Comprehensive Nutritional Approaches to Managing Multiple Sclerosis Effectively
This comprehensive guide explores five essential nutritional strategies for managing multiple sclerosis. It emphasizes the importance of anti-inflammatory foods, omega-3 fatty acids, vitamin D, and healthy fats. Implementing these dietary approaches can reduce inflammation, support nerve health, and improve quality of life for MS patients. Tailored nutrition, combined with medical advice, offers an effective way to manage symptoms and potentially slow disease progression. Discover practical tips and the best foods to incorporate into an MS-friendly diet for better health outcomes.

Comprehensive Nutritional Approaches to Managing Multiple Sclerosis Effectively
Multiple sclerosis (MS) is a complex, chronic autoimmune disease that affects the central nervous system, leading to a wide range of neurological symptoms. As a condition with no known cure, managing MS focuses heavily on symptom control, reducing flare-ups, and potentially slowing disease progression through lifestyle interventions. Among these, diet and nutrition play pivotal roles. An anti-inflammatory, nutrient-rich diet can significantly influence the course of the disease, improve quality of life, and help patients better handle symptoms such as fatigue, cognitive impairment, and muscular weakness.
In this detailed guide, we explore five vital dietary strategies and specific food choices that can support individuals living with MS. Adopting these nutritional practices can help optimize brain and nerve health, reduce systemic inflammation, and enhance overall well-being.
,
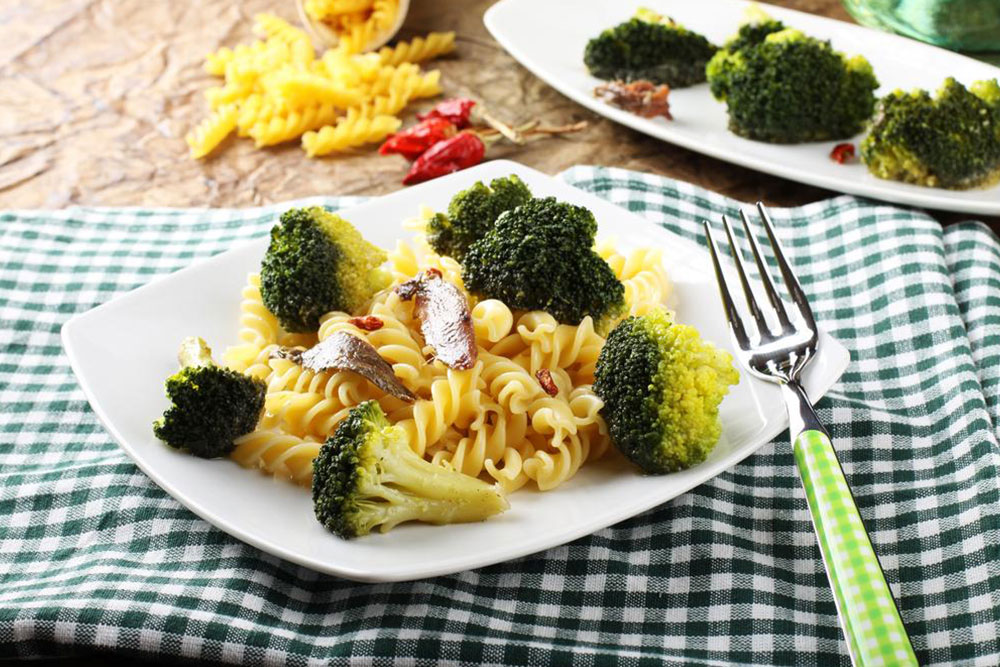
Incorporating Omega-3 Fatty Acid-Rich Seafood Fish such as salmon, mackerel, sardines, tuna, herring, and trout are powerhouses of omega-3 fatty acids, essential nutrients known for their potent anti-inflammatory effects. These healthy fats contribute to reducing neuroinflammation, a hallmark of MS pathology, and promote better cell membrane integrity. Prioritizing omega-3-rich fish in your diet can help counterbalance the omega-6 fatty acids that are often prevalent in Western diets, which tend to promote inflammation when consumed in excess.
Ensuring Adequate Vitamin D Intake Vitamin D deficiency is commonly observed among MS patients, and research indicates that insufficient levels may be linked to increased relapse rates and faster disease progression. While natural sunlight exposure remains ideal for maintaining vitamin D levels, dietary sources are equally important, especially in regions with limited sun. Foods high in vitamin D include eggs, low-fat dairy products, fatty fish like salmon, fortified cereals, and fortified orange juice. Supplementation can also be considered, but always under medical supervision to prevent toxicity.
Utilizing Anti-inflammatory Spices in Cooking Spices like turmeric, containing curcumin, have been recognized for their remarkable anti-inflammatory and neuroprotective properties. Regular inclusion of turmeric in your diet—whether in curries, soups, stews, or even smoothies—can help mitigate inflammation and may alleviate some MS symptoms. Curcumin's potential to slow disease progression is an area of ongoing research, and incorporating this spice is a flavorful way to benefit your health.
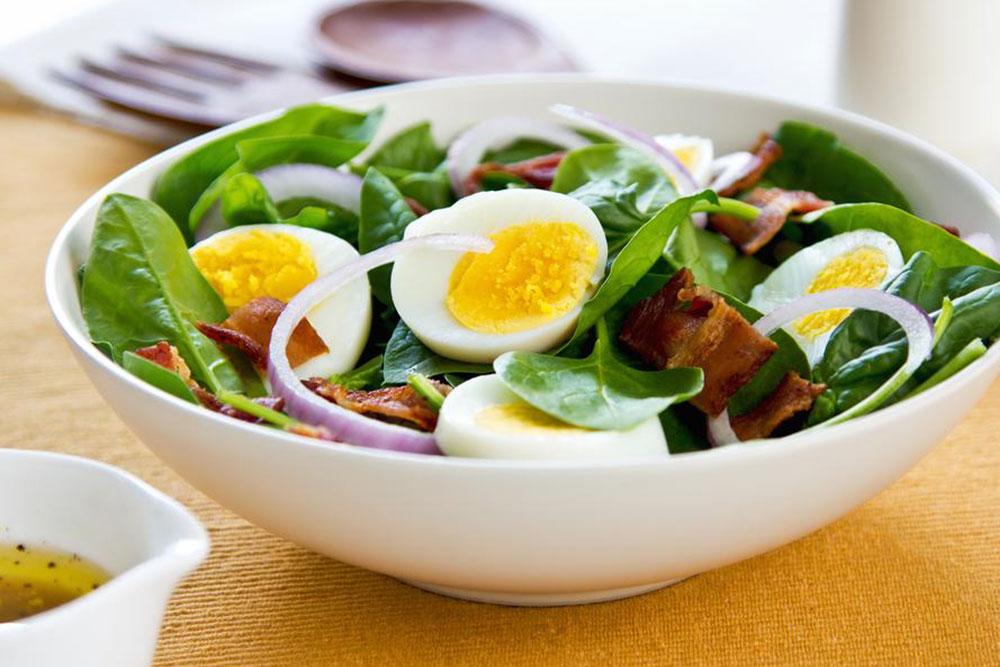
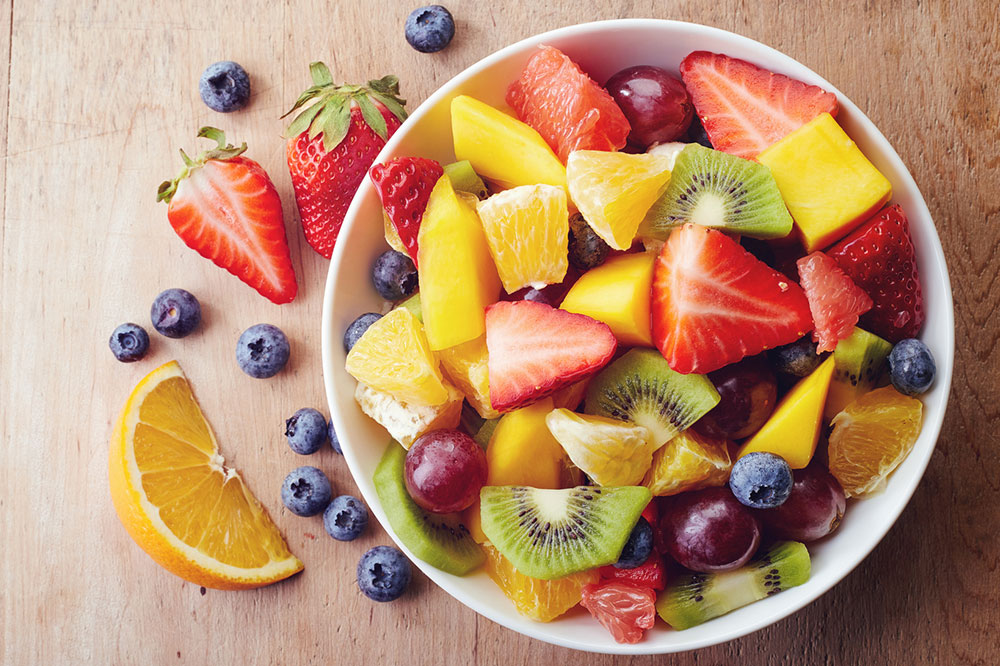
Consuming Colorful Fruits and Vegetables Rich in antioxidants, phytochemicals, vitamins, and minerals, fruits and vegetables form the backbone of an MS-friendly diet. Leafy greens like spinach, kale, and Swiss chard, along with berries, bananas, papaya, kiwi, and citrus fruits, help combat oxidative stress and inflammation. Their nutrient-dense profiles can contribute to improved nerve health, reduced pain, alleviation of fatigue, and enhanced cognitive function.
Choosing Healthy Fats for Brain and Heart Support Foods like avocados are excellent sources of monounsaturated fats, which support cardiovascular health and may help reduce inflammation. Avocados also contain antioxidants such as lutein and glutathione, along with vitamin E, which are beneficial for brain health and cell repair. Incorporating healthy fats into your diet is an effective strategy for managing MS symptoms and promoting overall neurological function.
In conclusion, an integrated nutritional approach focusing on anti-inflammatory foods, sufficient vitamin D intake, and healthy fats can play a vital role in managing multiple sclerosis. Consistency and a tailored diet plan developed in consultation with healthcare providers or dietitians can considerably impact the illness trajectory, symptom severity, and overall quality of life for individuals living with MS.
Adopting these dietary strategies not only supports neurological health but also enhances general well-being, making them an essential component of comprehensive MS management.