Comprehensive Guide to Selecting the Ideal Calcium Supplements for Optimal Health
Learn how to choose the right calcium supplements for optimal bone health. Discover the differences between various forms like carbonate and citrate, understand dosage guidelines, safe intake practices, and the significance of vitamin D in calcium absorption. This comprehensive guide helps you make informed decisions tailored to your lifestyle and health needs, ensuring safety and effectiveness for maintaining strong bones and overall well-being.

Comprehensive Guide to Selecting the Ideal Calcium Supplements for Optimal Health
Maintaining adequate calcium levels is vital for building strong bones, supporting muscle function, and ensuring overall cellular health. While a balanced diet rich in dairy products, leafy greens, and fortified foods is the best way to meet calcium needs, many individuals struggle to obtain sufficient calcium through diet alone. In such cases, calcium supplements become an essential part of maintaining healthy calcium levels. However, the wide variety of supplement options available on the market can make choosing the right product a daunting task. This comprehensive guide aims to help you understand what to look for when selecting calcium supplements, how to incorporate them safely into your routine, and factors to consider for optimal absorption and health benefits.
Understanding the calcium requirements is crucial. Most adult men and women should aim for about 1,000 mg of calcium per day. This requirement increases to about 1,200 mg for postmenopausal women and seniors over the age of 70, due to the higher risk of osteoporosis and bone density loss in these populations. Individuals on plant-based diets or those who consume limited dairy products due to lactose intolerance or personal preferences might also need supplemental calcium to meet their daily needs. Additionally, specific health conditions, such as osteoporosis, high protein intake, or digestive disorders, can influence calcium requirements. Recognizing these factors and adjusting your intake accordingly can help promote stronger bones and overall health.
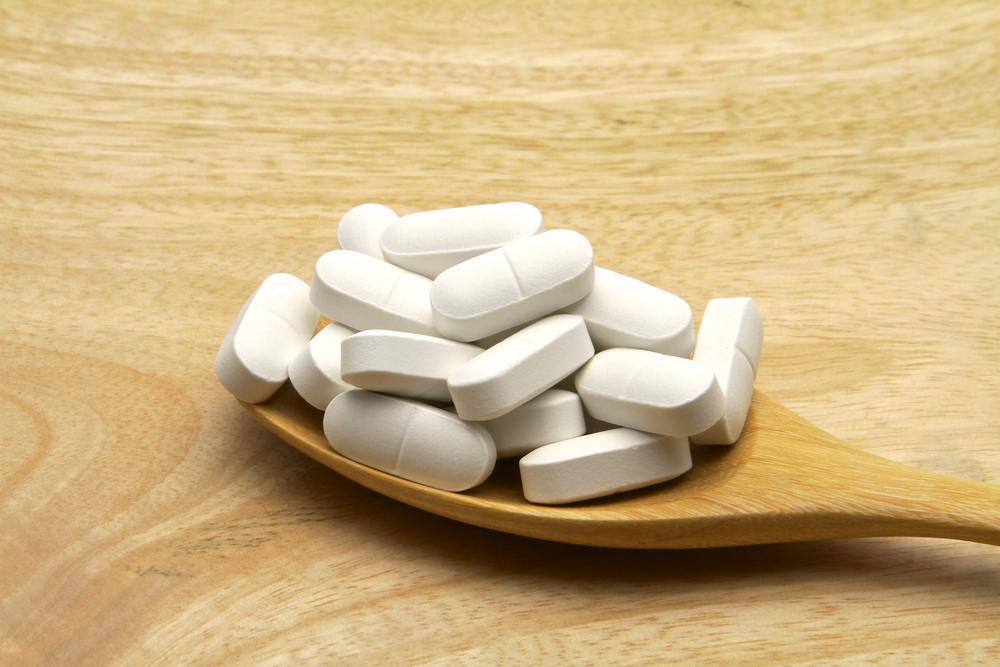
Calcium supplements are commonly combined with various compounds to improve absorption and efficacy. The two most widely used forms are calcium carbonates and calcium citrate. Calcium carbonate contains a higher percentage of elemental calcium—typically around 40%—but it requires an acidic environment in the stomach for proper absorption. Therefore, it is best taken with meals to enhance its effectiveness. On the other hand, calcium citrate is more easily absorbed, even on an empty stomach, although it contains a smaller amount of elemental calcium—about 21%. Due to its better bioavailability, calcium citrate is a suitable option for older adults or those with lower stomach acid levels.
Other forms include calcium gluconate and calcium lactate, which contain even less elemental calcium, at around 9% and 13%, respectively. While these are primarily used in intravenous applications, they are available as oral supplements but are less common for calcium intake due to their lower calcium content per dose.
Optimal Calcium Dosage and Timing
Although supplement labels may boast high percentages of calcium, it's essential to understand that the body can effectively absorb only about 500 mg of calcium at a time. Taking larger doses in a single sitting does not necessarily translate to better calcium intake; instead, it can lead to decreased absorption and increased risk of side effects such as kidney stones or constipation. For this reason, health professionals recommend splitting your daily calcium intake into two or three smaller doses, spaced evenly throughout the day. This approach maximizes absorption and ensures a steady supply of calcium to your bones and tissues, promoting better overall health.
Ensuring Safety: Avoiding Toxic Contaminants
Not all calcium supplements are created equal. Some products, especially those derived from unrefined sources like bone meal, oyster shells, or coral, may contain harmful contaminants, such as heavy metals like lead, mercury, or arsenic. These contaminants can pose severe health risks, particularly with long-term use. To ensure safety, it's advisable to select supplements from reputable brands that conduct rigorous testing for toxins and adhere to quality standards. Look for certifications from independent testing organizations to verify that the product is free from harmful contaminants, ensuring that your supplement promotes health without introducing additional risks.
Adhering to Recommended Dosages
While calcium is vital for health, excessive intake can have adverse effects, including the risk of kidney stones, cardiovascular issues, or calcification of soft tissues. As such, it's crucial to follow the dosage recommendations provided by your healthcare provider or indicated on the supplement label. Avoid self-prescribing high doses of calcium without medical supervision, as this can lead to toxicity and other health complications. Regular check-ups and blood tests can help monitor your calcium levels and prevent potential overdose scenarios, especially if you are taking other medications or have underlying health conditions.
Drug Interactions and Timing
Calcium supplements can interfere with the absorption and efficacy of certain medications. Notably, calcium can affect the absorption of zinc, iron, thyroid medications, and tetracycline antibiotics. To minimize interactions, it is recommended to take calcium supplements at least two to four hours apart from these drugs. Consulting with your healthcare provider about timing and potential interactions is essential to avoid compromising the effectiveness of your medications and ensuring that your calcium supplement provides maximum benefit.
The Critical Role of Vitamin D in Calcium Absorption
Vitamin D plays a fundamental role in enabling your body to absorb calcium efficiently. Without adequate vitamin D levels, calcium absorption in the intestines is significantly reduced, weakening bone health over time. Sun exposure is the most natural way to boost vitamin D, as ultraviolet rays trigger its synthesis in the skin. Dietary sources such as fortified foods, egg yolks, and fatty fish like canned salmon and mackerel can also contribute to maintaining optimal vitamin D levels. In some cases, healthcare providers might recommend vitamin D supplements, especially for individuals with limited sun exposure or specific deficiencies, to enhance calcium absorption and promote stronger bones.
In summary, choosing the right calcium supplement involves considering your individual health status, dietary habits, and specific needs. By understanding the different forms, proper dosages, safety considerations, and the importance of vitamin D, you can make informed decisions to support your bone health efficiently. Always consult with a healthcare professional before making significant changes to your supplement routine to ensure these choices are safe and tailored to your personal health profile.