Comprehensive Guide to Diabetic Eye Health: Recognizing Symptoms and Managing Diet for Vision Preservation
Learn about the early symptoms of diabetic eye complications and discover essential dietary tips to protect your vision. This comprehensive guide highlights common signs like floaters and blurry vision, discusses foods to limit such as refined grains and sugary fruits, and emphasizes the importance of regular eye exams and healthy eating habits for optimal eye health management in diabetics.

Comprehensive Guide to Diabetic Eye Health: Recognizing Symptoms and Managing Diet for Vision Preservation
Diabetes, particularly Type 2 diabetes, is a widespread condition impacting millions worldwide. Beyond blood sugar management, diabetic individuals must be vigilant about potential complications, especially those affecting vision. Diabetic eye diseases, such as diabetic retinopathy, macular edema, and glaucoma, are serious concerns that can lead to partial or total vision loss if unchecked. Recognizing early symptoms and adopting proper dietary habits are critical steps toward safeguarding eye health and maintaining quality of life.
Individuals living with diabetes face increased risks of specific eye conditions that are often insidious in their early stages. These issues develop gradually and may initially present with subtle signs that are easy to overlook. The most common eye complications associated with diabetes include diabetic retinopathy, which involves damage to the small blood vessels in the retina, and macular edema, characterized by fluid accumulation leading to swelling of the central retina. Another concern is glaucoma, which can sometimes be accelerated by diabetic-related changes within the eye.
Understanding Key Symptoms of Diabetic Eye Complications
Spotting Floaters and Fluctuating Vision
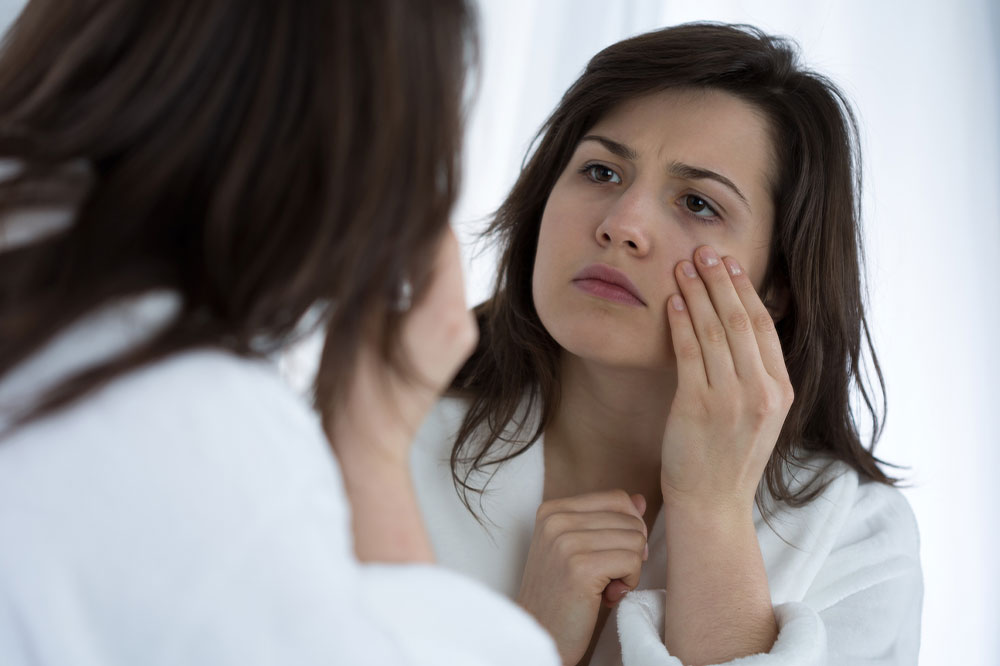
One of the earliest warning signs of diabetic eye problems is the appearance of floating spots or strings drifting across your field of vision. These floaters are often caused by small blood or tissue debris in the vitreous humor of the eye, a consequence of blood vessel damage due to prolonged high blood sugar levels. If you notice an increase in floaters, intermittent flashes of light, or a shadow blocking part of your vision, it's crucial to seek ophthalmologic consultation promptly, as these can indicate retinal detachment or hemorrhage.
Blurry Vision as an Early Indicator
Persistent blurriness or fluctuations in your vision are common initial symptoms of diabetic eye disease. When blood vessels in the retina leak fluid, blood, or lipids, it causes swelling that distorts vision, especially around the macula — the central part of the retina responsible for sharp vision. Over time, untreated fluid leakage can lead to the formation of abnormal blood vessels and scarring, further impairing sight. Regular eye examinations are vital for early detection and intervention.
Peripheral Vision Loss and Tunnel Vision
In some cases, diabetic eye complications can cause narrowing of the visual field, resulting in peripheral vision loss or tunnel vision. This symptom is often associated with increased intraocular pressure and fluid buildup in the anterior chamber of the eye, commonly linked to glaucoma. If untreated, this condition can lead to irreversible vision loss. Awareness of peripheral vision changes should prompt immediate ophthalmic evaluation.
Diet and Lifestyle Factors Affecting Diabetic Eye Health
Managing diet plays a pivotal role in controlling blood sugar levels and, consequently, in preventing or slowing the progression of diabetic eye disease. Certain foods are known to cause spikes in blood glucose and can exacerbate microvascular damage in the eyes. Making informed dietary choices is essential for preserving vision and overall eye health.
Foods to Limit or Avoid to Protect Eye Health
Refined Grain Products
Refined carbohydrate foods such as white bread, white rice, processed pasta, and baked goods made from refined flour have minimal fiber content and are rapidly digested, leading to swift increases in blood sugar levels. Elevated blood glucose can damage blood vessels in the retina, accelerating conditions like diabetic retinopathy. For better blood sugar control, opt for whole grains like brown rice, quinoa, and whole wheat alternatives, which are rich in fiber and have a lower glycemic index.
High-Sugar Fruits and Processed Snack Foods
Fruits naturally contain sugars, but some varieties have higher glycemic indexes that can cause substantial blood sugar spikes. Fruits like bananas, grapes, mangoes, and dried fruits should be consumed in moderation, especially by those with poorly controlled diabetes. Additionally, processed fruit snacks, flavored yogurts, and sweetened beverages are high in added sugars and should be avoided or limited to maintain stable blood glucose levels. Choosing low-glycemic fruits such as berries, apples, and pears can help in managing blood sugar.
Additional Dietary Considerations for Diabetic Eye Protection
Incorporate foods rich in antioxidants, vitamins, and minerals that support eye health — including leafy green vegetables (spinach, kale), omega-3 fatty acids (salmon, walnuts), and vitamin C-rich fruits (oranges, strawberries). Hydration, moderation in caffeine intake, and limiting processed foods high in saturated fats contribute to overall vascular health and reduce the risk of diabetic eye complications.
Preventive Measures and Routine Eye Exams
Regular eye examinations are essential for early detection of diabetic retinopathy and other ocular conditions. Screening should begin soon after diagnosis and be performed at least annually or more frequently if indicated. Effective management of blood sugar, blood pressure, and cholesterol levels, combined with a healthy diet and lifestyle, significantly reduces the risk of vision-threatening complications.
By understanding the early warning signs and adhering to a well-balanced, diabetes-friendly diet, individuals can take proactive steps to protect their vision. Awareness and timely intervention are the best defenses against diabetic eye diseases, helping ensure a clearer, healthier future.