Comprehensive Guide to Knee Replacement Surgery: What You Need to Know
This comprehensive guide covers everything about knee replacement surgery, including indications, types of procedures, and preoperative preparations. It provides valuable insights for patients considering this life-changing operation, helping them understand the process and set realistic expectations for recovery and improved mobility.
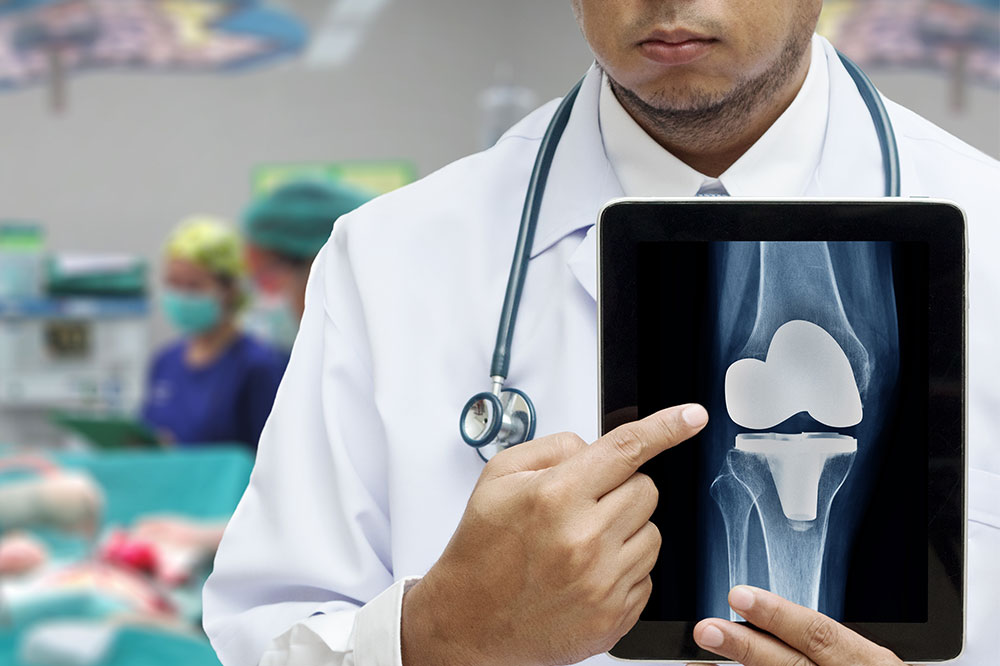
Your Complete Guide to Knee Replacement Procedures and Recovery
As individuals age, the wear and tear on their joints become increasingly evident, often leading to limitations in mobility and persistent discomfort. For many seniors and even middle-aged adults, knee problems are among the most common issues faced, impacting their daily lives significantly. Advances in medical science and surgical techniques now provide effective, life-changing solutions for those suffering from severe knee conditions. This comprehensive guide aims to walk you through everything you need to know about knee replacement surgeries, from the causes and symptoms to the different types of procedures and preoperative preparations.
One of the primary reasons people consider knee replacement surgery is osteoarthritis, a degenerative joint disease that deteriorates cartilage, causing bones to rub against each other. When such joint degeneration leads to chronic pain and mobility issues that do not respond to conservative treatments like medication, physical therapy, or lifestyle modifications, surgery becomes a highly viable option. The goal of knee replacement is to restore joint function, reduce discomfort, and improve overall quality of life.
Persistent knee pain, especially when it interferes with walking, climbing stairs, or sitting for extended periods, can severely decrease one’s range of motion and day-to-day comfort. The root cause of this pain is often osteoarthritis, which causes the deterioration of cartilage within the knee joint. As the cartilage wears down, bones begin to rub directly against each other, resulting in inflammation, stiffness, and significant pain. When non-surgical interventions such as NSAIDs, corticosteroids, weight management, or physical therapy fail to provide relief, surgical options like knee replacement are recommended by healthcare providers.
Understanding Knee Replacement Surgery
Knee replacement surgery, medically referred to as knee arthroplasty, involves replacing the damaged or diseased parts of the knee joint with artificial components made of metal, plastic, or ceramic materials. This procedure aims to eliminate pain, improve joint stability, and restore normal movement. For many patients, the thought of surgery can cause anxiety, but watching educational videos or tutorials available online can demystify the process. These resources provide a detailed visual explanation of what happens during the surgery, what to expect before and after, and tips for a smooth recovery.
When Should You Consider Knee Replacement?
Knee replacement is a common surgical procedure in the United States and is typically considered when conservative treatments have failed, and the patient's quality of life is significantly affected. Specific conditions that indicate the need for surgery include:
Rheumatoid arthritis: An autoimmune disease where the immune system attacks the synovial lining of your joints, causing swelling and destruction of the cartilage and bone.
Knee injuries: Severe ligament tears, fractures, or meniscal damage can accelerate cartilage breakdown, leading to osteoarthritis and persistent pain.
Deformities: Structural abnormalities such as bowlegs, knock-knees, or other misalignments can cause uneven stress on the knee joint, making replacement necessary.
Reduced blood flow: Impaired circulation to the knee area might contribute to joint deterioration, thus requiring surgical intervention.
Different Types of Knee Replacement Surgeries
The choice of specific procedure depends on the extent of joint damage, age, activity level, and overall health. Common types include:
Full knee replacement (total knee arthroplasty): This involves removing the damaged surfaces of the entire knee joint and replacing them with prosthetic components. It is suitable for widespread joint deterioration.
Partial knee replacement (uni-compartmental knee arthroplasty): Only the affected part of the knee, usually the medial or lateral compartment, is replaced. This approach preserves healthy bone and tissue, leading to quicker recovery.
Kneecap replacement (patellofemoral arthroplasty): Focuses on replacing the undersurface of the kneecap and the cartilage behind it when the damage is limited to this compartment.
Revision knee surgery: A complex procedure performed to replace or repair a previous knee prosthesis that has failed or become loose over time.
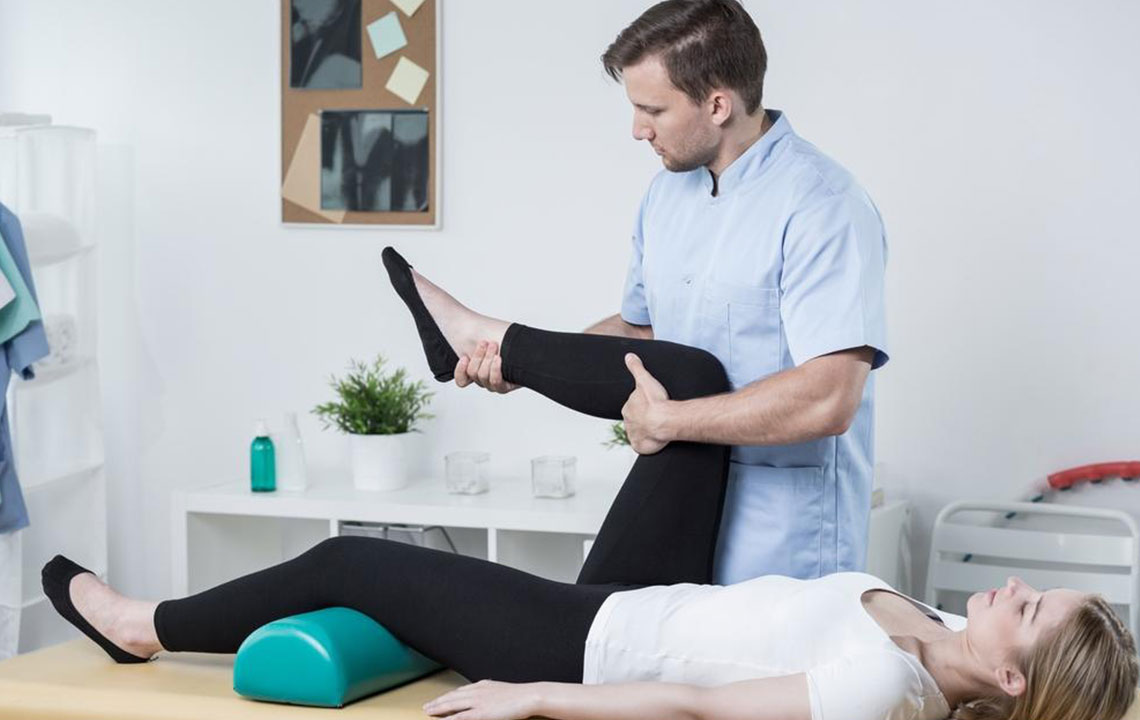
Preoperative Preparation: Using Online Resources
Preparing mentally and physically for knee replacement surgery can alleviate anxiety and improve outcomes. Reputable medical websites and platforms such as Arthritis-Health, WebMD, and Healthline offer detailed educational videos that illustrate the entire surgical process, preoperative steps, anesthesia, and postoperative care. Watching these videos helps patients understand the procedure, set realistic expectations, and prepare for rehabilitation. Additionally, consulting with your healthcare provider to discuss your specific case and any concerns is essential for personalized preparation.
In conclusion, knee replacement surgery is a highly successful procedure that offers relief from debilitating joint pain and restores mobility. By understanding the causes, types of surgeries, and preparation strategies, patients can make informed decisions and approach their surgery with confidence. Advances in surgical techniques and prosthetic materials continue to improve patient outcomes, making knee replacement one of the most effective solutions for severe knee conditions today.