Comprehensive Guide to Common Joint Disorders: Symptoms, Causes, and Prevention Strategies
This comprehensive article explores common joint disorders, highlighting symptoms, causes, and risk factors. It emphasizes the importance of early detection and preventive strategies such as weight management, injury care, and lifestyle choices to maintain joint health. An in-depth understanding can help individuals reduce their risk of developing conditions like osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis, ensuring better mobility and quality of life as they age.
Comprehensive Guide to Common Joint Disorders: Symptoms, Causes, and Prevention Strategies
Joint disorders are increasingly common health concerns, especially among aging populations, but they can affect people of all ages due to injuries or other medical conditions that impact bones and joints. These disorders encompass a broad spectrum of conditions, with arthritis being the most prevalent, comprising more than 200 different types. The severity and progression of joint problems can significantly influence daily activities, mobility, and overall quality of life. Recognizing the warning signs, understanding the underlying causes, and knowing the risk factors are essential steps toward early diagnosis, effective management, and prevention.
This comprehensive article explores the various symptoms linked to joint disorders, delves into their common causes, and examines the factors that increase susceptibility. With proper awareness and proactive health measures, individuals can better protect their joint health and maintain an active lifestyle well into old age.
Common Symptoms of Joint Disorders
Detecting joint problems early can greatly improve treatment outcomes. Here are some frequent symptoms associated with various joint conditions:
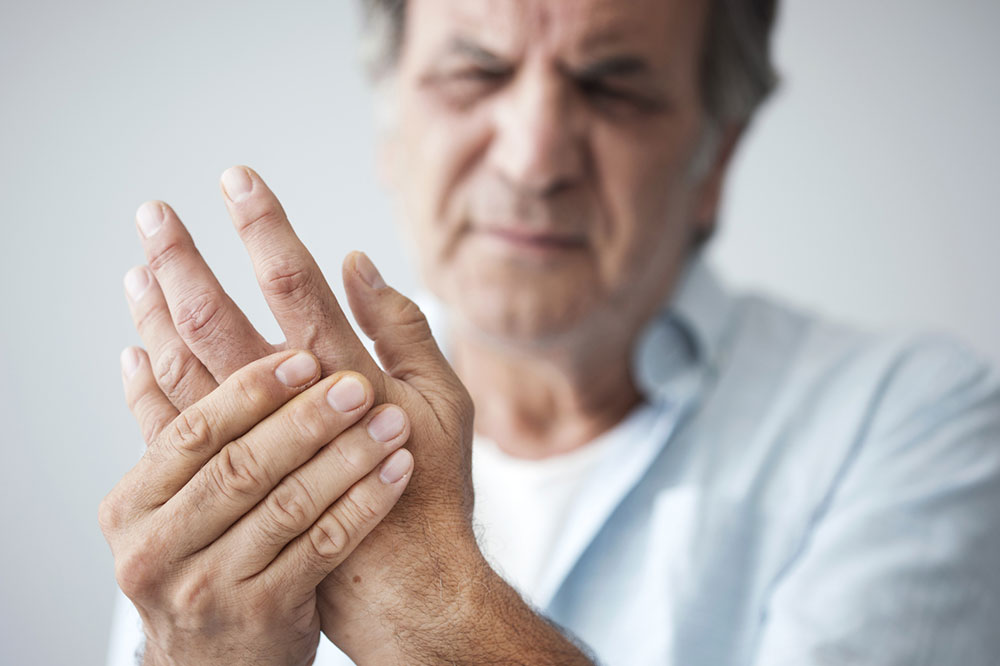
Persistent stiffness in affected joints, often worse after periods of inactivity or in the morning
Weakness or a feeling of instability, making joints feel loose or prone to giving way
Swelling, redness, and warmth around the joint, indicative of inflammation
Difficulty walking or limping due to pain or discomfort
Joints that lock, catch, or click during movement
Cartilage degradation leading to joint discomfort and limited mobility
Popular Joint Conditions and Their Causes
Understanding the specific types of joint disorders helps in identifying the appropriate treatment options. Here are some of the most common joint problems and their primary causes:
Osteoarthritis: Often referred to as "wear-and-tear" arthritis, osteoarthritis involves the gradual breakdown of cartilage—the protective cushioning between bones. As cartilage erodes over time, bones start rubbing against each other, causing pain, stiffness, and reduced mobility. This condition frequently affects weight-bearing joints such as hips, knees, and the lower back, as well as smaller joints like the fingers and wrists.
Rheumatoid Arthritis: An autoimmune disorder where the immune system mistakenly attacks healthy joint tissues, leading to inflammation, swelling, pain, and deformity. Rheumatoid arthritis can also affect other organs, including the eyes, skin, lungs, and blood vessels. It tends to be symmetrical, affecting both sides of the body equally, and can lead to chronic joint damage if untreated.
Gout: Caused by the accumulation of uric acid crystals within joints, gout results in sudden and severe episodes of pain, redness, and swelling. It often affects the big toe but can also involve other joints such as the ankles, knees, wrists, and elbows.
Post-Traumatic Arthritis: This form of arthritis develops following joint injuries or trauma, such as fractures, ligament tears, or dislocations. Damage to cartilage or bone during an injury can predispose joints to early degenerative changes.
The cartilage, which functions as a shock absorber and lubricant, is crucial for smooth joint function. Damage or deterioration here leads to increased friction, pain, and loss of mobility. Inflammatory processes are also at play, especially in autoimmune diseases like rheumatoid arthritis, which can cause permanent joint deformity if not managed effectively.
Several factors contribute to the development of joint issues, including lifestyle and genetic predispositions. Understanding these risk factors can help in adopting preventive measures.
Excess Body Weight: Being overweight puts added stress on weight-bearing joints like the hips, knees, and spine. This mechanical stress accelerates cartilage wear and tear, increasing the likelihood of developing osteoarthritis. Maintaining a healthy weight through balanced diet and regular exercise is vital for joint health.
Previous Joint Injuries: Past injuries, if not properly treated or rehabilitated, can lead to recurrent joint problems or accelerate degenerative changes. Supportive therapies and protective measures are crucial post-injury.
Age: As we age, bones tend to weaken, and the cartilage's resilience decreases, making joints more susceptible to damage and disease. Age-related degeneration necessitates proactive management to preserve mobility.
Genetic Factors and Family History: A family history of joint conditions, especially rheumatoid arthritis or osteoarthritis, suggests a genetic predisposition. Regular check-ups and early interventions can mitigate progression.
By understanding these symptoms, causes, and risk factors, individuals can take proactive steps such as engaging in regular exercise, maintaining an appropriate weight, and seeking early medical consultation if symptoms appear. Prevention and timely management are essential for preserving joint health and avoiding long-term disability.