Comprehensive Nutritional Strategies to Manage Arthritis Pain Naturally
Explore comprehensive dietary strategies to alleviate arthritis pain naturally. Learn about anti-inflammatory foods, omega-3 sources, antioxidant-rich fruits, and essential nutrients that support joint health. Implementing these nutritional tips can help reduce inflammation, improve mobility, and enhance overall well-being for individuals managing arthritis. Incorporate delicious and beneficial foods like fatty fish, berries, cruciferous vegetables, and more into your diet for optimal joint care. Consult healthcare providers for personalized advice and enjoy a healthier, more comfortable life with strategic nutrition.

Key Dietary Choices to Alleviate Arthritis Symptoms and Promote Joint Health
Arthritis is a common chronic condition characterized by inflammation of the joints, leading to pain, stiffness, and swelling that can significantly impair daily activities and reduce overall quality of life. There are several types of arthritis, with osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis being the most prevalent. The underlying causes involve joint tissue degeneration, immune system responses, and inflammatory processes. While there is no definitive cure for arthritis, research increasingly shows that dietary habits play a vital role in managing symptoms and slowing disease progression.
Adopting an anti-inflammatory diet rich in specific nutrients can be incredibly beneficial for individuals suffering from arthritis. Selecting the right foods can help reduce joint inflammation, alleviate pain, and enhance mobility. Here, we explore in detail the most effective food groups and nutrients that you should incorporate into your diet to support joint health and manage arthritis symptoms effectively.
Fatty Fish
Fatty fish such as salmon, mackerel, sardines, and tuna are among the top recommended foods for arthritis management. These fish are abundant sources of omega-3 fatty acids, specifically eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA). Multiple studies have demonstrated that omega-3s possess potent anti-inflammatory properties, helping to reduce the production of inflammatory cytokines and prostaglandins that contribute to joint swelling and pain. Regular consumption of omega-3-rich fish has been shown to decrease joint stiffness and improve overall joint function, particularly in rheumatoid arthritis patients. Incorporating this food into your weekly diet can be a natural way to combat inflammation and support joint tissue repair.
Soy and Plant-Based Omega-3 Sources
For those who prefer plant-based options, soy products such as tofu, tempeh, edamame, and soy milk are excellent sources of alpha-linolenic acid (ALA), a plant-derived omega-3 fatty acid. Although ALA needs to be converted in the body to EPA and DHA, it still offers anti-inflammatory benefits. In addition to omega-3s, soy products are high in fiber, antioxidants, and phytochemicals that contribute to overall health and may help reduce systemic inflammation. Incorporating soy into your diet can provide essential nutrients while supporting joint health without the need for animal products.
Healthy Dietary Fats
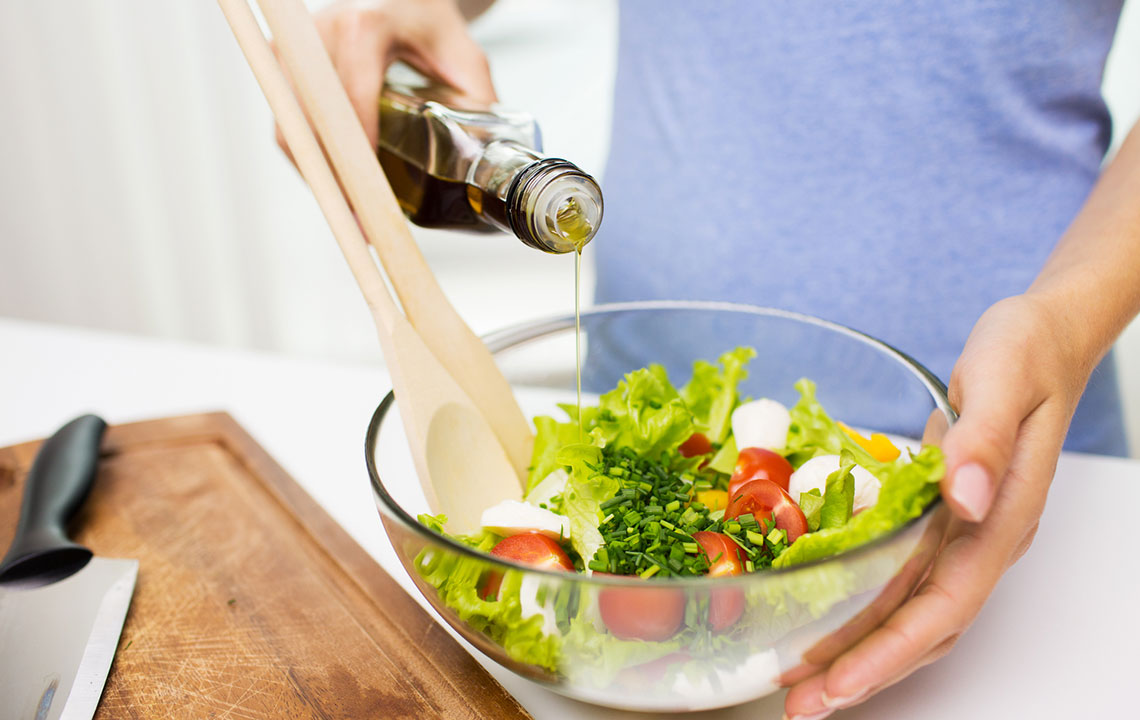
Not all fats are created equal. Monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats found in oils like extra virgin olive oil, avocado oil, and walnut oil have documented anti-inflammatory effects. Extra virgin olive oil, high in oleocanthal, can help slow inflammation in joints. Walnut oil, which contains a higher concentration of omega-3s compared to olive oil, provides an extra anti-inflammatory boost. Choosing these healthy oils for salad dressings, cooking, or drizzling over vegetables can contribute significantly to an anti-inflammatory dietary pattern, ultimately alleviating arthritis symptoms.
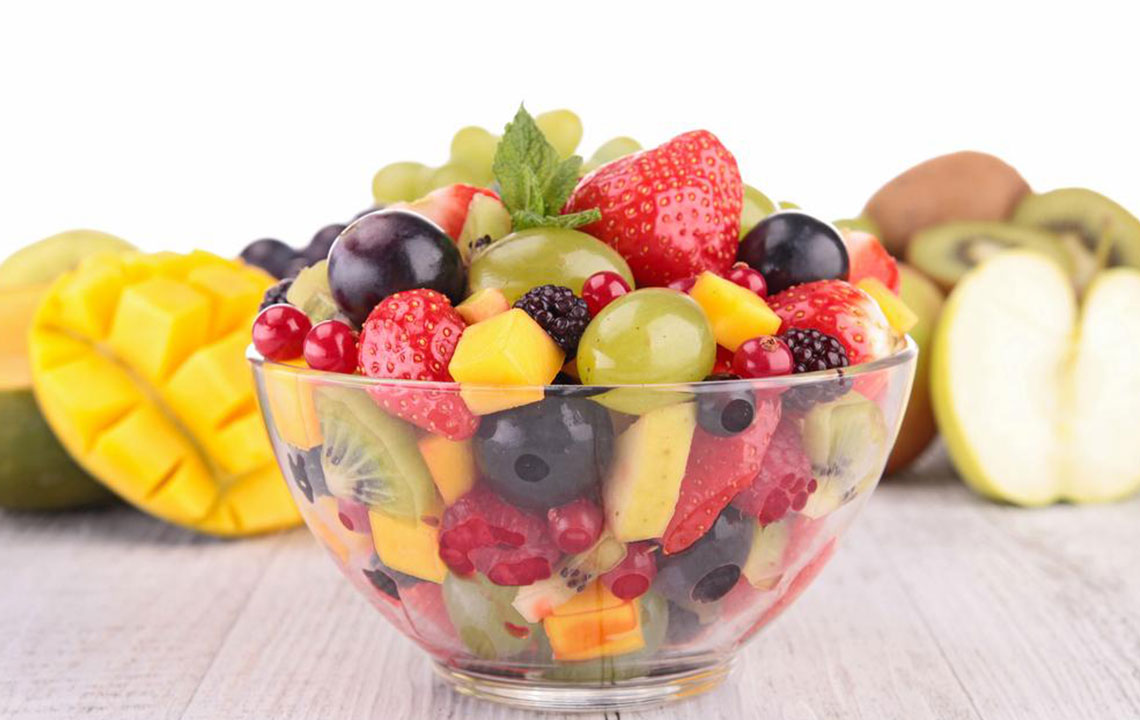
Antioxidant-Rich Fruits: Cherries and Berries
Fruits rich in antioxidants, particularly cherries and berries, have been associated with decreased joint pain and inflammation. Cherries contain anthocyanins, powerful phytochemicals that inhibit inflammatory pathways and have been shown to reduce gout attacks and joint swelling. Berries such as blueberries, raspberries, and blackberries are also loaded with antioxidants, vitamins, and fiber that help combat oxidative stress and inflammation. Regular consumption of these colorful fruits may lessen arthritis flare-ups and support joint tissue repair over time.
Low-Fat Dairy Products
Dairy products like yogurt, milk, and cheese are rich sources of calcium, vitamin D, and other nutrients essential for maintaining strong bones and immune health. Adequate calcium intake is crucial for preventing osteoporosis, which often coexists with arthritis. Vitamin D facilitates calcium absorption and modulates immune responses, potentially reducing autoimmune activity in rheumatoid arthritis. For people with lactose intolerance, fortified plant-based alternatives can serve as suitable substitutes. Proper nutrition with dairy or fortified options under professional guidance helps support overall skeletal health and reduces joint degeneration.
Cruciferous Vegetables: Broccoli and Kale
Vegetables such as broccoli, Brussels sprouts, and kale pack a nutritional punch with vitamins K, C, and phytochemicals like sulforaphane. Sulforaphane has been shown to inhibit enzymes that damage cartilage, thus potentially slowing osteoarthritis progression. These vegetables also contain antioxidants that neutralize free radicals, reducing inflammation and oxidative stress within joint tissues. Including cruciferous vegetables regularly in your meals can help maintain joint integrity, strengthen bones, and potentially prevent cartilage breakdown.
Citrus Fruits for Joint Vitality
Citrus fruits including lemons, oranges, grapefruits, and limes are rich in vitamin C, an essential antioxidant that supports collagen formation and tissue repair. Vitamin C also plays a role in reducing inflammation and strengthening blood vessels around joints, which improves overall joint health. Consuming citrus fruits daily as part of a balanced diet can help promote collagen synthesis and sustain joint tissue resilience, reducing stiffness and pain associated with arthritis.
Legumes and Beans
Legumes like kidney beans, pinto beans, chickpeas, and lentils are valuable sources of high-quality plant protein, fiber, and micronutrients. The fiber content in beans promotes gut health and reduces inflammatory markers in the body. Their phytochemicals can also modulate immune responses. Regular consumption of beans supports muscle maintenance, bone density, and reduces systemic inflammation, making them an important component of an arthritis-friendly diet.
Garlic and Its Therapeutic Properties
Garlic contains sulfur compounds such as diallyl disulfide, which have demonstrated anti-inflammatory and cartilage-protective properties. Studies suggest that garlic inhibits enzymes responsible for cartilage degradation, decreasing the risk or severity of osteoarthritis. Incorporating fresh garlic into your meals not only adds flavor but also provides bioactive compounds that bolster joint health and reduce inflammation.
In summary, while diet alone may not cure arthritis, strategic nutritional choices can significantly improve the quality of life for individuals with the condition. Emphasizing foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids, antioxidants, vitamins, and minerals will help combat inflammation, support joint structure, and promote overall health. Combining these dietary strategies with appropriate medical treatment and a healthy lifestyle can lead to better management of arthritis symptoms and potentially slow disease progression. Always consult with healthcare professionals or registered dietitians to tailor dietary plans suited to your specific health needs.