Comprehensive Guide to Hypertension: Causes, Types, and Effective Management Techniques
This comprehensive guide delves into hypertension, exploring its causes, classification, and management strategies. It emphasizes lifestyle changes such as diet, exercise, and stress management to control blood pressure. Understanding primary and secondary hypertension helps in targeted treatment, reducing risks associated with this silent condition. The article highlights practical tips and medical advice to prevent complications, aiming to educate and empower individuals to maintain healthy blood pressure levels and improve overall heart health.
Comprehensive Guide to Hypertension: Causes, Types, and Effective Management Techniques
High blood pressure, medically known as hypertension, is a prevalent cardiovascular condition that significantly impacts global health. It is a silent yet dangerous disease that increases the risk of heart attacks, strokes, kidney failure, and even death if left unmanaged. Hypertension occurs when the force of blood against the walls of arteries remains consistently elevated over a prolonged period, exerting undue stress on the vascular system.
Understanding the different classifications and causes of hypertension is crucial for effective prevention and treatment. According to guidelines by prominent health organizations, blood pressure levels are categorized as follows:
Normal Blood Pressure (less than 120/80 mm Hg)
Prehypertension (120-139/80-89 mm Hg)
Hypertension Stage 1 (140-159/90-99 mm Hg)
Hypertension Stage 2 (160 or higher/100 or higher mm Hg)
Hypertensive Crisis (greater than 180/120 mm Hg), which requires immediate medical attention
When blood pressure spikes into hypertensive crisis territory, symptoms such as severe headaches, chest pain, shortness of breath, or visual disturbances may manifest, signaling an urgent need for medical intervention. Hypertension without an identifiable cause, known as primary or essential hypertension, accounts for most cases, whereas secondary hypertension has underlying other health conditions as its root cause.
Understanding Different Types of Hypertension
Primary hypertension typically develops gradually over years and is influenced by genetic, environmental, hormonal, and lifestyle factors. It often results from a combination of factors such as hormonal imbalances, increased blood volume, and arterial stiffness. Lifestyle factors, including chronic stress, physical inactivity, poor diet, and excessive salt intake, further contribute to its development.
Secondary hypertension, on the other hand, arises from specific root causes like kidney disease, hormonal disorders (such as hyperaldosteronism or pheochromocytoma), certain medications, pregnancy-related conditions (such as preeclampsia), and obesity. Recognizing the underlying cause is vital for targeted treatment and management strategies.
Effective Management and Prevention Strategies for Hypertension
While some cases of hypertension require medication, lifestyle modifications play a pivotal role in controlling blood pressure levels and reducing associated risks. Implementing healthy habits can prevent the progression of hypertension and improve overall cardiovascular health.
Limit alcohol consumption: Excessive alcohol intake is a known risk factor for high blood pressure. Men should restrict alcohol consumption to no more than two drinks per day, and women should limit intake to no more than one drink per day. Moderation is key to maintaining optimal blood pressure levels.
Adopt a heart-healthy diet: Emphasize the consumption of fruits, leafy green vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats. Reducing intake of saturated fats, trans fats, processed foods, and sugars benefits vascular health and helps maintain balanced blood pressure levels.
Engage in regular physical activity: Consistent exercise, such as brisk walking, cycling, swimming, or aerobics, for at least 150 minutes per week, can significantly lower blood pressure. Physical activity helps strengthen the heart and improve arterial flexibility.
Maintain a healthy weight: Obesity is closely linked to high blood pressure. Achieving and sustaining a healthy weight through diet and exercise reduces the strain on the heart and arteries.
Reduce sodium intake: The recommended daily sodium intake should not exceed 2,300 milligrams, with further reduction to 1,500 milligrams serving those with hypertension or at risk.
Limit caffeine intake: Excessive caffeine consumption can temporarily increase blood pressure, so moderation is advisable for individuals sensitive to caffeine.
Manage stress effectively: Engaging in stress-relieving activities such as mindfulness, deep-breathing exercises, yoga, or meditation can help lower blood pressure and improve overall health.
Adequate sleep and avoiding tobacco: Quality sleep and smoking cessation are vital components of hypertension management, contributing to better cardiovascular outcomes.
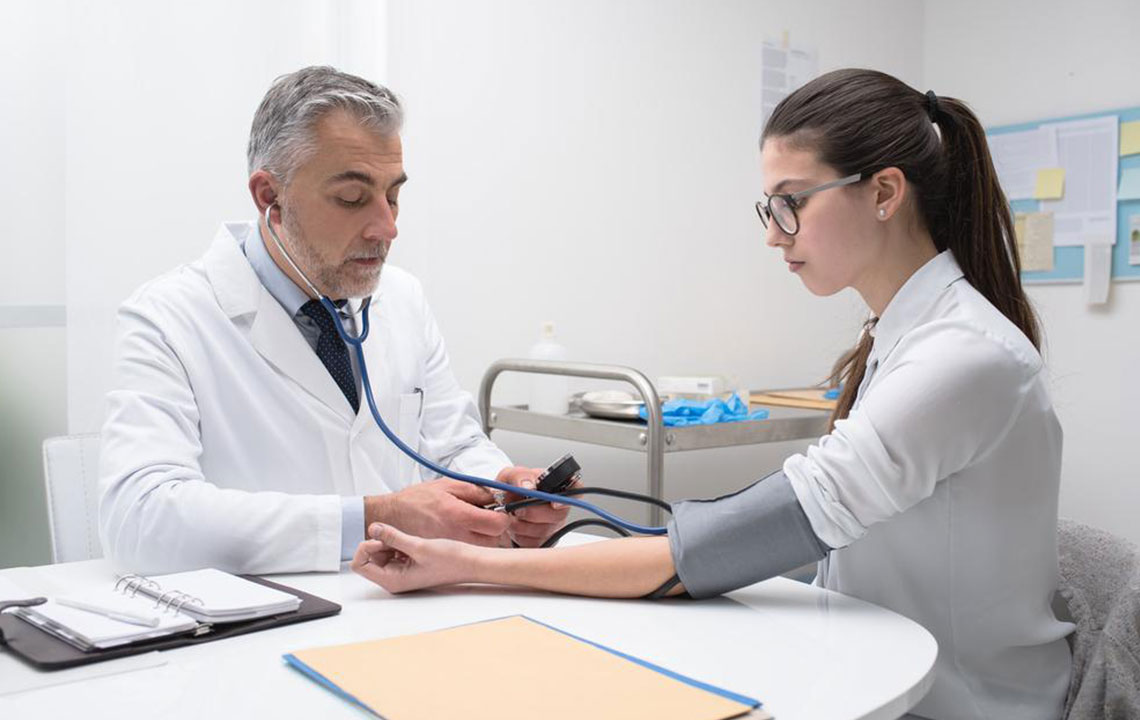
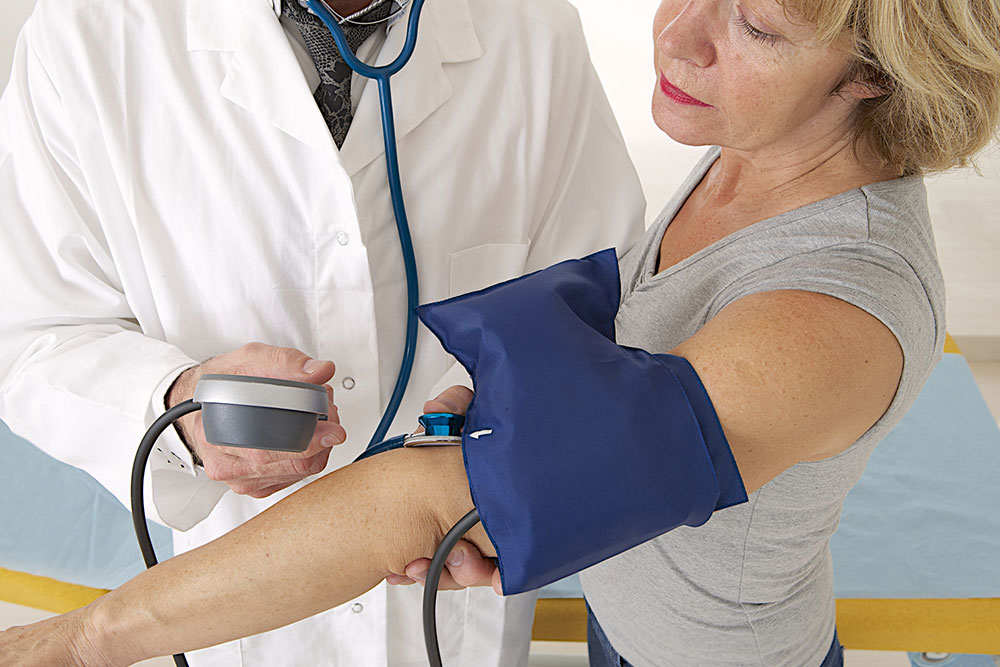
In some cases, lifestyle modifications are insufficient to control hypertension, necessitating antihypertensive medications prescribed by healthcare providers. Regular monitoring of blood pressure, adherence to medication, and routine check-ups are essential to prevent complications.
Early detection and consistent management can significantly reduce the health risks associated with hypertension. By understanding its causes, risk factors, and adopting healthy lifestyle habits, individuals can effectively control their blood pressure and enjoy a healthier life.
In conclusion, hypertension is a manageable condition with proper medical care and lifestyle adjustments. Recognizing the early signs, maintaining a healthy diet, exercising regularly, limiting harmful habits, and monitoring blood pressure are key steps toward prevention and effective control of this silent yet perilous disease.