Comprehensive Guide to Managing and Treating Leg Cellulitis Effectively
Discover an in-depth, comprehensive guide to understanding, managing, and treating leg cellulitis effectively. Learn about causes, symptoms, treatment options, preventive measures, and when to seek medical help to avoid serious complications and promote quick recovery.
Comprehensive Guide to Managing and Treating Leg Cellulitis Effectively
Leg cellulitis is a common and potentially serious skin infection that affects thousands of adults every year. This condition typically presents as redness, swelling, warmth, pain, and sometimes blistering on the skin, especially around the lower legs. Despite being a well-known medical issue, many individuals are unaware of the causes, symptoms, and proper treatments, which can lead to complications if not managed promptly and correctly.
Understanding the causes of leg cellulitis is essential for effective prevention and treatment. The infection is primarily caused by bacteria — most often streptococcus and staphylococcus species — entering the skin through cracks, cuts, or other skin traumas. These bacteria can quickly multiply under conducive conditions, leading to inflammation and infection. Various factors increase the risk of developing cellulitis, including poor hygiene, open wounds, skin trauma, insect bites, or contact with contaminated surfaces. People with compromised immune systems or chronic health conditions such as diabetes, hypertension, or venous insufficiency are at higher risk of developing severe infections.
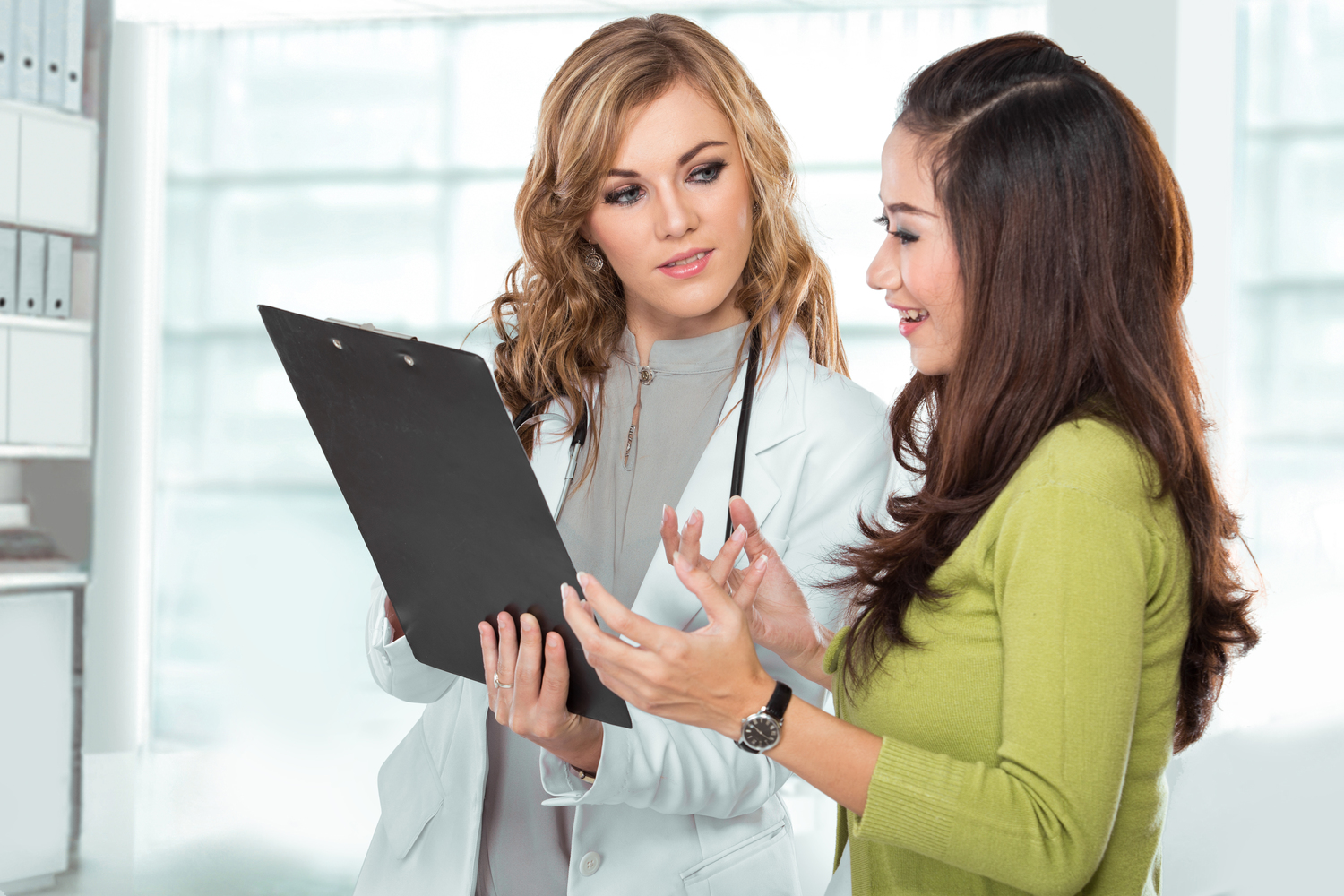
Accurate diagnosis is crucial to distinguish cellulitis from other skin conditions. Healthcare professionals generally examine the affected area, assess symptoms, and may order blood tests or imaging if necessary. Prompt diagnosis ensures timely treatment, which can prevent complications such as abscess formation, sepsis, or the spread of infection to deeper tissues.
Effective management of leg cellulitis involves a comprehensive approach that includes both medical interventions and supportive care. Typically, treatment aims to eliminate bacteria, reduce inflammation, and alleviate symptoms. One common procedure is drainage of blisters or abscesses if present, which helps relieve pressure and removes infected fluid. Medications, especially antibiotics, form the cornerstone of treatment. Depending on the severity of the infection, doctors might prescribe either oral antibiotics or, in more serious cases, intravenous medications administered in a hospital setting.
Adherence to the prescribed treatment plan is vital to ensure complete eradication of bacteria and prevent recurrence. The duration of antibiotic therapy usually ranges from 10 to 21 days. Completing the full course is essential, even if symptoms improve before the medication finishes, as incomplete treatment can lead to resistant infections and relapse. Pain management strategies, such as NSAIDs, and keeping the affected limb elevated can significantly reduce swelling and discomfort.
In cases where symptoms persist or worsen despite initial treatment, further medical intervention might be necessary. This can include additional imaging, stronger antibiotics, or hospitalization for close monitoring. Patients with high fevers, systemic symptoms, or underlying health conditions like diabetes or immune deficiency may require more intensive management to prevent serious complications.
Prevention strategies play a crucial role in reducing the incidence of cellulitis. Maintaining good personal hygiene, cleaning wounds thoroughly, applying prescribed ointments, and covering cuts or abrasions with sterile dressings can significantly lower the risk of bacterial invasion. Additionally, managing chronic health conditions and avoiding skin trauma can help prevent disease progression.
Understanding the importance of early medical intervention and proper wound care can drastically improve outcomes for individuals prone to leg cellulitis. If you notice signs of infection such as increased redness, swelling, warmth, or pain, it is essential to seek medical attention immediately. Early treatment can lead to faster recovery, reduce complications, and improve overall quality of life.