Understanding Hearing Loss: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment Options
Hearing loss is a common issue that can result from aging, noise exposure, genetics, and health factors. Early detection and treatment options like hearing aids and surgery can help maintain communication and quality of life. This comprehensive guide covers causes, symptoms, and prevention tips to protect your auditory health over time.
Understanding Hearing Loss: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment Options
Hearing is one of our most vital senses, allowing us to communicate, enjoy music, and stay aware of our environment. While many are born with perfect hearing, aging and environmental factors can lead to hearing impairment over time. Recognizing the causes, symptoms, and available treatments is essential for maintaining auditory health and improving quality of life. This comprehensive guide explores everything you need to know about hearing loss, from risk factors to management strategies.
Hearing loss affects millions worldwide, transcending age, culture, and lifestyle. Although often associated with aging, it can result from various factors including environmental exposure, genetics, certain medications, and underlying health conditions. The good news is that early detection and appropriate intervention can significantly improve outcomes, helping individuals regain hearing or mitigate further deterioration.
Understanding the causes of hearing loss is crucial for prevention and management. Age-related hearing decline, exposure to loud noises, genetic predispositions, medication side effects, and health conditions like infections or trauma all play roles in the development of hearing impairments. Being aware of these factors can help you take proactive steps to protect your auditory health.
Age is one of the primary risk factors. As individuals grow older, especially past the age of 60, the structures within the inner ear—such as hair cells—begin to degenerate, leading to presbycusis or age-related hearing loss. Frequent exposure to loud environments accelerates this process by causing damage to hair cells in the cochlea, the part of the inner ear responsible for converting sound waves into electrical signals for the brain.
Prolonged noise exposure is particularly detrimental. Regular exposure to noise levels ranging from 80 to 110 decibels—such as concerts, construction sites, or loud machinery—can cause irreversible inner ear damage. It is essential to wear appropriate hearing protection, such as earmuffs or earplugs, in noisy environments to prevent long-term hearing issues. Sudden loud sounds like explosions or gunfire can also cause instant hearing loss, emphasizing the importance of protective gear in high-risk settings.
Genetics also play a significant role. If hearing impairment runs in your family, your likelihood of experiencing similar issues increases. Hereditary factors influence the development and resilience of inner ear structures and auditory nerves. Understanding your family history can help you seek early screenings and interventions.
Medications are another critical factor. Certain drugs, including specific antibiotics (aminoglycosides), chemotherapy agents, high doses of aspirin, and other pain relievers, can be ototoxic—meaning they can damage the inner ear or auditory nerve. If you are prescribed these medications, discussing potential side effects with your healthcare provider and monitoring hearing function regularly becomes vital.
Health conditions like infections (e.g., meningitis), chronic diseases, or head trauma can also lead to hearing loss. Infections can cause inflammation or damage within the cochlea or auditory nerve, while physical injuries may impair the delicate structures essential for hearing. Managing underlying health issues and seeking prompt treatment can help reduce the risk of permanent damage.
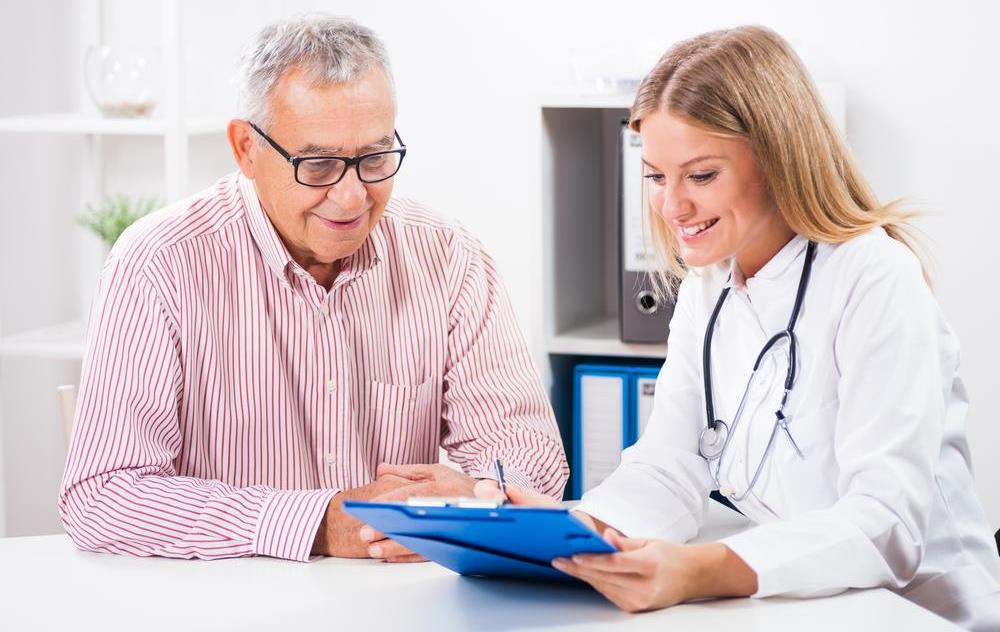
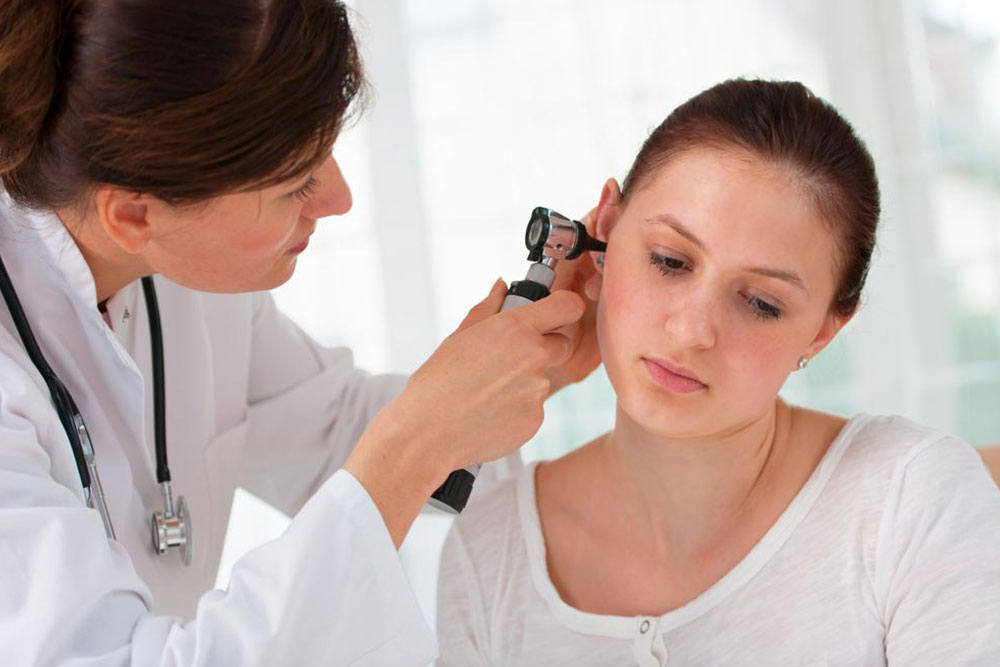
Early detection of hearing impairment is crucial for effective management. Recognizing early warning signs allows for timely intervention, which can prevent further deterioration and improve quality of life. Regular hearing tests are recommended for vulnerable populations, especially older adults and those frequently exposed to loud environments.
Common symptoms include muffled or distorted sounds, difficulty understanding speech—particularly in noisy settings—and the need to ask others to repeat themselves. Other signs involve increasing volume on devices like televisions, trouble distinguishing consonants in speech, and social withdrawal due to communication barriers. If these symptoms persist, consult an audiologist for comprehensive evaluation and personalized treatment options.
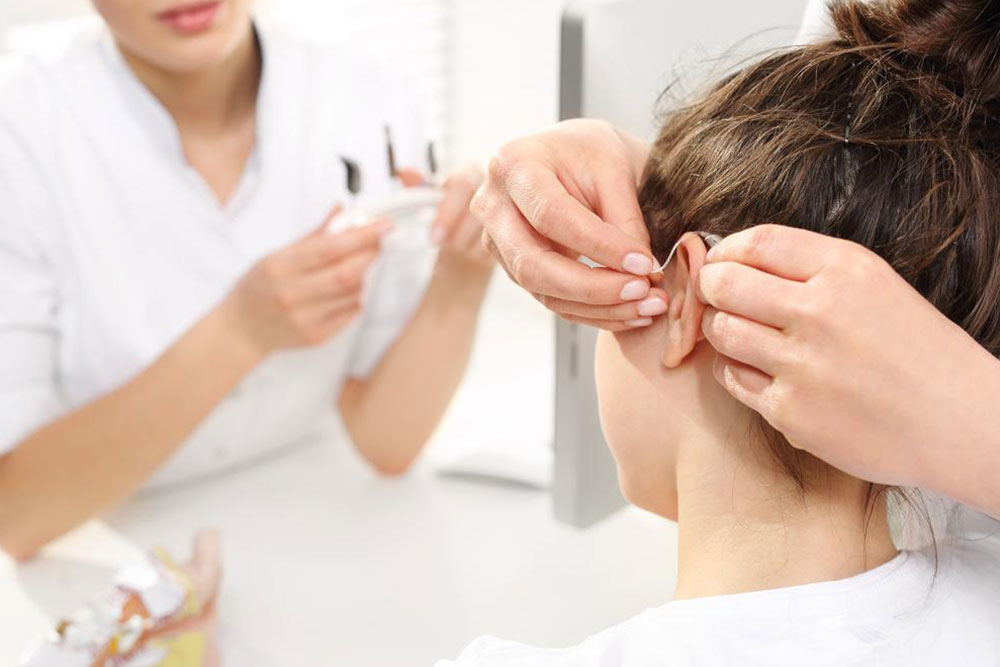
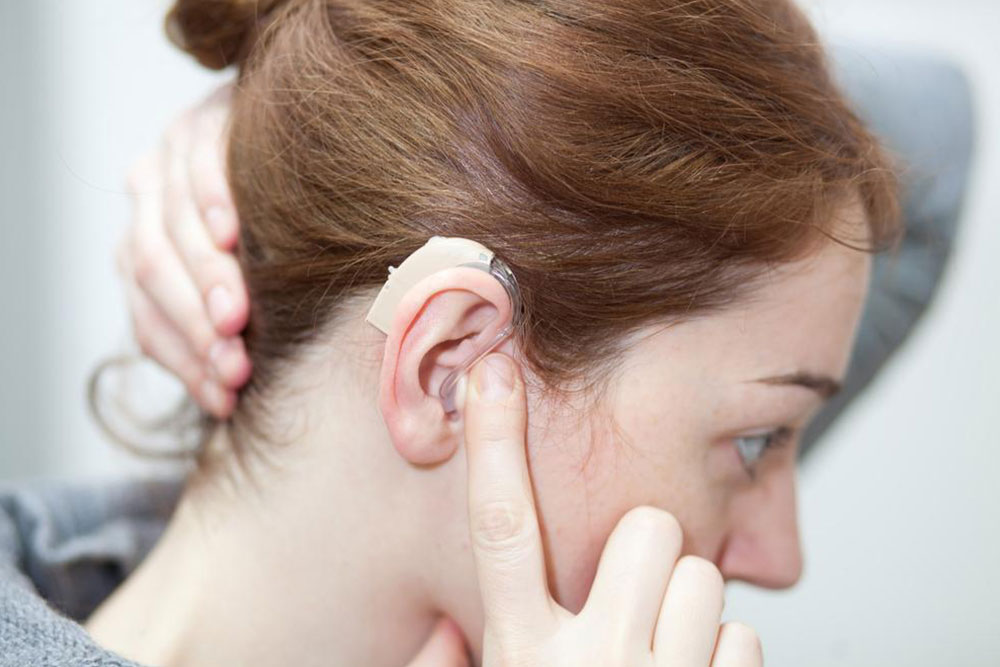
If untreated, hearing loss can get worse over time, leading to social isolation, depression, and heightened stress levels. It can also impact cognitive functions and reduce overall well-being. Fortunately, numerous solutions are available, ranging from hearing aids and assistive listening devices to surgical procedures and cochlear implants, especially when inner ear damage or blockage occurs.
Hearing aids have advanced significantly, offering customized amplification suited to individual needs and lifestyles. Surgical options, including cochlear implants, are effective for severe cases where natural hearing cannot be restored. Additionally, lifestyle changes like managing exposure to loud noises and protecting the ears can prevent further damage. Consulting with hearing specialists can help determine the most appropriate course of action for each individual.
In summary, understanding the causes and symptoms of hearing loss, along with early intervention, can significantly improve outcomes. Regular check-ups, ear protection, and awareness of risk factors are essential measures to preserve hearing health throughout your life. Staying informed about latest advances in audiology and hearing technology ensures that those affected can live comfortably and communicate effectively, maintaining their independence and quality of life.