling after receiving vaccines due to the immune response triggered by the vaccine components. This type of swelling is usually mild and temporary, but monitoring is recommended.
Breast Cancer Indicators: Enlarged nodes in the armpit can sometimes be linked to breast cancer, especially if the tumor has spread to nearby lymphatic tissues. Any persistent swelling associated with other symptoms like pain, skin changes, or lumps in the breast warrants prompt medical evaluation.
Benign Tumors like Fibroadenomas: These non-cancerous growths are common in the breast tissue but may sometimes cause neighboring lymph nodes to swell.
Infections—Bacterial or Viral: Infections such as mononucleosis, common colds, or bacterial skin infections can cause lymph nodes in the armpit to enlarge as part of the body's immune response.
Blood Cancers, Including Leukemia: Certain blood cancers may present with swollen lymph nodes, fatigue, weight loss, or other systemic symptoms.
Lupus and Autoimmune Conditions: Autoimmune diseases like lupus can lead to lymph node swelling along with symptoms affecting joints, skin, and internal organs.
Benign Fatty Growths or Lipomas: These soft, painless, slow-growing tumors composed of fat tissue can sometimes be mistaken for swollen nodes but typically do not require treatment unless causing discomfort.
Allergic Reactions and Fungal Infections: Allergies or fungal infections can cause localized lymphadenopathy, often accompanied by other signs of irritation.
Lymphatic System Cancers—Lymphoma: Malignant conditions affecting the lymphatic system can present with persistent, enlarging lymph nodes, fever, night sweats, and weight loss.
How Healthcare Professionals Assess Armpit Swellings
When a patient presents with an armpit swelling, healthcare providers undertake a detailed assessment to determine its nature and cause. This begins with a thorough medical history, including recent infections, vaccination history, systemic symptoms, personal or family history of cancer, and any recent injuries or skin conditions.
Following the history-taking, a physical examination focuses on the texture, size, tenderness, mobility, and consistency of the swelling. The provider may also examine adjacent areas such as the breast tissue, chest wall, and neck to identify any related abnormalities.
In cases where the swelling appears benign and resolves on its own, limited intervention may be required. However, persistent or suspicious swellings necessitate further investigations to rule out serious conditions, especially cancers or systemic illnesses.
Diagnostic Procedures for Swelling in the Armpit
When initial physical assessments suggest that further testing is necessary, doctors may recommend specific diagnostic procedures, including:
Complete Blood Count (CBC): A blood test that evaluates your overall health and detects signs of infection or blood disorders.
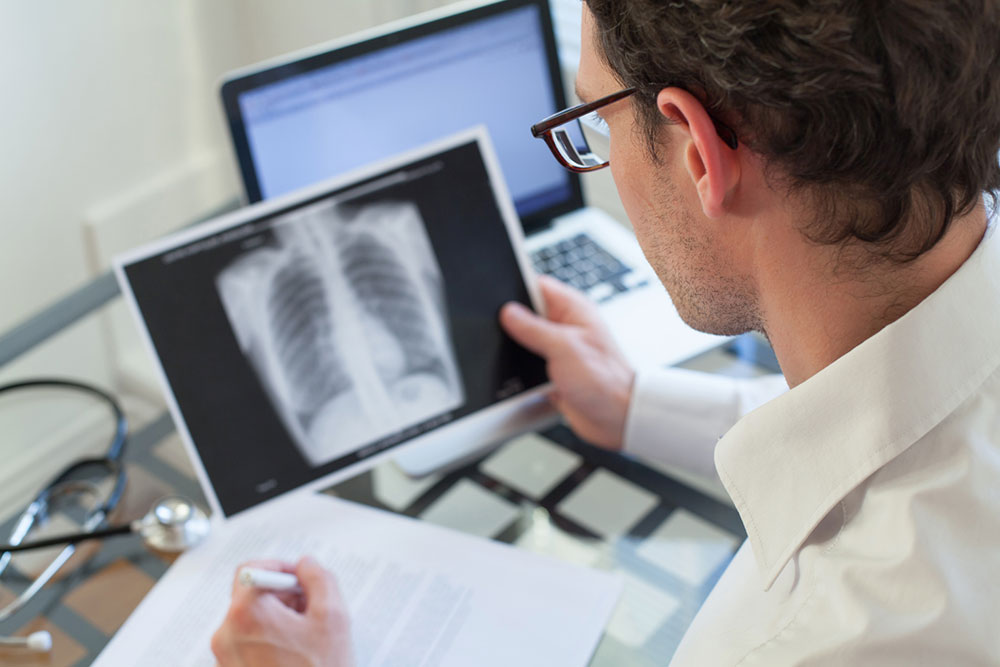
X-ray Imaging: Chest and breast X-rays help identify any abnormalities in the chest cavity, lungs, or breast tissue that could be linked to lymph node swelling.
Biopsy of the Affected Lymph Node: A definitive diagnostic test where a small sample of tissue is extracted for microscopic examination to determine whether the swelling is benign or malignant.
Allergy Testing: If allergic reactions are suspected as a cause, allergy tests can help identify specific sensitivities.
In some cases, additional imaging such as ultrasound, MRI, or PET scans may be recommended to further evaluate the condition.
Most armpit swellings are not emergencies and often resolve with minimal treatment or on their own. However, proper medical consultation is vital for accurate diagnosis and appropriate management, especially when the swelling persists, enlarges, or is associated with other symptoms like fever, night sweats, weight loss, or unexplained pain.