Comprehensive Guide to Kidney Stone Removal and Prevention
This comprehensive guide offers effective strategies for kidney stone elimination, including natural remedies, treatment options, and preventive measures. It details how kidney stones form, symptoms to watch for, and when to seek medical care, aiming to help patients manage and prevent this painful condition more effectively.
Comprehensive Guide to Kidney Stone Removal and Prevention
Effective strategies for eliminating kidney stones
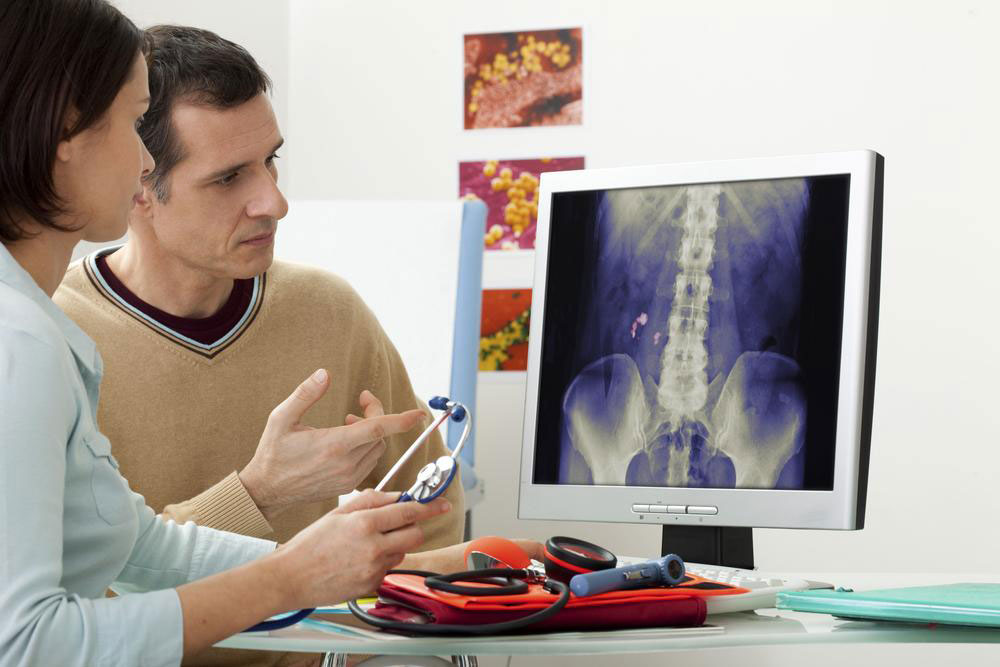
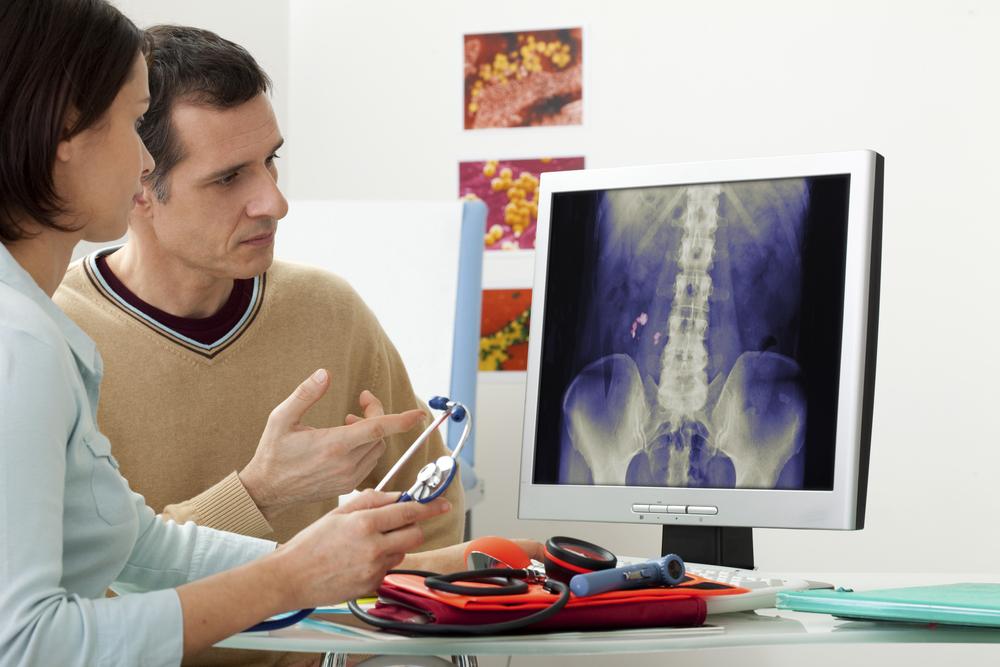
Kidney stones are hard deposits made of minerals and salts that develop within the kidneys. They can vary in size from tiny grains to larger masses, and their formation is influenced by various factors including diet, hydration levels, and genetic predispositions. When the stones are small, they often pass through the urinary system naturally, causing little to no discomfort. However, larger stones can lead to severe pain, urinary obstruction, infection, and other complications. Understanding the mechanisms of stone development and exploring various treatment options are essential to managing this condition successfully. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the causes of kidney stones, symptoms, treatment options, preventive measures, and natural remedies to help you maintain urinary tract health.
Kidney stones are formed when minerals such as calcium, oxalate, uric acid, and phosphate crystallize in the kidneys. These mineral deposits develop under conditions like dehydration, which reduces urine volume and increases mineral concentration. When urine is concentrated, salts and minerals tend to accumulate, leading to stone formation. Although stones originate in the kidneys, they can travel through the urinary tract and block urine flow at any point, resulting in pain and other symptoms. Proper understanding of their formation, early detection, and appropriate treatment are essential for effective management.
How to treat small kidney stones?
Small kidney stones, typically less than 5mm in diameter, often pass through the urinary tract without the need for invasive interventions. Here are some widely recommended approaches:
Hydration – Drinking 2 to 3 liters of water daily helps dilute urine and facilitates stone passage.
Pain management – Over-the-counter analgesics such as acetaminophen or ibuprofen can help control pain associated with stone movement.
Medical therapies – Doctors may prescribe medications like alpha-blockers (e.g., tamsulosin) to relax the muscles in the ureter, easing the passage of stones.
Recognizing the symptoms of kidney stones
Common signs indicating the presence of stones include:
Persistent and severe pain in the back, side, groin, or lower abdomen
Frequent urination with a burning sensation
Cloudy, dark, or foul-smelling urine
Blood in urine (hematuria)
Nausea and vomiting
Natural home remedies for promoting stone passage
Several natural remedies can support the movement of kidney stones and promote overall kidney health, including:
Consuming ample water to stay well-hydrated
Drinking lemon juice, which contains citrate to prevent stone formation
Horsetail extract, known for its diuretic properties
Kidney bean broth, traditionally used to support kidney function
Juices from celery, basil, wheatgrass, and pomegranate
Dandelion root, which promotes urine flow
Apple cider vinegar, believed to dissolve stones
Hydration remains the cornerstone of natural treatment, often supplemented with these remedies to facilitate the natural passage of stones.
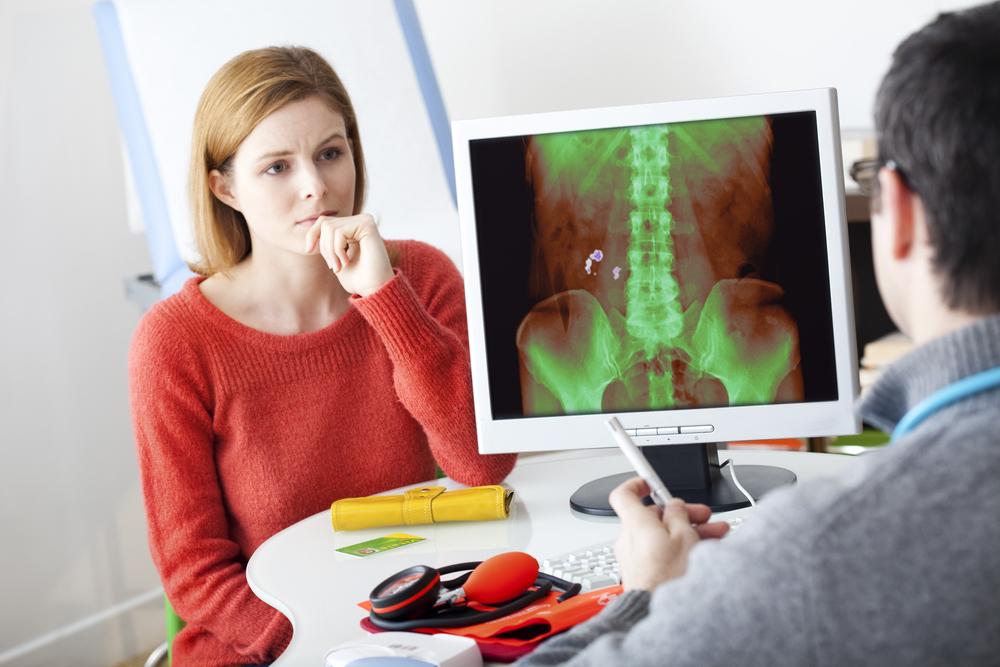
When should you seek medical attention?
If a kidney stone persists for more than six weeks, or if symptoms worsen—including increased pain, fever, chills, nausea, or blood in urine—it is imperative to consult a healthcare provider promptly. Medical professionals will assess the size, location, and severity of the stone using imaging techniques and recommend appropriate treatments. These may include medications, minimally invasive procedures such as extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy (ESWL), ureteroscopy, or, in some cases, surgical intervention to remove larger or stubborn stones.