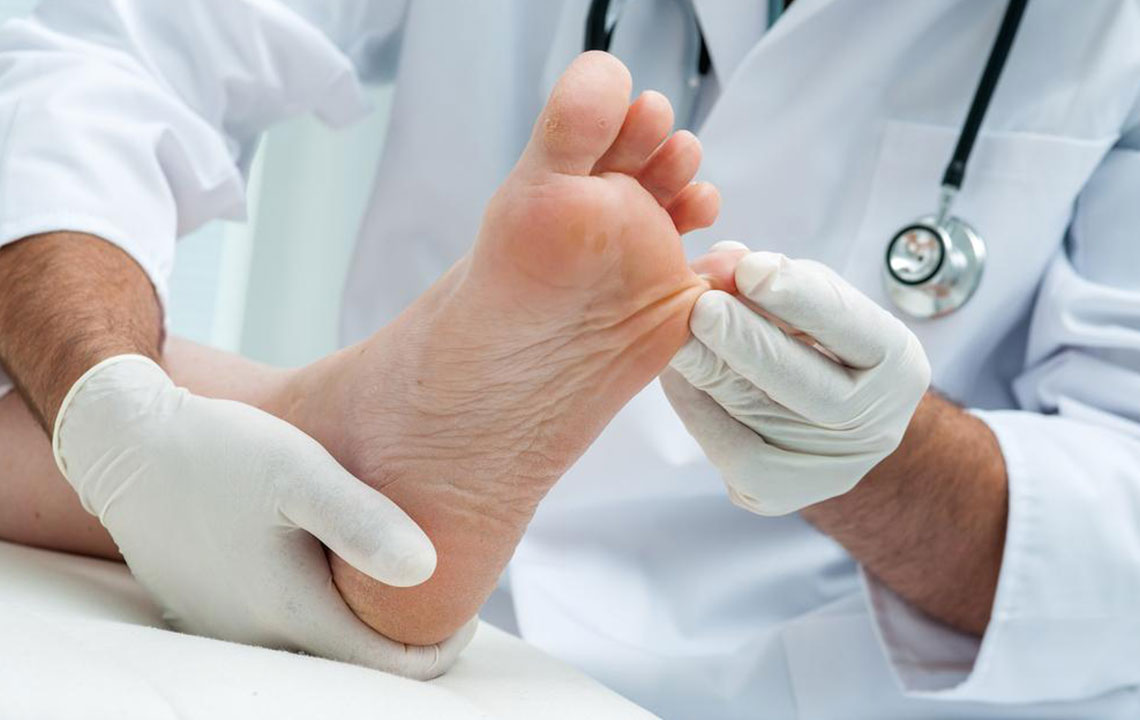
Comprehensive Guide to Recognizing and Treating Ingrown Toenails
This comprehensive article provides in-depth information about ingrown toenails, covering causes, symptoms, prevention, and treatment options. It emphasizes proper foot and nail care, identifies risk factors, and offers practical self-care tips. For persistent or severe cases, consulting a podiatrist is recommended to avoid complications. The guide aims to educate readers on early recognition and effective management techniques to maintain healthy, pain-free toes and prevent recurring issues.
Comprehensive Guide to Recognizing and Treating Ingrown Toenails
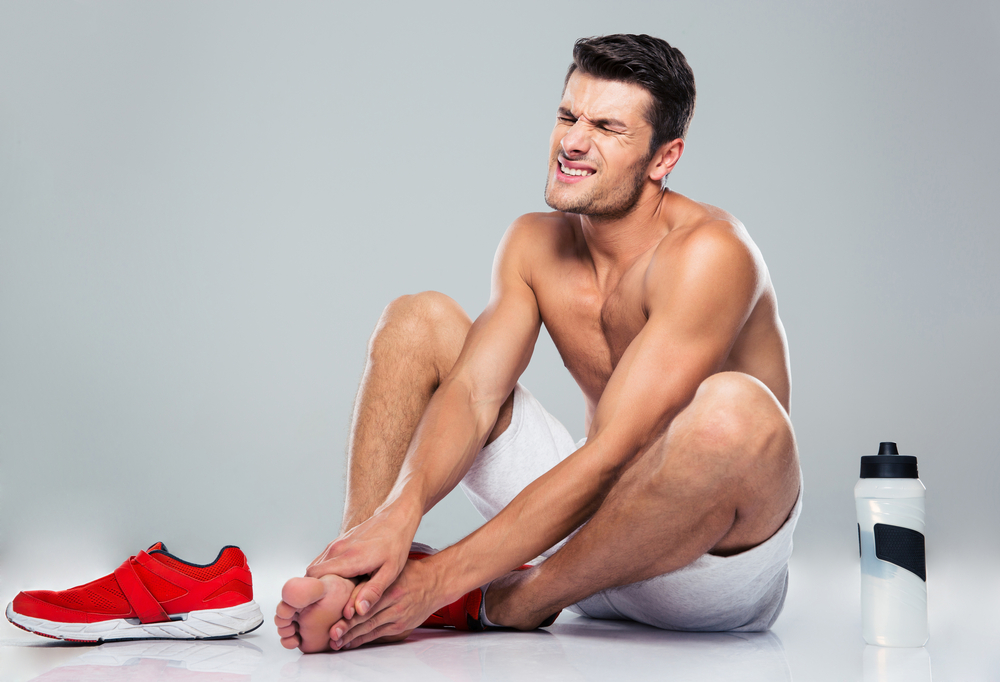
Have you ever experienced discomfort, swelling, or redness around your toenails after a long day? These signs could point to an ingrown toenail, a common yet often overlooked foot condition. Wearing tight or ill-fitting shoes can exacerbate the problem, leading to increased pain and potential infections if left untreated. Recognizing the early symptoms and understanding the proper treatment methods are vital for maintaining healthy feet and preventing severe complications.
In this detailed guide, we will explore what ingrown toenails are, the causes behind them, and practical ways to manage and treat this condition. From daily foot care practices to professional medical intervention, learn how to keep your toes healthy and pain-free.
Understanding ingrown toenails begins with knowing their causes. Typically, an ingrown toenail develops when the nail grows into the surrounding skin instead of over it, leading to pain, inflammation, and sometimes infection. While they can occur on any toe, they are most common on the big toe.
The leading causes include improper nail trimming techniques, such as cutting nails too short, rounding the edges rather than straight across, or failing to maintain proper hygiene. Wearing shoes that are too tight or have a narrow toe box increases pressure on the toes, which can push the nail edges into the skin. Foot injuries that damage the nail or nail bed can also result in abnormal growth. Additionally, genetic predispositions, fungal infections, or conditions like psoriasis may contribute to the development of ingrown toenails.
Preventive measures are essential to avoid this painful condition. Proper foot hygiene and nail care are the foundation. Always cut toenails straight across, avoiding rounded or pointed edges, and refrain from cutting them too short. Choosing footwear that fits well—preferably with a wide toe box—helps reduce pressure on the toes. Regularly inspecting your feet, especially if you have existing health conditions such as diabetes or circulatory issues, is crucial.
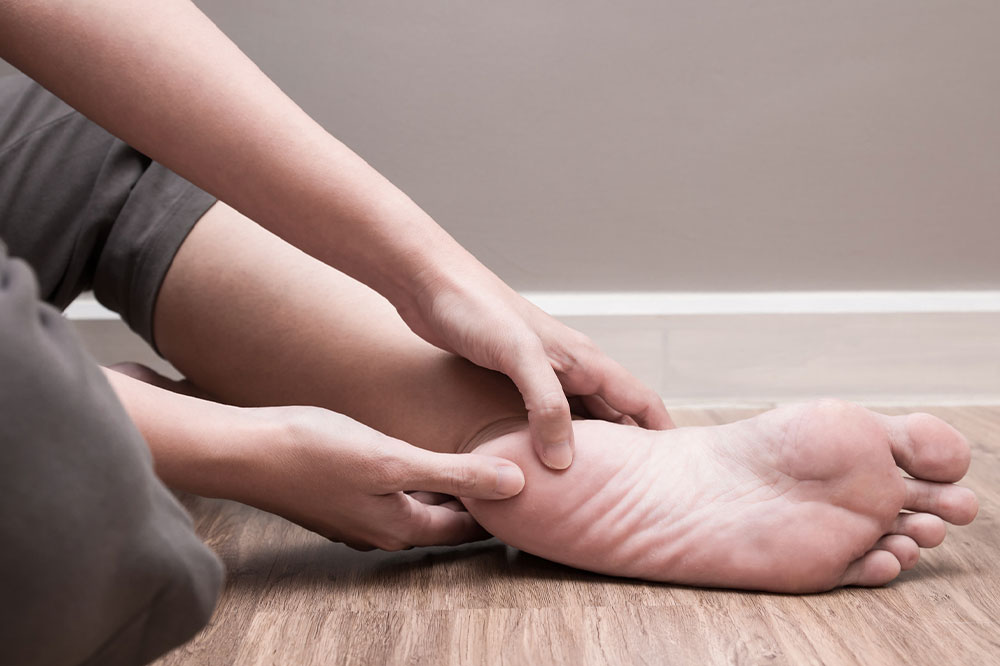
When an ingrown toenail occurs, prompt care can prevent it from worsening. Soaking the affected foot in warm salted water for 10-15 minutes several times a day softens the nail and reduces swelling. After soaking, gently lift the nail edge and place a small piece of cotton or dental floss underneath to prevent further embedding. Applying an over-the-counter antibiotic ointment and covering the area with a sterile bandage helps prevent infection.
In cases where discomfort persists, worsening, or signs of infection emerge—such as pus, increased redness, or severe swelling—it is imperative to consult a healthcare professional, typically a podiatrist. A medical professional can perform minor surgical procedures, such as removing part of the nail or correcting the nail bed, to provide long-term relief. Maintaining good foot hygiene and ensuring the right footwear are crucial steps in preventing recurrences.
Overall, healthy foot habits, awareness, and early treatment are your best defenses against the pain and complications of ingrown toenails. Whether you’re managing minor cases at home or seeking professional care, understanding this condition is essential for foot health.