Comprehensive Strategies to Relieve Hip Bursitis Pain Naturally and Effectively
This comprehensive guide explores effective strategies for managing and alleviating hip bursitis pain through natural methods, targeted exercises, medical treatments, and preventive tips. By understanding the causes and utilizing a combination of lifestyle changes and medical interventions, individuals can effectively reduce inflammation, relieve discomfort, and prevent recurrence of this common hip condition. The article emphasizes the importance of early diagnosis and consistent care for optimal recovery and long-term hip health.
Comprehensive Strategies to Relieve Hip Bursitis Pain Naturally and Effectively
Hip bursitis is a common condition characterized by inflammation of the bursae—small, fluid-filled sacs that cushion the bones, tendons, and muscles around your hip joint. This inflammation can cause significant discomfort, pain, and stiffness, especially during physical activities such as walking, running, or even simple movements like bending or climbing stairs. Recognizing the underlying causes and understanding the precise location of the affected bursae are crucial steps to managing and alleviating this condition effectively. In this detailed guide, we explore the causes, symptoms, and comprehensive treatment options for hip bursitis, emphasizing natural remedies, physical therapy, and medical interventions tailored to promote recovery and prevent recurrence. Whether you're experiencing mild discomfort or persistent pain, this article provides valuable insights into effective strategies for managing hip bursitis and restoring mobility.
Hip bursitis involves inflammation of one or more bursae located around the hip joint, which act as cushioning sacs reducing friction between moving tissues. Understanding the specific location of inflamed bursae aids in targeted treatment. The four main bursae in the hip include the trochanteric bursa, gluteus medius bursa, iliopsoas bursa, and ischial bursa. Each is situated near different tendons and muscles, playing unique roles in hip movement and stability. Accurate identification of the affected bursa is essential for effective management.
Effective management of hip bursitis involves a combination of lifestyle adjustments, physical therapy, pharmacological treatments, and, in severe cases, surgical intervention. The goal is to reduce inflammation, relieve pain, strengthen hip muscles, and restore normal activity levels while preventing future episodes. Here, we delve into the most effective methods for achieving these goals, emphasizing natural and conservative approaches first, and outlining when medical procedures may be necessary.
Understanding the Causes and Symptoms of Hip Bursitis
Before exploring treatment options, it’s important to understand what causes hip bursitis and how to identify its symptoms. Common causes include repetitive movements that strain the hip, prolonged pressure on the hip area, injury or trauma, poor posture, and ergonomic issues. Additionally, underlying conditions such as arthritis or infections can contribute to bursitis. Symptoms typically include sharp or aching pain on the outer part of the hip, tenderness over the affected bursa, swelling, stiffness, and increased discomfort during activity or when lying on the affected side. Recognizing these signs early allows for prompt intervention and more effective treatment.
Natural and Lifestyle-Oriented Approaches to Managing Hip Bursitis
Many individuals find relief through natural methods that focus on reducing inflammation, alleviating pain, and improving joint function. These approaches can often be combined with medical treatments to enhance recovery outcomes. Key strategies include:
Rest and Activity Modification: Limiting activities that exacerbate pain, avoiding prolonged pressure or repetitive motions, and incorporating periods of rest help reduce inflammation.
Ice Therapy: Applying ice packs to the affected area for 15-20 minutes several times a day can significantly decrease swelling and discomfort.
Anti-inflammatory Diet: Consuming foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids, antioxidants, and anti-inflammatory compounds such as turmeric and berries supports joint health and reduces inflammation.
Proper Footwear and Posture: Wearing supportive shoes and maintaining good posture prevent undue stress on the hips and surrounding tissues.
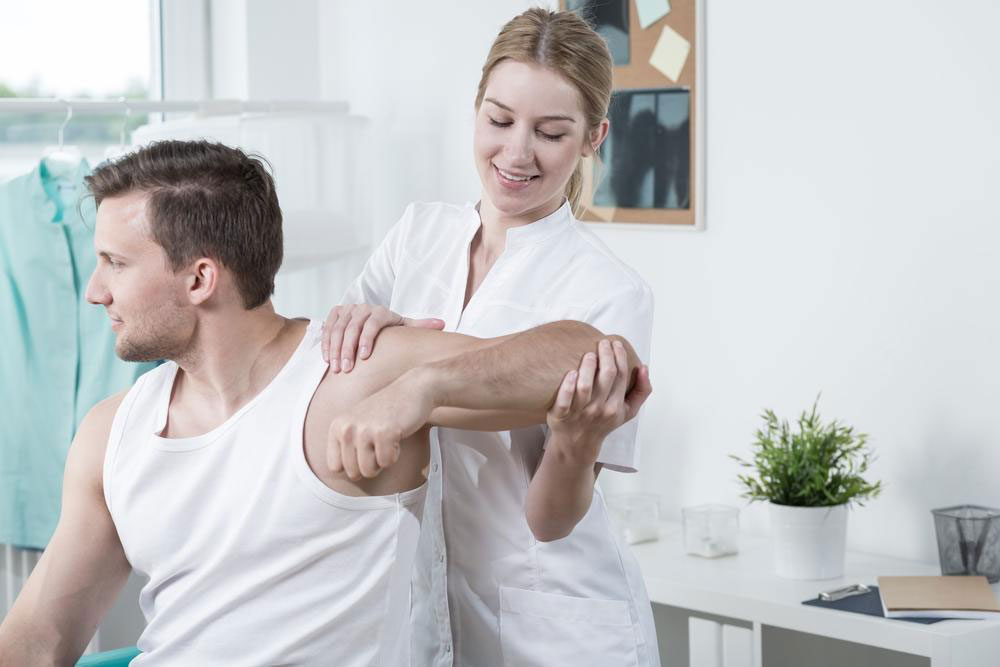
Targeted Exercises and Physical Therapy for Hip Bursitis
Physical therapy plays a pivotal role in the recovery process, especially exercises that strengthen the hip muscles, improve flexibility, and stabilize the joint. These exercises, when performed consistently and correctly, help reduce strain on inflamed bursae and prevent future episodes. Here are some of the most recommended physical therapy techniques:
Strengthening Exercises: Focused on building muscles around the hip, such as the gluteus medius, gluteus maximus, and quadriceps, these exercises help in providing better support to the hip joint. Examples include clamshells, bridges, and resistance band exercises.
Stretching Routines: Gentle stretching of hip flexors, hamstrings, and iliotibial band can relieve tightness and improve joint mobility.
Lateral Leg Raises: Targeting the hip abductors, these raise the leg laterally to strengthen the muscles supporting side-to-side movement.
Leg Circles and Mobility Exercises: Small circular motions and joint mobility drills enhance flexibility and help maintain a healthy range of motion in the hip joint.
Performing these exercises regularly—aiming for five sets of 15-20 repetitions—can accelerate recovery, strengthen supporting muscles, and reduce recurrence risk.
Medical Treatments for Persistent or Severe Hip Bursitis
In cases where conservative measures fail to alleviate symptoms, or the pain is severe and persistent, medical interventions may be necessary. These options include:
NSAIDs and Pain Relievers: Over-the-counter non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) like ibuprofen can reduce inflammation and ease pain.
Steroid Injections: Corticosteroid injections directly into the affected bursa can provide rapid and significant relief from inflammation and discomfort.
Physical Therapy and Rehabilitation: Customized therapy plans can improve joint function and reduce pain more effectively.
Surgical Intervention: In rare, severe cases where bursitis is unresponsive to other treatments, surgical removal of the inflamed bursa (bursectomy) may be performed to relieve symptoms and restore mobility.
Always consult with an orthopedic specialist to determine the most appropriate treatment approach for your specific condition, especially if pain persists or worsens over time.
Prevention Tips to Avoid Future Hip Bursitis Episodes
Prevention is key to managing hip bursitis effectively. Incorporating simple lifestyle habits can drastically reduce the risk of recurrence. Some preventive strategies include:
Regular Exercise: Engaging in low-impact activities like swimming or cycling can strengthen hip muscles without putting excessive strain on bursae.
Maintaining a Healthy Weight: Reducing excess weight decreases pressure on the hips, alleviating stress on the bursae.
Proper Technique: Using correct form during sports and physical activities minimizes strain on the hips.
Good Posture and Ergonomics: Maintaining proper posture during daily activities prevents abnormal stress on the hips and pelvis.
Stretching and Warm-up: Always warm up and stretch before engaging in vigorous activities to prepare the muscles and protect the joints.
Implementing these habits can help keep your hips healthy, reduce the chances of inflammation, and maintain a high quality of life.
In conclusion, managing hip bursitis requires a holistic approach that combines natural remedies, physical therapy, medical interventions, and lifestyle modifications. Early diagnosis and consistent effort in rehabilitation can significantly improve outcomes, reduce pain, and restore functional mobility. If you experience persistent hip pain, consult a healthcare professional promptly to develop a personalized treatment plan tailored to your needs.