Comprehensive Guide to Medical Botox: Therapeutic Uses, Benefits, and Cost Insights
Botox, or botulinum toxin, has expanded beyond cosmetics into a vital medical tool for treating various health conditions. This comprehensive guide explores its primary medical uses such as migraines, muscle spasms, hyperhidrosis, and more, including treatment costs and benefits. Learn how Botox improves quality of life for many patients through targeted, effective interventions. Understand the mechanisms, procedures, and latest research developments behind this versatile neurotoxin, making it an essential component of modern medicine.
Medical Applications and Advantages of Botox
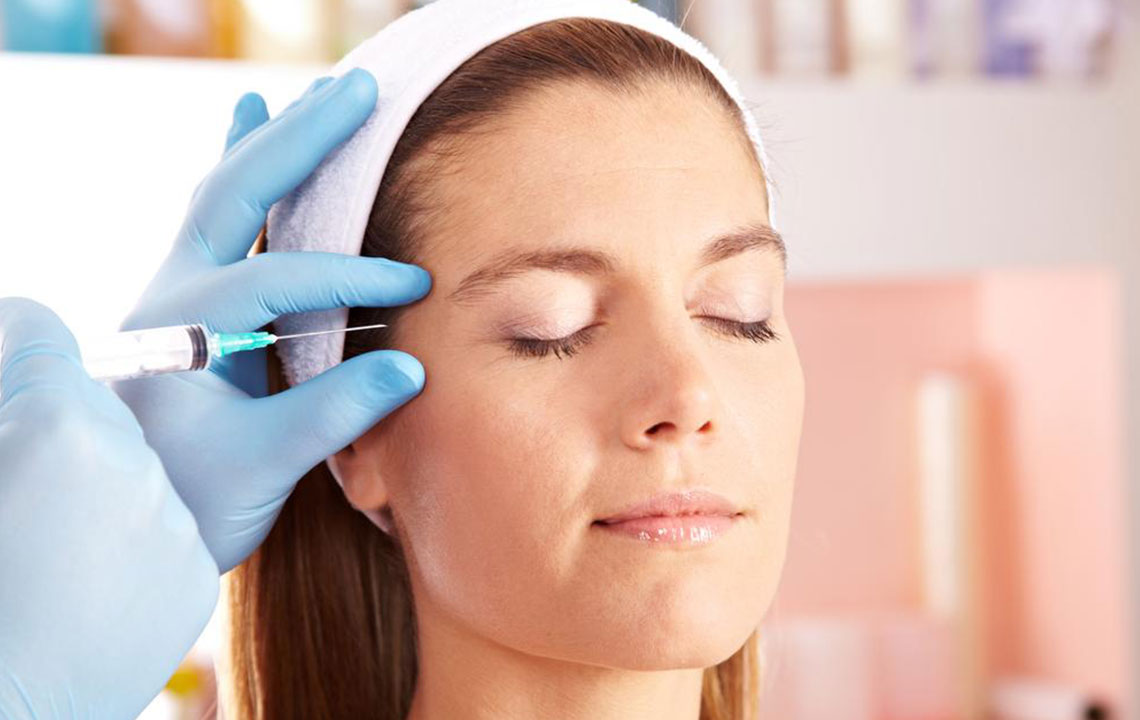
Botulinum toxin, widely known by its trade name Botox, has revolutionized both cosmetic and medical treatments since its discovery. While initially famous for its wrinkle-reducing properties, Botox has gained substantial recognition in the medical field for its ability to alleviate a variety of health conditions. Its function hinges on blocking nerve signals to muscles, which prevents unwanted muscle contractions. This mechanism provides relief in medical scenarios that involve muscle overactivity or nerve-related issues.
Despite its potency as a neurotoxin, when administered in controlled doses, Botox offers remarkable therapeutic benefits with minimal side effects. The versatility of Botox in medicine is evident through its expanding list of approved and experimental uses. The cost of treatment varies widely depending on the specific condition being addressed, the dosage required, and the formulation used. Several formulations like Dysport, Xeomin, and Myobloc are available to cater to different medical needs, each with its own dosing and pricing structure.
Below, we take an in-depth look at the primary medical uses of Botox, analyzing their effectiveness, procedures involved, and typical costs associated with each application:
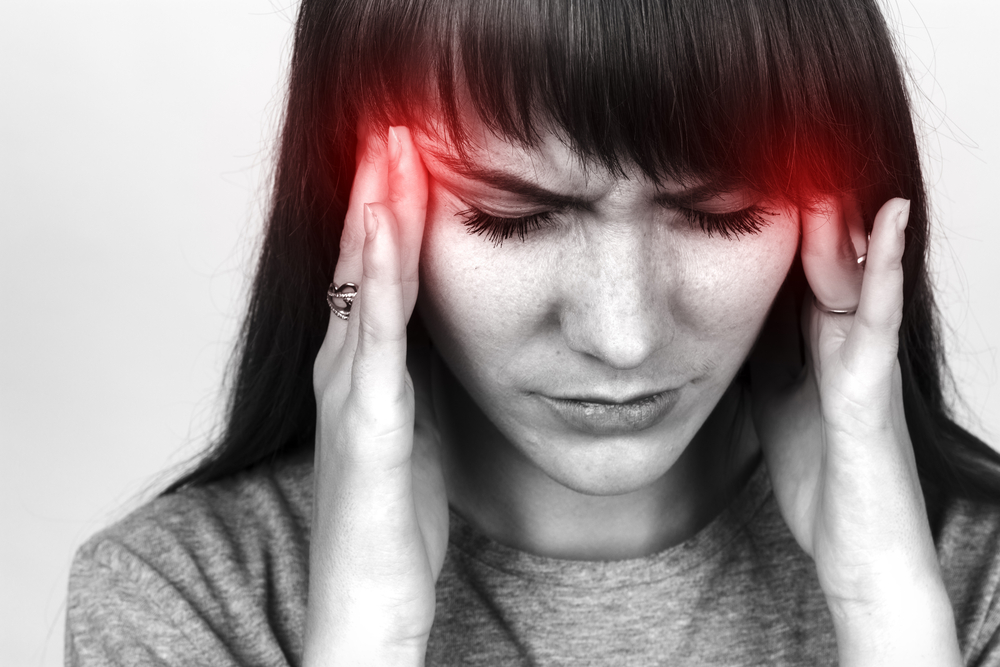
Chronic Migraines: One of the earliest FDA-approved uses of Botox, it effectively reduces the frequency and severity of migraines. Patients typically receive multiple injections around the scalp and neck, which can significantly improve quality of life. The average cost for treating chronic migraines with Botox is approximately $525 for each 100-unit vial, with multiple vials often needed in a treatment session. This procedure requires a trained healthcare provider to administer injections at specific trigger points, usually every 12 weeks.
Neck Muscle Spasms (Cervical Dystonia): Botox offers relief for patients suffering from cervical dystonia, a painful condition characterized by involuntary neck muscle contractions. The treatment involves precise injections into the affected muscles, with costs varying based on the number of units required. The procedure is quick, usually completed within minutes, and provides relief that can last for several months.
Hyperhidrosis (Excessive Sweating): FDA-approved Botox treatment for severe underarm sweating (axillary hyperhidrosis) can also be applied to other areas such as palms, soles, and face. The treatment involves injecting small amounts directly into the sweat glands. The typical cost for hyperhidrosis treatment is around $1200, especially in severe cases where conservative measures are insufficient. The effects are long-lasting, generally providing relief for 6 to 12 months.
Overactive Bladder: In cases of urinary incontinence caused by overactive bladder, Botox can relax bladder muscles, reducing leakage episodes. The procedure involves cystoscopic injections into the bladder wall and requires careful patient selection. The costs and potential side effects vary among patients, and the procedure should be performed by specialized urologists. Benefits include improved quality of life, but caution is necessary due to possible side effects such as urinary retention.
Depression and Mood Disorders: Emerging research indicates that Botox may have a role in psychological health by relaxing facial muscles associated with negative expressions, which can influence mood. Although not yet FDA-approved for treating depression, some studies suggest Botox treatments can improve depressive symptoms, especially in patients unresponsive to traditional antidepressants.
Premature Ejaculation: Current clinical trials explore Botox's capability to help delay ejaculation by relaxing perineal muscles. The ongoing studies aim to establish safety, efficacy, and optimal dosing strategies, potentially offering a new avenue for treating this common issue.
Strabismus (Crossed Eyes): Botox has long been used to correct eye misalignments by weakening overactive eye muscles. The treatment involves precise injections into the affected muscles, typically costing around $300. The procedure is quick, with minimal recovery time, and often provides both functional and cosmetic improvement.
In summary, Botox has become an invaluable tool in the medical field, addressing a broad spectrum of health conditions that significantly impact patients' quality of life. With ongoing research and expanding applications, Botox's role in therapeutics continues to grow, offering hope to many suffering from chronic and debilitating conditions.