Comprehensive Guide to Hypertension: Risks, Prevention, and Lifestyle Strategies
This comprehensive article explores the risks associated with hypertension and offers detailed strategies for prevention and management. It highlights the importance of lifestyle changes such as a healthy diet, regular exercise, and avoiding harmful substances. Understanding and controlling high blood pressure can significantly reduce the risk of heart attacks, strokes, kidney damage, and vision problems. Emphasizing early detection and consistent lifestyle adjustments, this guide empowers readers to take proactive steps for a healthier, longer life by managing hypertension effectively.

Comprehensive Guide to Hypertension: Risks, Prevention, and Lifestyle Strategies
Hypertension, commonly known as high blood pressure, is a prevalent health concern worldwide. It occurs when the force of blood against the artery walls remains consistently elevated, exerting stress on vital organs and increasing the risk of serious health conditions. Understanding the underlying causes, recognizing the associated risks, and implementing effective preventive measures are essential steps toward maintaining cardiovascular health and overall well-being.
Healthy arteries are characterized by their resilience and flexibility, allowing them to expand and contract smoothly during blood circulation. However, when blood pressure remains high over time, it can impair the normal functioning of these arteries. Elevated pressure causes the muscular walls of arteries to thicken—a process called hypertrophy—leading to reduced elasticity and narrowing of the blood vessel lumen. This process, known as arteriosclerosis, significantly hampers blood flow and increases the workload on the heart.
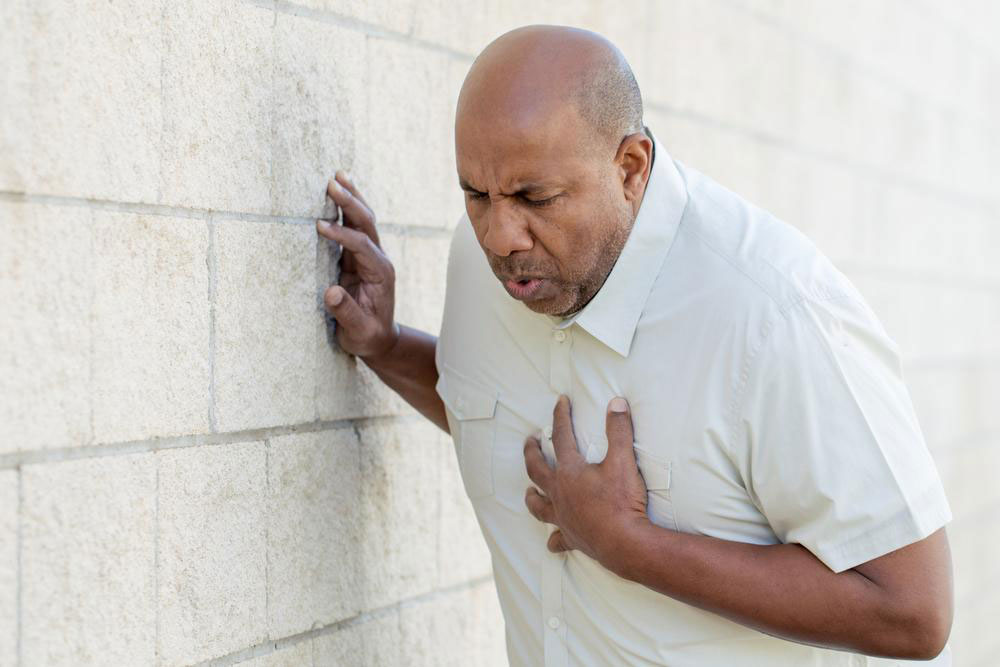
One of the most dangerous consequences of uncontrolled hypertension is the increased likelihood of cardiovascular events such as heart attacks and strokes. The persistent high pressure can cause arterial walls to weaken, develop plaques, or even rupture, causing life-threatening complications. Moreover, hypertension damages small blood vessels in critical organs such as the kidneys and eyes. Damage to renal blood vessels impairs kidney function, potentially leading to chronic kidney disease or failure. Similarly, fragile blood vessels in the eyes can bleed, causing vision problems, including blurred vision or complete vision loss.
Hypertension also influences other aspects of health. It can decrease blood flow to reproductive organs, resulting in sexual dysfunction. Excess calcium levels in urine, often associated with high blood pressure, can affect bone health by reducing bone density over time, increasing susceptibility to osteoporosis.
Preventing and managing hypertension relies heavily on lifestyle modifications. Maintaining a healthy weight through balanced nutrition and regular physical activity can significantly lower blood pressure levels. The DASH (Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension) diet emphasizes fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and low-fat dairy, all of which have been shown to effectively reduce hypertension risks. Limiting salt intake is crucial; excessive salt consumption causes water retention, which increases blood volume and pressure.
In addition to dietary adjustments, moderating alcohol consumption and avoiding tobacco use are vital. These substances constrict blood vessels and elevate blood pressure, exacerbating cardiovascular risks. Regular exercise, such as brisk walking, cycling, or swimming, has been proven to strengthen the heart and improve arterial flexibility. Stress management techniques—like meditation, deep breathing, and mindfulness—also contribute to healthier blood pressure levels.
Medications may be necessary for some individuals, especially when lifestyle changes do not sufficiently control hypertension. A healthcare provider can recommend antihypertensive drugs tailored to the individual's specific needs and monitor their effectiveness over time. Routine blood pressure screenings are essential for early detection, particularly because hypertension often presents no symptoms until complications occur.
Adopting a proactive approach to managing blood pressure can prevent severe health consequences and enhance quality of life. Regular check-ups, maintaining a healthy lifestyle, and adhering to medical advice are the pillars of effective hypertension control. Recognizing the importance of these measures can empower individuals to take charge of their health and reduce their risk of cardiovascular and systemic diseases.