Comprehensive Guide to Recognizing Head Injury Symptoms in Adults and Children
This comprehensive guide details the vital signs and symptoms of head injuries in both adults and children. It covers mental, behavioral, sensory, and physical indicators that warrant immediate medical attention. Recognizing these signs early can prevent severe complications, brain damage, and save lives. Understanding the nuanced differences between adult and pediatric head trauma is essential for caregivers, teachers, and healthcare providers. Prompt action and thorough evaluation following any head injury are crucial for ensuring proper treatment and recovery. Stay informed, stay alert, and prioritize safety after head trauma.
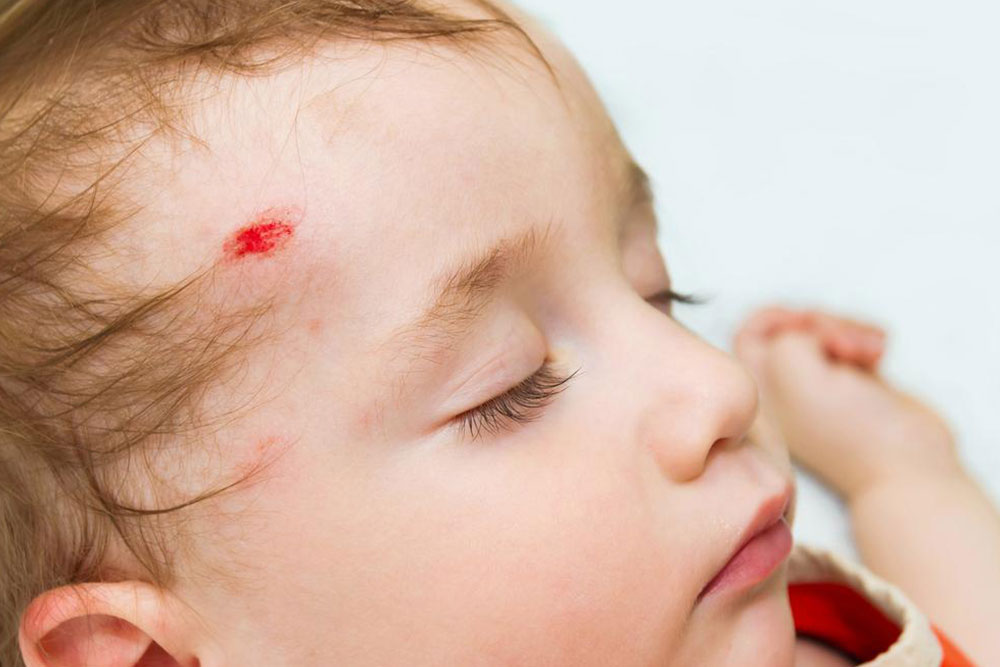
Identifying Signs of Head Trauma in Both Adults and Kids
Head injuries can manifest through a wide spectrum of symptoms that affect both the physical and mental health of individuals. Recognizing these signs promptly is crucial for timely medical intervention, regardless of whether the injury appears mild, moderate, or severe. While some symptoms become evident immediately after trauma, others may surface hours or even days later. Understanding these varied presentations can help caregivers and individuals seek appropriate care swiftly. This comprehensive guide aims to detail the common signs and symptoms associated with head injuries in both adults and children to aid in early detection and treatment.
Mental and Psychological Symptoms
Mental changes often indicate brain involvement. These symptoms include memory issues, such as gaps in recall or forgetfulness, which can be temporary or persistent. Difficulty concentrating or focusing on tasks can also be a red flag, alongside mood disturbances like irritability, depression, or anxiety. Cognitive impairments may present as confusion or disorientation, making it difficult for individuals to recognize their surroundings or remember recent events. Severe cases may develop into agitation, slurred speech, or unconsciousness (coma), emphasizing the importance of monitoring these symptoms carefully. Recognizing psychological changes early can prevent further complications and facilitate prompt medical evaluation.
Behavioral and Emotional Changes
Certain traumatic brain injuries can lead to noticeable behavioral shifts. These may include unexpected crying or laughter without clear reason, increased irritability, aggressive behaviors, or impulsive actions. Repetitive speech, actions, or a lack of restraint in actions are also signals of neurological distress. Such behavioral alterations may be subtle initially but can worsen if not addressed, and they highlight the importance of close observation, especially in children or vulnerable adults who may not easily communicate their symptoms.
Sensory Symptoms
Sensory disturbances are common indicators of head injury. These may involve blurred or double vision, ringing in the ears (tinnitus), or altered taste and smell sensations. Patients might also experience heightened sensitivity to light (photophobia) or sound (hyperacusis), which can significantly affect daily life. Recognizing these symptoms early can lead to prompt evaluation and management, reducing the risk of long-term sensory deficits.
Physical Indicators of Head Injury
Physical signs of head trauma can range from mild to severe. These include persistent headache, seizures, and signs of nerve injury. Bleeding — either external wounds or bleeding inside the skull — is a serious concern. Other physical symptoms include muscle stiffness, bruising or swelling, fractures of the skull, and loss of consciousness. Prompt diagnosis and treatment are vital to prevent complications such as brain damage or death.
Some of the most frequent physical signs that demand immediate medical attention are:
Loss of consciousness or coma
Persistent nausea or vomiting
Drainage of fluids from ears or nose, possibly indicating skull fracture
Numbness or tingling in fingers or toes
Difficulty waking or extreme fatigue
Pupil dilation or unequal pupils (anisocoria)
Disorientation or confusion about surroundings or recent events
Problems with coordination or balance, such as stumbling or falls
Sleep disturbances, including trouble falling asleep or sleeping excessively
Prolonged periods of sleep which may indicate brain injury
Head Injuries in Children: Special Considerations
Children, notably infants and toddlers, are particularly vulnerable to head injuries due to their developing brains and high activity levels. Falls are the leading cause of pediatric head trauma. Immediate assessment after any suspected injury is essential because symptoms can be subtle and easily overlooked. Watch for behavioral changes such as persistent crying, irritability, or a reduction in eating and appetite. Changes in sleep patterns, a decrease in interest in toys, or sudden difficulty paying attention can also be symptoms. If a child's physical condition or behavior changes significantly after a fall or bump, seeking urgent medical evaluation is critical to prevent long-term sequelae.
Being vigilant about recognizing the early signs of head injuries can save lives and prevent permanent damage. If you notice any of these symptoms in yourself or others following trauma, seek emergency medical care immediately. Proper diagnosis, imaging, and treatment are pivotal to ensuring the best possible recovery outcomes. Educating oneself about these symptoms and acting promptly can make a substantial difference in managing head injuries effectively.