Comprehensive Guide to Bone Density Testing: Key Insights and Procedures
This comprehensive guide explores the importance, procedures, and benefits of bone density testing. It emphasizes early detection of osteoporosis, risk factors, different testing devices, and how this vital diagnostic tool can prevent fractures. Suitable for at-risk groups, the article highlights the significance of regular screening in maintaining bone health and ensuring prompt treatment to enhance quality of life.
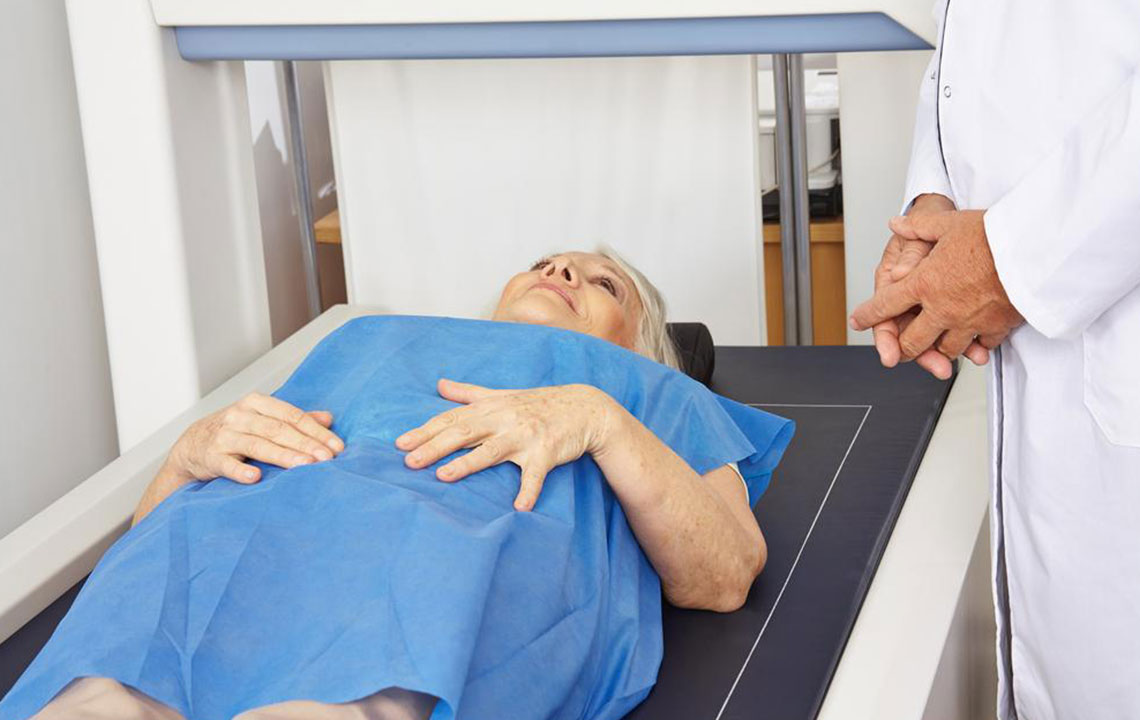
Introduction to Bone Mineral Density Evaluation
Bone density testing is an essential diagnostic tool used to evaluate bone strength and detect osteoporosis early. Osteoporosis is a condition characterized by decreased bone mass and deterioration of bone tissue, leading to fragile bones that are prone to fractures. Traditionally, osteoporosis was diagnosed only after a fracture occurred, often resulting in severe consequences and limited treatment options. Modern medical advancements now allow for precise measurement of bone mineral content, enabling proactive diagnosis and management.
This comprehensive assessment uses specialized imaging techniques, primarily X-ray based, to analyze the mineral density in bones. The most commonly examined sites are the hip, spine, and forearm due to their susceptibility to fractures linked with osteoporosis. Early detection through bone density testing helps healthcare providers implement effective interventions to prevent fractures and related complications. It also plays a crucial role in monitoring the effectiveness of ongoing treatments for osteoporosis, ensuring that patients maintain or improve their bone health over time.
The importance of bone density testing cannot be overstated, especially for individuals at increased risk of osteoporosis. This includes postmenopausal women, older adults, and those with lifestyle factors or medical conditions that compromise bone health. The test provides valuable insights into the current state of skeletal strength and helps doctors formulate personalized treatment plans. Moreover, it aids in early detection of bone density loss, allowing preventive measures to be taken before fractures occur, significantly enhancing patients’ quality of life and reducing healthcare costs.
Eligibility for bone density testing is broad and includes various groups based on risk factors. For example, individuals experiencing unexplained height loss, those with a history of fractures, or patients on medications like corticosteroids that weaken bones are recommended to undergo screening. Other high-risk categories include postmenopausal women, men undergoing hormone therapy, organ transplant recipients, and individuals with certain chronic diseases that affect bone metabolism. The procedure is typically quick, non-invasive, and painless, involving minimal exposure to radiation, making it suitable for routine screening.
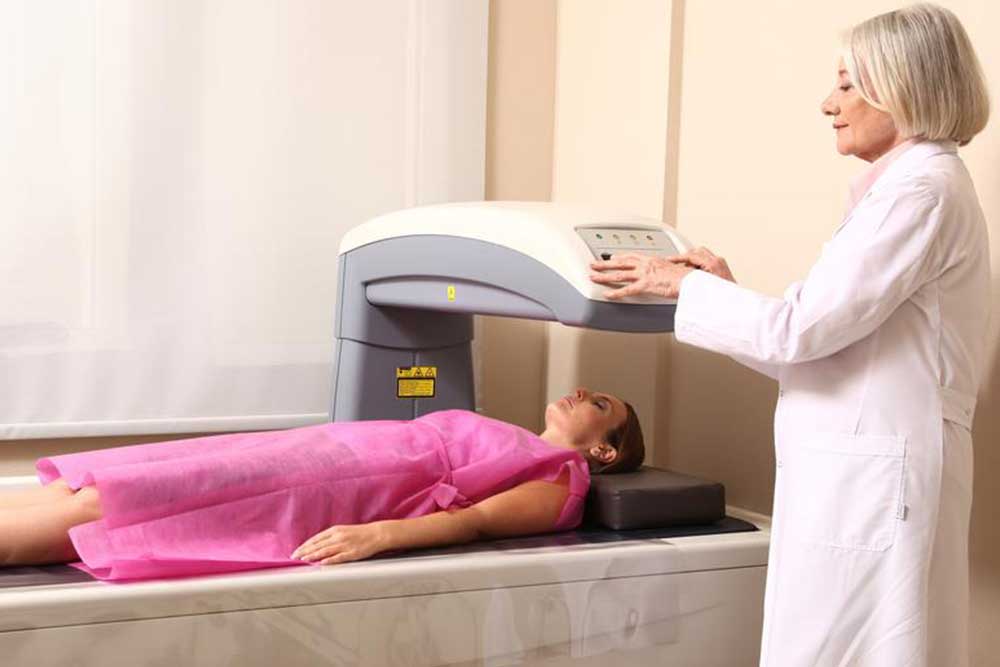
There are different types of devices used for measuring bone density. Central devices, which assess the hip and spine, offer the most accurate results and are considered the gold standard in osteoporosis diagnosis. Peripheral devices, such as those measuring the heel, finger, or wrist, are more accessible and cost-effective but tend to be less precise. Insurance coverage for bone density testing varies depending on the health plan and individual circumstances, so it’s advisable to verify coverage details beforehand. The procedure generally lasts between 10 to 30 minutes and involves lying on a scanning table while the device captures images with low-dose X-ray technology. The process is safe, with negligible radiation exposure, and typically requires no special preparation.
In summary, bone density testing is a crucial component of osteoporosis management and prevention. It enables early diagnosis, guides treatment decisions, and assists in monitoring disease progression or response to therapy. Regular screening for at-risk populations can significantly reduce fracture risk, enhance mobility, and improve overall health outcomes. Advances in technology continue to make these tests more accessible and accurate, supporting better patient care across diverse healthcare settings.