Comprehensive Guide to Concussions: Causes, Symptoms, and Prevention Strategies
This comprehensive guide explores the causes, symptoms, and prevention of concussions, emphasizing the importance of early detection and medical care. Concussions can have serious consequences if overlooked, making awareness and proper management crucial for all age groups involved in physical activity or prone to falls. Learn how to recognize signs, seek urgent treatment when needed, and adopt preventative strategies to minimize risks.
Comprehensive Guide to Concussions: Causes, Symptoms, and Prevention Strategies
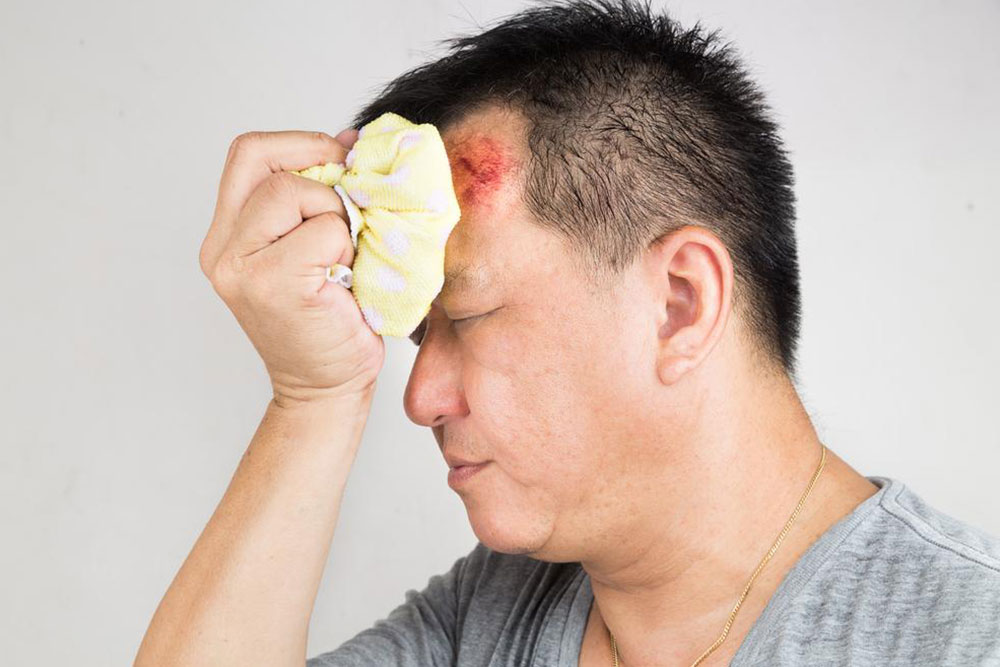
A concussion, medically known as a mild traumatic brain injury, occurs when an external force causes the brain to move rapidly within the skull. This sudden movement can lead to a cascade of chemical reactions, damage to brain cells, and can sometimes cause bleeding within the brain tissue. While often mistaken for minor injuries, concussions can have serious short-term and long-term consequences if not identified and treated promptly.
The human brain is well-protected by cerebrospinal fluid and the skull, acting as a cushion against minor bumps and shocks. Nevertheless, significant impacts from accidents, falls, sports injuries, or other trauma can overrule these protective layers, resulting in a concussion. These injuries are particularly common among athletes, children, and elderly individuals, making awareness crucial for early detection and prevention.
Symptoms of a concussion are diverse and can affect individuals differently. Typical signs include feelings of fatigue, dizziness, nausea, and vomiting, which often appear shortly after injury. Cognitive disturbances such as confusion, difficulty concentrating, and memory issues are also common. Physical symptoms like ringing in the ears, blurred vision, and heightened sensitivity to light and sound are frequently observed. Sleep disturbances, mood swings, and a general lack of interest in usual activities may also be indicative of a concussion. In some cases, individuals experience seizures or loss of consciousness, highlighting the potential severity of these injuries.
It is vital to monitor the progression of symptoms carefully. Mild concussions often resolve within days to weeks with appropriate rest and care. However, severe cases require immediate medical attention, especially if symptoms worsen or if the individual loses consciousness. Repeated concussions or untreated injuries can lead to long-term cognitive deficits, chronic headaches, or even brain damage, emphasizing the importance of prompt diagnosis and management.
Medical professionals utilize various methods for diagnosing concussions, including neurological examinations, cognitive assessments, and imaging tests like CT scans or MRIs when necessary. Treatment typically involves physical and cognitive rest, pain management, and gradual return to normal activities under medical supervision. Preventative measures such as wearing protective gear during sports and ensuring safe environments at home and work are essential for reducing the risk of concussions.