Complete Guide to Skin Abscess Treatment and Management
This comprehensive guide elaborates on skin abscess management, covering causes, symptoms, and detailed treatment options including antibiotics, drainage, and surgery. Learn how to prevent recurrence and ensure effective healing with expert advice on wound care and hygiene practices for better health outcomes.

Complete Guide to Skin Abscess Treatment and Management
Essential Insights on Managing Skin Abscesses
Skin abscesses are localized collections of pus that form beneath or within the layers of the skin, usually resulting from bacterial infections. These painful lumps can develop on various parts of the body, including areas like the chest, buttocks, face, armpits, and groin, especially in hairy regions. The formation of an abscess begins when bacteria invade the skin, often after minor injuries, friction, or excessive sweating, leading to the immune system's response and pus accumulation. When multiple infected hair follicles cluster together, they can form larger, more painful lumps known as carbuncles. Such infections require timely and appropriate medical intervention to prevent complications.
Doctors typically start treatment with targeted antibiotic therapy to combat bacterial infection. In addition, they often recommend applying warm compresses to the affected area, which helps reduce inflammation and encourages natural drainage of the pus. The management of skin abscesses depends greatly on their size, depth, and location, and different procedures are employed accordingly.
Treatment Procedures for Large Skin Abscesses
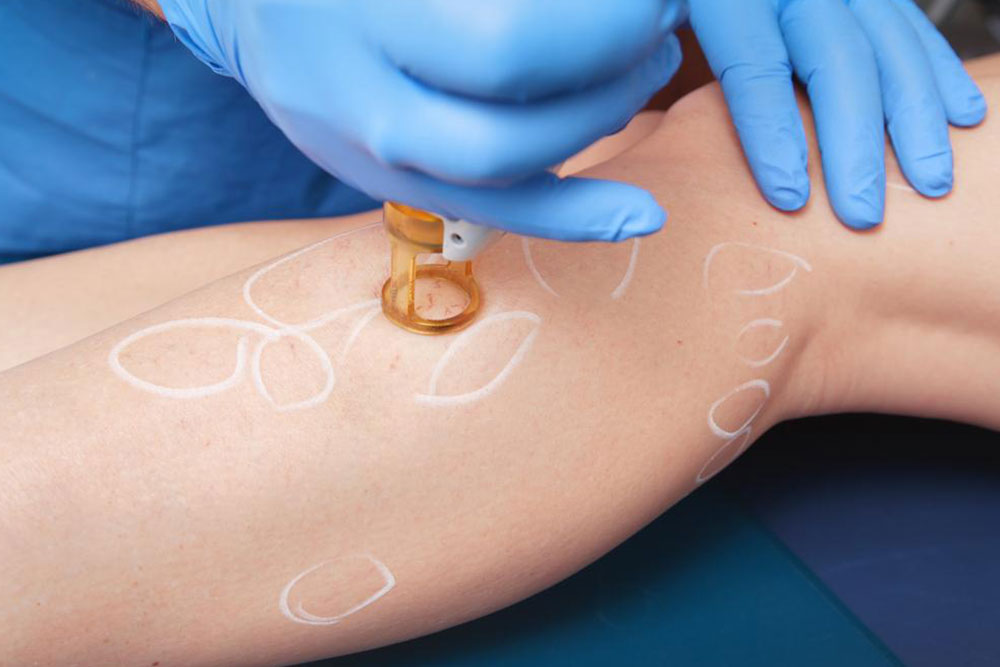
When abscesses are sizable and require drainage, minor surgical procedures are performed under local anesthesia, which is sufficient to numb the area while allowing the patient to remain conscious and comfortable.
The healthcare provider makes an incision over the abscess directly on the skin surface to facilitate the release of pus. After drainage, the wound might be left open with a dressing applied to protect it from infection, sometimes with the addition of sterile saline solution to promote healing and keep the wound clean.
For deeper, more complex abscesses, inserting a gauze wick into the incision site may be necessary to keep the drainage path open. This technique ensures continuous removal of pus and prevents the wound from sealing prematurely, which could trap infection inside. This method might leave a small scar, but it promotes proper healing and minimizes risks of recurrence.
How Are Internal Abscesses Treated?
Internal abscesses, which occur inside the body and can involve organs or tissues, require specialized procedures for drainage. These can include percutaneous needle drainage, where imaging guidance such as computed tomography (CT) scans or ultrasound is used to accurately locate the abscess and guide needle insertion.
Depending on the size and complexity, some internal abscesses may need surgical intervention to remove or drain the infected tissue. Post-procedure, antibiotics are prescribed—either orally or intravenously—to eradicate residual bacteria, prevent spreading, and facilitate recovery.
Percutaneous Abscess Drainage Explained
This minimally invasive procedure involves inserting a needle into the abscess under local or general anesthesia, often with imaging assistance like CT scans for precise placement. Once the needle is inserted, a catheter can be left in situ to enable continuous drainage of pus.
The drainage process may require an overnight hospital stay, especially for larger or more complicated abscesses. Scar tissue formation at the puncture site is possible but generally considered a manageable aspect of treatment.
When Is Surgery the Last Resort?
Surgical intervention becomes necessary if less invasive methods, such as needle drainage, fail to resolve the abscess. It may also be indicated for large, inaccessible, or recurrent abscesses that cannot be effectively managed with other treatments.
Surgical procedures involve making an incision to excise the abscess and remove infected tissue, followed by careful postoperative care and monitoring to ensure successful healing and minimize scarring.
Preventing Skin Abscess Recurrence
Taking proactive measures to prevent the recurrence of abscesses is crucial. Maintaining proper hygiene by washing the affected areas regularly with antibacterial soap can significantly lower infection risks.
Properly caring for cuts, scratches, and wounds by cleaning and protecting them until they are fully healed helps prevent bacteria from entering and causing new infections.
Additionally, managing underlying conditions such as diabetes, which can impair immune responses, is vital to reducing future abscess formation.
In summary, effective management of skin abscesses involves timely diagnosis, appropriate medical procedures, and diligent wound care practices. Whether through antibiotics, drainage, or surgical removal, targeting the infection efficiently can prevent complications, reduce pain, and speed up recovery. If you suspect a skin abscess, seeking prompt medical attention ensures the best possible outcome and minimizes long-term effects such as scarring or recurrent infection.