Complete Guide to Bone Density Testing: Ensuring Bone Health and Preventing Osteoporosis
Learn about the importance of bone density testing, how it’s performed, and steps to maintain strong bones. This comprehensive guide helps high-risk individuals understand how early detection can prevent osteoporosis and fractures, promoting better bone health through lifestyle choices and medical assessments.

Understanding Bone Density Assessments: A Crucial Step Towards Bone Wellness
Introduction to Bone Density Testing
Bone health is a vital aspect of overall well-being, especially as we age. Bone density testing is an essential diagnostic tool that helps healthcare professionals assess the strength and density of bones, enabling early detection and management of conditions like osteoporosis. This comprehensive guide explores the importance, procedures, and preventive measures related to bone density assessments. By understanding how these tests work and who should consider undergoing them, individuals can proactively maintain their skeletal health and reduce the risk of fractures.
What Is Bone Density Testing?
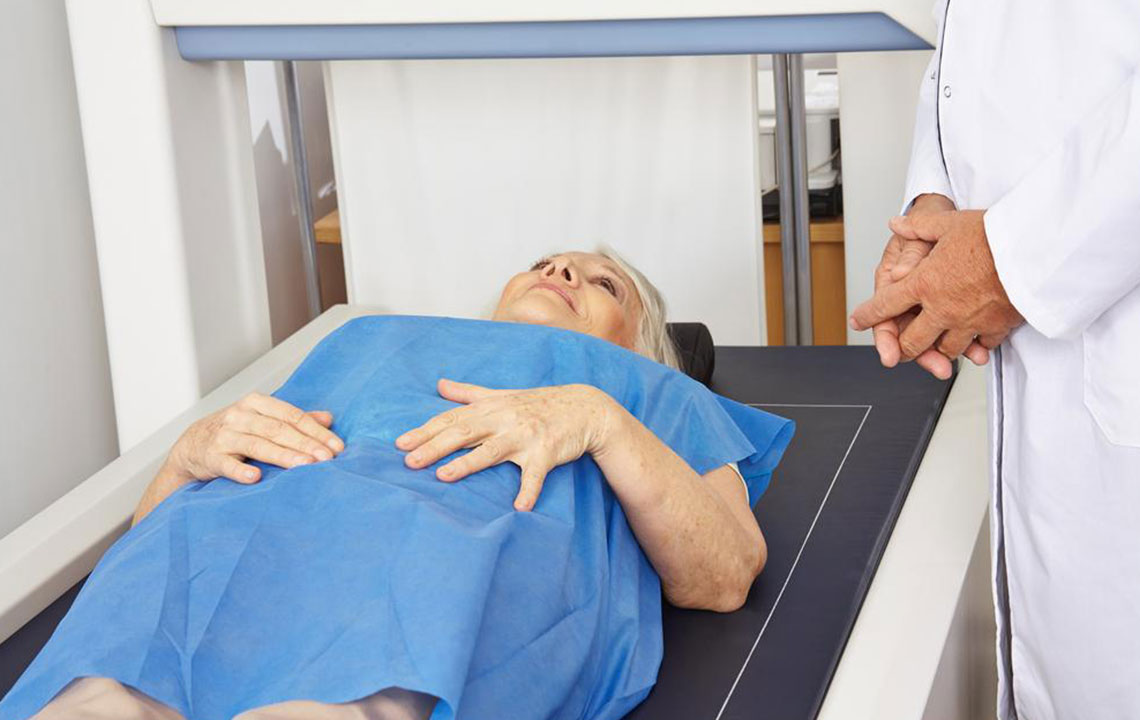
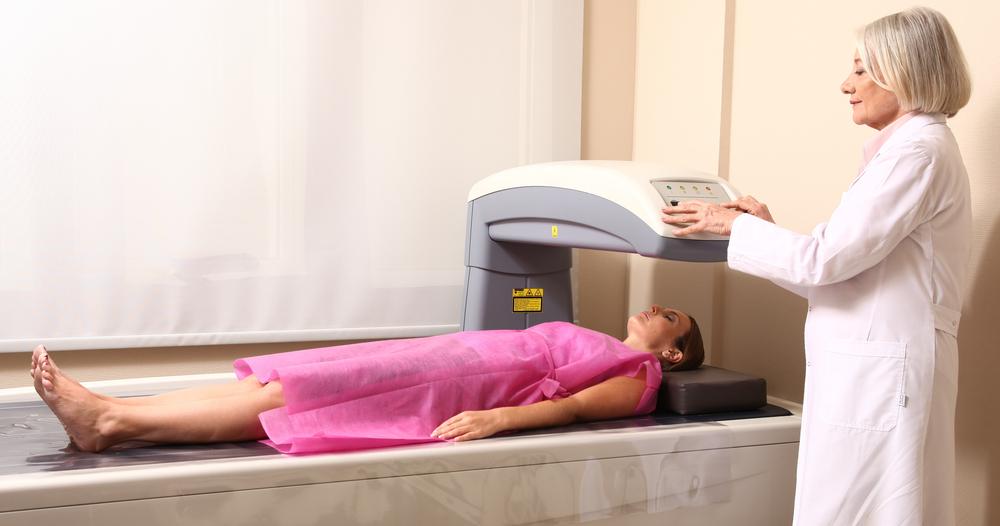
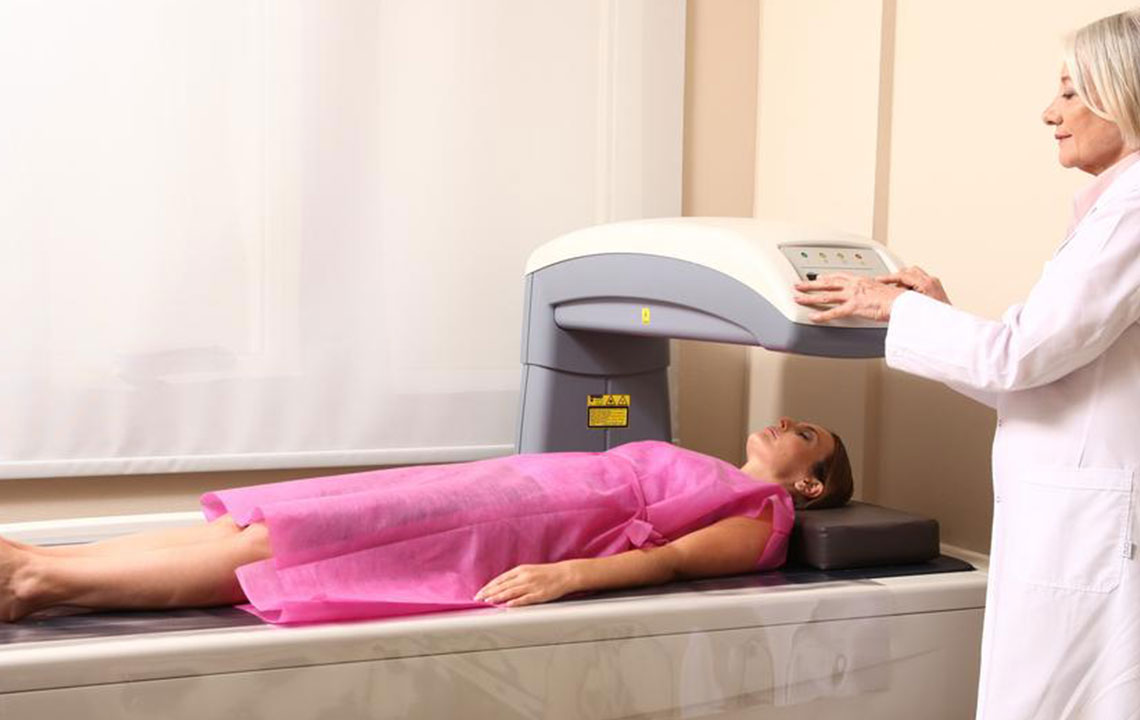
Bone density testing, often referred to as a bone mineral density (BMD) scan, is a non-invasive procedure designed to measure the mineral content in bones. The most commonly used method is Dual-Energy X-ray Absorptiometry (DEXA or DXA), which involves low-dose X-ray technology to accurately assess calcium and other mineral levels in critical areas such as the hips, spine, and forearms. These regions are chosen because they are most susceptible to fractures caused by weakened bones.
The primary purpose of this test is to determine the density and quality of bones, which directly correlates to their strength. It provides valuable insights into whether a person is at risk of developing osteoporosis or other bone-related conditions, allowing for early interventions to prevent fractures and associated complications.
The Significance of Bone Density Testing in Healthcare
Bone density testing plays a crucial role in preventive healthcare, especially for populations at higher risk of bone loss. It aids in identifying individuals who might otherwise remain asymptomatic until a fracture occurs, facilitating early intervention through lifestyle modifications, medications, or other treatments.
Why Is Bone Density Testing Important?
Regular bone density assessments are recommended for various reasons, including:
Monitoring bone strength and preventing fractures through early detection.
Assessing an individual’s risk of osteoporosis and related fractures.
Tracking the effectiveness of osteoporosis treatments over time.
Guiding clinical decisions regarding preventive and therapeutic strategies.
Who Should Consider Getting a Bone Density Test?
People experiencing unexplained height loss, which may indicate spinal fractures due to osteoporosis.
Individuals who fracture with minimal trauma, such as during everyday activities like coughing or bending.
Patients on long-term medications known to affect bone health, such as corticosteroids.
Individuals who have undergone organ or bone marrow transplants, as these procedures can increase osteoporosis risk.
Persons with hormonal imbalances or sudden drops in estrogen or testosterone levels.
Differences Between Bone Density Test and Bone Scan
A bone scan uses nuclear imaging techniques to detect specific issues like tumors, infections, or fractures.
This method involves injecting a radioactive tracer into the bloodstream for detailed imaging.
Bone scans can identify conditions such as fractures, arthritis, or bone tumors.
In contrast, bone density testing measures mineral content to evaluate bone strength and fracture risk without radiation-based tissue imaging.
Who Should Consider Bone Density Screening?
Individuals aged 50 to 69 with risk factors such as low body weight, smoking, alcohol consumption, previous fractures, or use of corticosteroids should consider screening. Early detection in these groups can significantly reduce the risk of serious fractures and improve quality of life.
Potential Risks and Limitations of Bone Density Testing
Although radiation exposure from the test is minimal, cumulative effects should be considered.
Cost can be a concern, especially if multiple tests are required, and insurance coverage varies.
While the results provide insights into bone health, they do not identify the underlying causes of low bone density—further tests may be necessary.
Preparing for Your Bone Density Test
The procedure is straightforward, painless, and typically completed within 10-30 minutes.
No special fasting or preparation is generally required, but it’s advisable to inform your healthcare provider about any health issues or recent imaging procedures.
Wear comfortable clothing and avoid metallic objects around the scanning area.
How to Maintain Healthy Bones
Engage in weight-bearing exercises such as walking, jogging, or resistance training daily to strengthen bones.
Consume a diet rich in calcium sources like dairy products, leafy greens, and fortified foods.
Ensure adequate vitamin D intake through sunlight exposure and dietary supplements if necessary.
Avoid habits detrimental to bone health, including smoking and excessive alcohol consumption.
Consult healthcare providers before starting any medications or supplements that could impact bone density.
In conclusion, if you fall into a high-risk category or notice symptoms like height reduction or frequent fractures, scheduling a bone density test becomes an essential step in safeguarding your skeletal health. Early diagnosis and proactive management can prevent severe complications, ensuring a healthier, more active life.