Comprehensive Guide to the Top Medical Applications of Botox Treatment
This detailed article explores the top 10 medical applications of Botox beyond cosmetics, including treating blepharospasm, migraines, hyperhidrosis, and more. It emphasizes the importance of professional administration for safety and effectiveness, providing insights into how Botox improves quality of life for various health conditions.
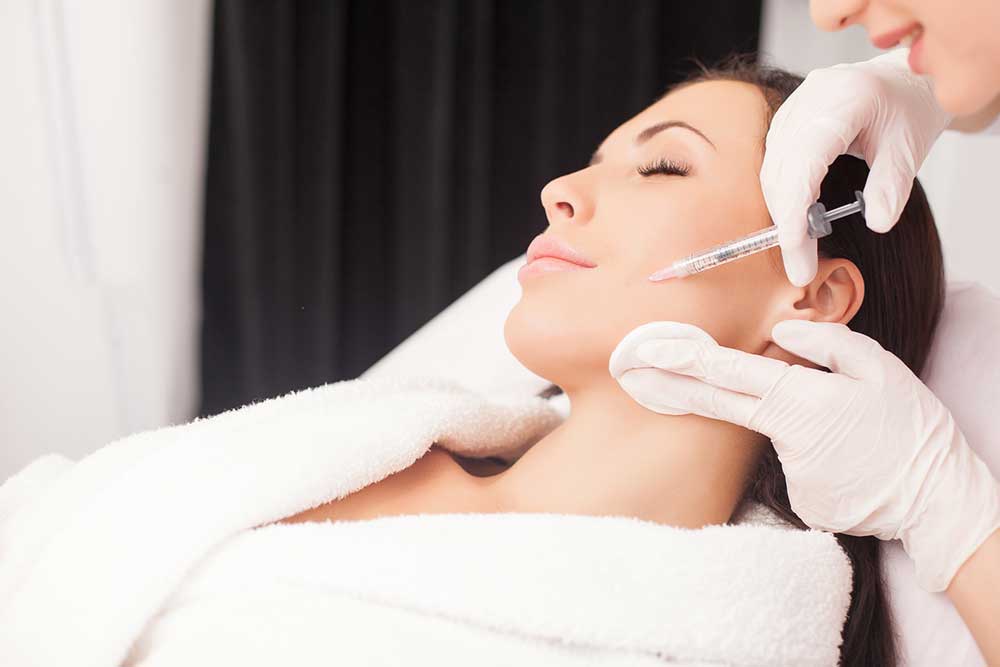

Exploring the 10 Most Significant Medical Uses of Botox
Botulinum toxin, popularly known as Botox, is a neurotoxic protein produced by the bacterium Clostridium botulinum. This bacterium is naturally found in various environments such as soil, lakes, and forests. Additionally, traces of this toxin are present in the intestines of different animals, including mammals and aquatic life forms. While Botox gained widespread fame for its cosmetic role in smoothing facial wrinkles and fine lines, its medical applications have grown significantly over recent years. Today, Botox is approved to treat a diverse array of more than 20 medical conditions, highlighting its versatility as a therapeutic agent.
In this comprehensive guide, we delve into the top 10 medical conditions that benefit from Botox treatments, explaining how it works, the benefits, and considerations for patients seeking this therapy.
Blepharospasm (Eye Twitching)
One of the primary therapeutic uses of Botox is in managing blepharospasm, a condition characterized by involuntary spasms or twitching of the eyelid muscles. This disorder can interfere with normal vision and daily activities, leading to discomfort and social embarrassment. Botox provides relief by blocking nerve signals to the affected muscles, which temporarily reduces spasms. The treatment involves targeted injections into the eyelid muscles, allowing for smoother eyelid function and improved quality of life.
Blepharospasm results in uncontrollable eye twitching and eyelid drooping, which can impair vision and communication. Botox interrupts nerve signals at the neuromuscular junction, providing significant symptomatic relief.
Strabismus (Crossed Eyes)
Originally approved by the FDA for treating strabismus, Botox effectively relaxes overactive eye muscles that cause misalignment. The procedure involves injecting Botox into specific eye muscles to restore proper alignment, often serving as an alternative to surgery. This minimally invasive approach is preferred by many patients for its safety profile and effectiveness, especially in congenital cases or trauma-induced misalignment.
Excessive Salivary Secretions (Hypersalivation)
Overproduction of saliva, a condition that may result from neurological disorders, medication side effects, or other health issues, can be managed with Botox. ENT specialists perform these injections by targeting the salivary glands, reducing nerve signals that stimulate saliva production, thus alleviating symptoms and improving comfort.
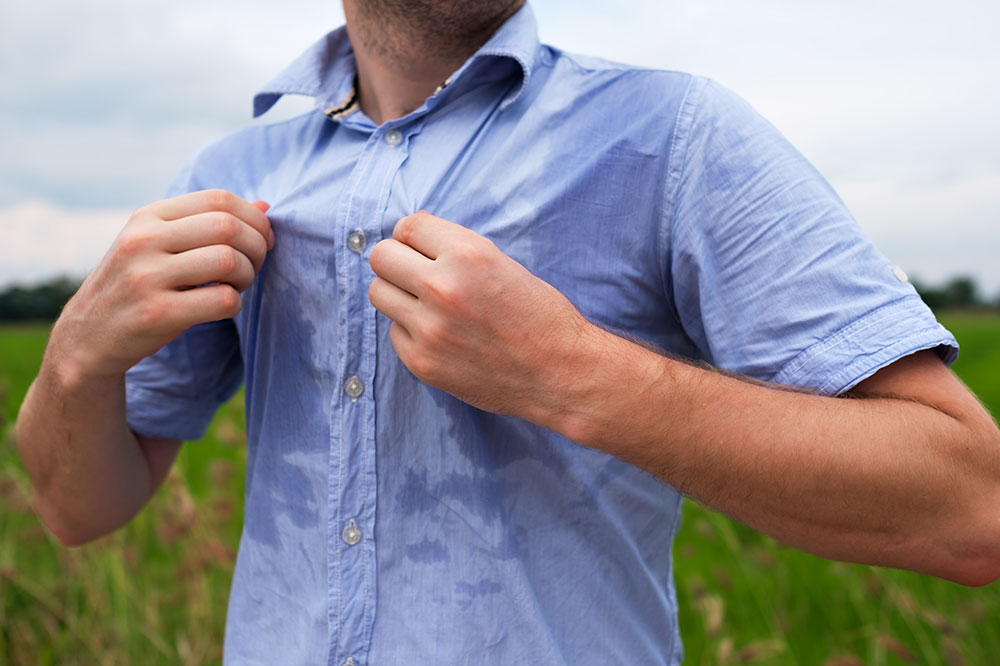
Severe Hyperhidrosis (Excessive Sweating)
For individuals suffering from hyperhidrosis, particularly on the face, scalp, armpits, palms, or feet, Botox offers a highly effective treatment. Clinical studies have demonstrated the ability of Botox to reduce sweating by up to 80%, significantly enhancing quality of life and reducing the risk of skin infections caused by moisture buildup. Treatments involve injecting Botox into the affected areas to block sweat gland activation.
Chronic Migraines
Botox has been FDA-approved for preventing chronic migraines. It works by relaxing muscles in the forehead, temples, neck, and shoulders, alleviating tension that contributes to headache pain. Many patients report a reduction in headache frequency and severity after repeated Botox treatments, making it a valuable option for those with persistent migraines unresponsive to traditional medications.
Spasmodic Dysphonia (Voice Disorder)
This neurological disorder causes strained, tremulous voice due to abnormal muscle spasms around the vocal cords. Botox injections provide relief by softening these spasms, resulting in a clearer, more natural voice. Treatment is typically customized based on the severity and specific needs of each patient.
Bell’s Palsy (Facial Paralysis)
Bell's Palsy manifests as temporary paralysis or weakness of facial muscles, causing drooping and asymmetry. Botox can help by relaxing the unaffected muscles to balance facial appearance or reducing spasm-related discomfort in some cases, facilitating faster recovery and improved aesthetics.
Thyroid Eye Disease (Graves’ Orbitopathy)
In autoimmune conditions like Graves’ disease, patients often experience bulging eyes and eyelid retraction. Botox injections relax the eyelid muscles, helping to reduce protrusion and retraction, thereby improving eyelid function and facial harmony.
Neck Spasms (Cervical Dystonia)
Causes such as neurological disorders or trauma can lead to painful neck muscle spasms. Botox injections near the neck help decrease these spasms, reducing pain and improving mobility. The treatment is often combined with physical therapy for optimal results.
Arrhythmias (Irregular Heartbeat)
Emerging research suggests that Botox may have a role in preventing arrhythmias during certain cardiac surgeries, although this application is still under clinical investigation. If proven effective, it could offer a novel approach to managing dangerous heart rhythm disturbances.
When considering Botox for medical purposes, selecting an experienced and qualified healthcare provider is essential. A board-certified dermatologist, neurologist, or specialist with extensive experience in therapeutic Botox applications will ensure safe and effective treatment. Proper injection techniques minimize risks such as eyelid drooping, facial asymmetry, or unintended muscle relaxation. Patients should discuss their specific conditions, expectations, and potential side effects thoroughly with their provider.
In conclusion, Botox is a versatile medical tool that extends far beyond cosmetic enhancements. Its ability to manage a variety of neurological, muscular, and glandular conditions makes it an invaluable treatment option. As research continues, the scope of Botox applications is likely to expand further, offering relief to millions suffering from diverse health issues. If you're contemplating Botox treatment for a medical condition, consult a qualified healthcare professional to explore whether this innovative therapy suits your needs and to ensure optimal outcomes.