Ultimate Guide to Knee Replacement Surgery: What Patients Need to Know
This detailed guide covers everything about knee replacement surgery, from identifying when it's needed to preparing for the procedure and managing recovery. Learn about causes, procedures, risks, costs, and tips for maintaining knee health to make informed decisions and ensure a smooth surgical journey.
Ultimate Guide to Knee Replacement Surgery: What Patients Need to Know
The knee joint is one of the most essential and complex joints in the human body, enabling us to perform vital activities such as walking, running, jumping, and climbing. It bears the weight of our entire body during daily movements, making its health critical to our overall mobility and quality of life. However, due to injury, aging, overuse, or degenerative diseases, the knee joint can suffer significant damage, leading to pain, stiffness, and limited mobility. When these issues become severe and conservative treatments fail to provide relief, knee replacement surgery often becomes the recommended course of action.
This comprehensive guide aims to provide you with a detailed understanding of knee replacement procedures, causes of knee problems, preparation tips, and post-operative care. By gaining knowledge about this common surgical intervention, patients can make more informed decisions and prepare effectively for a successful recovery.
Understanding the Need for Knee Replacement Surgery
Knee replacement surgery, also known as knee arthroplasty, involves removing damaged cartilage and bone from the knee joint and replacing them with artificial components called implants or prostheses. This procedure aims to reduce chronic pain, improve joint function, and restore mobility for individuals with severe knee damage. Several conditions can necessitate knee replacement, including osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, post-traumatic arthritis, and certain knee deformities.
Causes of Knee Damage and When Surgery Becomes Necessary
Common causes leading to the need for surgical intervention include:
Progressive osteoarthritis, where cartilage wears down over time, exposing bone and causing pain.
Rheumatoid arthritis, an autoimmune disorder resulting in joint inflammation and destruction.
Knee injuries from sports, accidents, or trauma that damage ligaments, cartilage, or bones.
Overuse injuries in athletes or laborers involving repetitive stress on the knee joint.
Aging-related degeneration that diminishes the joint's cushioning capacity.
If conservative treatments like medication, physical therapy, and lifestyle modifications fail to alleviate symptoms, and if pain or disability hinders daily life, knee replacement surgery becomes a viable option.
Recognizing Symptoms That Indicate Surgery Is Needed
Patients should consider surgical intervention when:
Experiencing severe, persistent knee pain that does not improve with non-surgical methods.
Difficulty walking or performing routine activities due to joint stiffness or pain.
Significant loss of joint function or deformity affecting quality of life.
Failure of conservative treatments like anti-inflammatory medications, injections, or physical therapy.
It is crucial to consult with an orthopedic specialist for a thorough assessment and personalized treatment plan.
Preparing for Knee Replacement Surgery
Proper preparation can enhance surgical outcomes and facilitate faster recovery. Key steps include:
Comprehensive medical evaluation: Undergo pre-operative tests, including blood work, imaging scans, and medical history review.
Weight management: Maintaining a healthy weight reduces stress on the knee and improves surgical results.
Exercise and physical therapy: Strengthening leg muscles can support the new joint and improve post-operative mobility.
Planning for recovery: Arrange transportation, assistive devices, and post-surgical support systems.
Patient education: Understand the procedure, risks, benefits, and post-operative care requirements.
The Knee Replacement Procedure: What to Expect
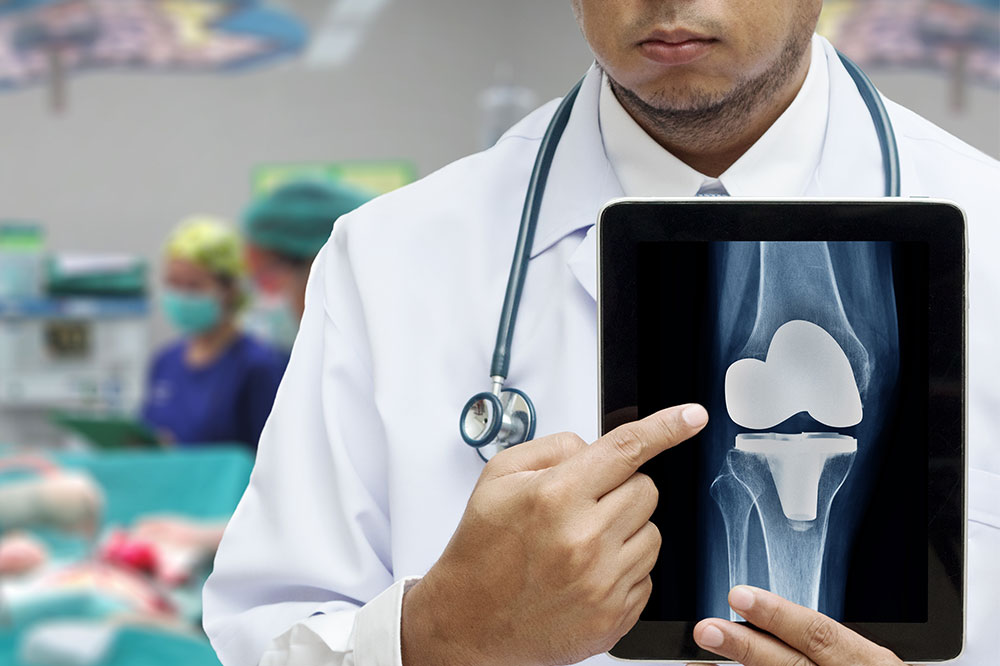
Knee replacement surgery is typically performed under anesthesia with the patient either sedated or fully anesthetized. The surgeon makes an incision over the knee and removes damaged cartilage and bone. The prosthetic components—usually made from metal, plastic, or ceramic—are then securely fixed to the remaining bone. The entire procedure generally lasts 1 to 2 hours.
Postoperative Care and Rehabilitation
Successful recovery depends on diligent postoperative care and physical therapy. Immediately after surgery, you may experience swelling, pain, and limited mobility. Your healthcare team will manage pain with medications and guide you through early rehabilitation exercises. Physical therapy plays a critical role in restoring joint function, improving strength, and preventing complications like blood clots.
Discharge timelines vary, but most patients begin weight-bearing and mobility exercises within a day or two. Follow-up appointments will monitor healing and prosthesis stability, and your therapist will tailor a personalized rehabilitation plan to optimize recovery outcomes.
Risks and Potential Complications of Knee Replacement
As with any surgical procedure, knee replacement carries certain risks. Common complications include:
Blood clots in the legs or lungs.
Infection at the surgical site.
Persistent pain or stiffness.
Loosening or wear of the prosthetic over time.
Nerve or blood vessel injury.
Monitoring symptoms closely after surgery and seeking prompt medical attention can mitigate these risks and ensure a smoother recovery.
Cost and Insurance Considerations
The financial aspect of knee replacement depends on various factors such as geographic location, hospital charges, surgeon’s fees, and patient health conditions. Insurance coverage varies, but many plans partially or fully cover the procedure, especially when medically necessary. Pre-operative consultations and planning with your healthcare provider can help clarify coverage options and out-of-pocket expenses.
Enhancing Knee Longevity and Prevention Tips
While some degeneration is inevitable with age, proactive measures can prolong joint health:
Maintain a healthy weight: Reduces joint stress and delays wear.
Engage in low-impact exercise: Activities like swimming, cycling, and walking minimize joint strain.
Strengthen leg muscles: Supports the knee and absorbs shocks.
Avoid repetitive overuse: Take breaks and avoid activities that cause pain.
Seek medical advice early: Address knee discomfort promptly to prevent deterioration.
Adopting these habits can help preserve your knee health and postpone the need for surgical intervention.
Conclusion: Making an Informed Decision
Knee replacement surgery is a highly effective solution for individuals suffering from severe knee damage and persistent pain. Understanding the causes, procedures, risks, and recovery process allows patients to make well-informed decisions and approach surgery with confidence. Working closely with your healthcare team, preparing thoroughly, and adhering to postoperative guidelines can lead to successful outcomes and restored mobility, significantly improving quality of life.