Comprehensive Guide to Managing and Treating Asthma Effectively
This comprehensive guide explores effective strategies for managing and treating asthma. It emphasizes personalized treatment plans, medication use, trigger avoidance, lifestyle modifications, and the importance of working with healthcare providers. Proper management can significantly reduce symptoms, improve lung function, and enhance quality of life for asthma patients. Learn how to proactively control your condition, respond to emergencies, and participate actively in your health journey to lead a healthier life.

Comprehensive Strategies for Asthma Management and Treatment
Asthma is a prevalent chronic respiratory disease characterized by airway inflammation and hyperreactivity, affecting millions worldwide. While there is currently no definitive cure for asthma, proper management through a combination of medication, lifestyle adjustments, and proactive monitoring can significantly improve quality of life for individuals living with this condition. Proper education about asthma, understanding triggers, and adherence to personalized treatment plans are critical components in controlling symptoms and preventing severe attacks. This comprehensive guide aims to provide detailed insights into effective asthma management strategies, treatment options, lifestyle modifications, and the importance of working closely with healthcare professionals to maintain optimal lung health.
Many patients experience a reduction in symptom severity or complete remission as they age, highlighting the importance of early and continuous management. Recognizing the benefits of effective control can motivate patients to stay committed to their treatment regimens and lifestyle changes, ultimately leading to improved daily functioning and overall well-being.
Effective asthma management offers numerous benefits:
Significantly reduces the frequency and severity of symptoms such as shortness of breath, chest tightness, coughing, and wheezing.
Decreases dependency on quick-relief inhalers, thereby minimizing potential side effects and overuse risks.
Helps maintain stable lung function, reducing the likelihood of exacerbations and hospital visits.
Facilitates restful sleep by preventing nighttime symptoms, which in turn improves daytime functioning.
Enables individuals to participate fully in daily activities, including work, sports, and social engagements.
Prepares individuals to respond swiftly and appropriately to emergency asthma attacks, reducing the risk of serious complications.
Achieving effective asthma control involves active collaboration with healthcare providers. It’s essential to follow prescribed medication routines precisely, understand your condition thoroughly, and implement lifestyle changes tailored to your specific triggers. Through consistent management strategies, individuals can enjoy improved health outcomes and a better quality of life.
Active Participation in Asthma Management
Engagement in your own care is vital. Here are some practical tips for effective management:
Gain a comprehensive understanding of your asthma condition—including symptom patterns, common triggers, and warning signs of worsening symptoms.
Work closely with your healthcare team to create or refine a personalized asthma action plan, ensuring it is regularly reviewed and updated.
Learn to identify your specific triggers, such as allergens (pollen, pet dander), environmental pollutants, smoke, cold air, and respiratory infections, and take steps to avoid them whenever possible.
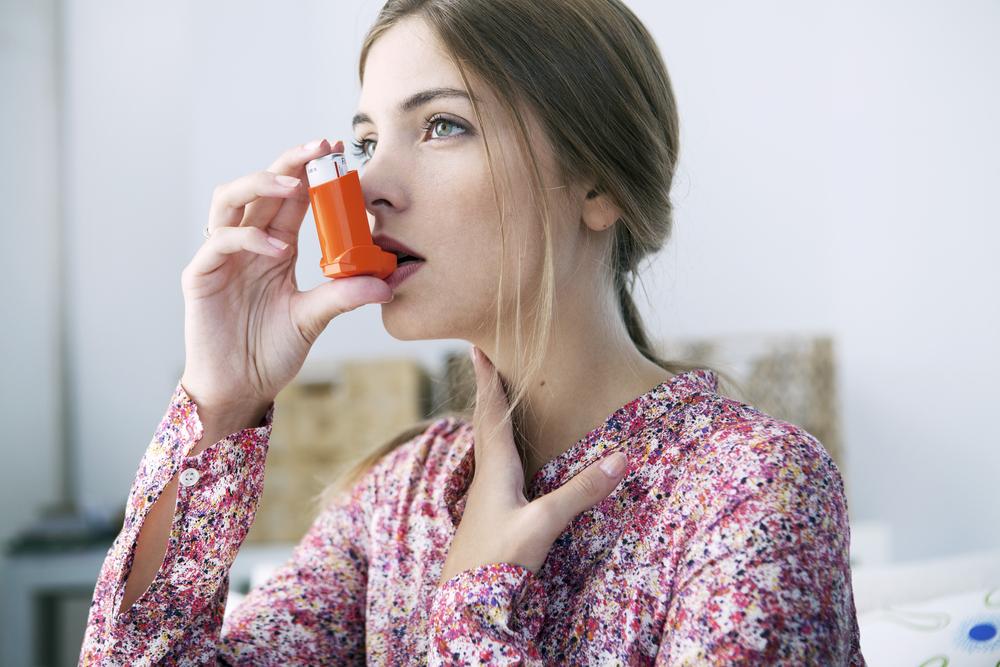
Maintain a medication routine, ensuring proper use of inhalers and other prescribed treatments, and understand the differences between controller and rescue medications.
Stay physically active within your capabilities. Regular exercise boosts overall health, lung capacity, and can prevent comorbidities. For some, medications can support safe activity participation during exercise.
Implement and adhere to a written asthma action plan that details medication use, trigger management, monitoring techniques, and emergency procedures.
Keep an updated record of symptom patterns and medication effectiveness to facilitate discussions with your healthcare provider.
Primary Treatment Options for Asthma
Rescue or Quick-Relief Medications: These are fast-acting inhalers such as short-acting beta-agonists, used during an acute attack to quickly relieve symptoms.
Long-Term Control Medications: Maintained daily to reduce airway inflammation and prevent attacks. Common categories include inhaled corticosteroids, leukotriene modifiers, long-acting beta-agonists (LABAs), and combination inhalers.
The goal of long-term control medications is to minimize airway inflammation, decrease symptom frequency, and improve lung function. Rescue medications provide immediate relief during sudden episodes but should not be relied upon for daily management.
Asthma severity and response to treatment vary greatly among individuals, influenced by environmental factors, physical activity, and exposure to triggers. Therefore, personalized treatment plans are essential. Healthcare providers may adjust medication dosage based on ongoing monitoring and symptom control.
Special populations such as children, pregnant women, athletes, seniors, and patients with comorbid conditions require tailored approaches to optimize safety and efficacy. Identifying and avoiding triggers like pollen, pet fur, pollutants, and tobacco smoke remains crucial. When avoidance isn’t sufficient, allergy immunotherapy (allergy shots) might be recommended. Additionally, managing related conditions like sinus infections, gastroesophageal reflux, or psychological stress can improve overall asthma control. Regular check-ups are necessary to assess treatment effectiveness and make adjustments as needed.
In conclusion, managing asthma is a dynamic process that necessitates education, proactive lifestyle choices, and active engagement with healthcare professionals. By implementing personalized strategies, adhering to medication plans, and avoiding known triggers, individuals can lead active, healthy lives despite their diagnosis.