Comprehensive Guide to Managing and Relieving Symptoms of Enlarged Prostate
This detailed guide offers men comprehensive strategies to manage and alleviate symptoms of enlarged prostate (BPH). It covers natural remedies, lifestyle adjustments, and medical treatments, emphasizing early detection and personalized care. Learn about herbal options, dietary changes, minimally invasive procedures, and surgical options to improve urinary health and quality of life effectively.

Comprehensive Strategies for Managing and Relieving Symptoms of Enlarged Prostate
Enlargement of the prostate gland, medically termed benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), is a common health concern among aging men. One of the earliest signs of this condition is an increased need to urinate during the night, known as nocturia. While initially a mild disturbance, this symptom tends to progress over time, significantly interfering with daily routines and sleep patterns. The condition results from age-related changes, involving the abnormal growth of prostate cells, which can obstruct the flow of urine through the urethra. If left untreated, BPH can cause discomfort, persistent urinary issues, and potentially lead to more serious health complications.
In this extensive guide, we explore the key symptoms associated with an enlarged prostate, effective home remedies, lifestyle modifications, medical treatments, and advanced procedures designed to alleviate symptoms and enhance quality of life for affected individuals. Understanding these strategies can empower men to take proactive steps toward healthier urinary function and overall well-being.
Understanding Enlarged Prostate and Its Causes
The prostate is a small, walnut-shaped gland located below the bladder in men. Its primary role is to produce seminal fluid, which nourishes and transports sperm. With age, hormonal changes—particularly the decline in testosterone and the relative increase in dihydrotestosterone—trigger an increase in prostate cell growth. This benign process leads to enlargement, typically affecting men over the age of 50. By the age of 60, nearly 50% of men show clinical signs of BPH, and this prevalence increases as men age further.
The reason for this unwanted growth involves complex hormonal and cellular mechanisms. The overgrowth of prostate tissue exerts pressure on the urethra, narrowing the passageway and causing urinary obstruction. This impairs normal urine flow and leads to a spectrum of bothersome symptoms. Although BPH is benign, its impact on quality of life can be significant if untreated.
Recognizing the Symptoms of Enlarged Prostate
Those suffering from an enlarged prostate typically experience a range of urinary symptoms, which vary in severity. Key signs include a persistent feeling of bladder fullness or pressure, slow or weak urine flow, and an increased frequency of urination, especially during the night—a condition known as nocturia. Men may also have difficulty initiating urination, experience interrupted streams, or notice dribbling after voiding. These symptoms collectively affect daily routines, sleep quality, and overall comfort.
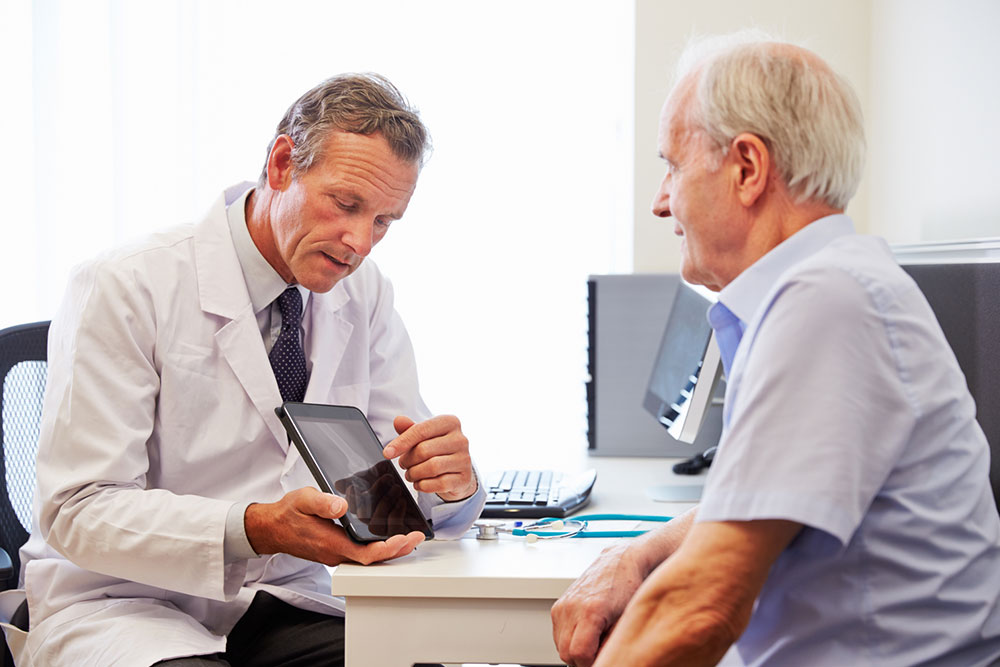
If the condition progresses untreated, it can lead to serious complications. These may include urinary tract infections due to incomplete bladder emptying, hematuria (blood in urine), formation of bladder stones, and even potential kidney damage. Recognizing these symptoms early is crucial for timely intervention and management. In complex cases, associated conditions like prostate inflammation or even prostate cancer need to be ruled out by medical professionals.
Natural and Lifestyle Remedies for BPH Relief
While medical treatments are effective, many men seek natural remedies and lifestyle modifications to manage mild to moderate symptoms. Several herbal and dietary supplements have shown promise in alleviating the discomfort caused by an enlarged prostate.
Saw Palmetto: Extracted from the berries of the Serenoa repens plant, saw palmetto is one of the most popular herbal remedies. It has been used for centuries in traditional medicine to support urinary health by reducing prostate inflammation and inhibiting the conversion of testosterone to dihydrotestosterone (DHT), a hormone linked to prostate growth.
Beta-Sitosterol: This plant-derived compound, found in foods like nuts, seeds, and vegetable oils, helps improve urinary flow and decrease residual urine volume. Clinical studies have demonstrated its effectiveness in reducing symptoms associated with BPH.
Pygeum Africanum: Derived from the bark of the African plum tree, Pygeum has anti-inflammatory properties that can reduce urinary symptoms, including nocturia and difficulty urinating.
Herbal Extracts and Pollen: Ryegrass pollen extract, obtained from Timothy grass and other cereal pollens, has been shown to improve nighttime urination and overall urinary symptoms. It is often used as a complementary therapy alongside other treatments.
In addition to supplements, simple lifestyle changes can support prostate health:
Maintaining a healthy weight through diet and exercise
Reducing alcohol and caffeine intake, which can irritate the bladder
Avoiding fluids before bedtime to reduce nocturia
Engaging in regular physical activity to improve overall circulation
Medical and Surgical Treatments for Enlarged Prostate
For moderate to severe cases or when natural remedies do not provide sufficient relief, various medical therapies are available. These treatments aim to shrink the prostate, relax the bladder neck muscles, or relieve urinary obstruction.
Medications: Prescription drugs like Alpha Blockers (e.g., tamsulosin, alfuzosin) work by relaxing the smooth muscles in the prostate and bladder neck, making urination easier. 5 Alpha-Reductase Inhibitors (e.g., finasteride, dutasteride) decrease prostate size over time by blocking hormonal pathways involved in prostate growth. These medications often improve symptoms gradually and may be combined for enhanced effect.
Minimally Invasive Procedures: Techniques such as Transurethral Microwave Therapy (TUMT) use microwave energy to destroy excess prostate tissue, reducing obstruction without the need for surgery. Other options include Transurethral Needle Ablation (TUNA) and Laser therapies, which precisely target problematic tissue.
Surgical Interventions: When conservative treatments fail, procedures like Transurethral Resection of the Prostate (TURP) or prostectomy are considered. These surgeries involve removing or vaporizing enlarged tissue to restore normal urine flow. While effective, they carry risks such as bleeding, infection, or retrograde ejaculation, and are typically reserved for extreme cases.
Choosing the appropriate treatment depends on individual health status, prostate size, symptom severity, and patient preferences. Consulting a urologist is essential to determine the best course of action.
In conclusion, managing an enlarged prostate involves a comprehensive approach that includes awareness of symptoms, lifestyle modifications, natural remedies, and medical interventions. Early detection and tailored treatment plans can significantly improve quality of life and prevent complications from progressing.