Comprehensive Approaches to Managing and Treating Knee Discomfort for Better Joint Health
Discover comprehensive strategies to manage and treat knee discomfort effectively. This detailed guide covers causes, diagnosis, and modern treatment options, including physiotherapy, medications, minimally invasive surgeries, and regenerative therapies. Ensuring proper care can help restore joint function, reduce pain, and improve quality of life for those suffering from knee issues.
In-Depth Guide to Understanding Knee Discomfort and Exploring Effective Treatment Strategies
Knee discomfort is one of the most common issues affecting millions worldwide. It can impact daily life significantly, limiting mobility and causing persistent pain. The knee joint, being one of the most complex and weight-bearing joints in the human body, is susceptible to various injuries and degenerative conditions. Understanding the root causes and exploring comprehensive treatment options are essential steps toward alleviating discomfort and restoring function. This article provides an extensive overview of knee pain, its causes, diagnosis methods, and popular treatment strategies, including emerging innovations in orthopedic medicine.
Knee discomfort manifests through symptoms like swelling, stiffness, tenderness, and persistent ache that can vary in intensity. For many, the problem is a result of injuries sustained during physical activities such as sports, falls, or accidents. Others develop chronic issues due to aging, repetitive stress, or underlying health conditions such as osteoarthritis or gout. As we age, cartilage, the cushioning tissue in the joint, begins to break down, leading to increased friction and pain. Excess weight adds additional stress to the knee joints, accelerating wear and tear, especially in individuals over 50. The complexity of the knee, with its ligaments, tendons, and blood vessels, makes it vulnerable to various types of injuries—ranging from minor strains to severe ligament tears or cartilage damage.
Every individual's experience with knee pain is unique, influenced by the cause, severity, and underlying health factors. Common causes include traumatic injuries like ligament tears, meniscus injuries, fractures, or dislocations. Repeated movements such as running or heavy lifting can result in overuse injuries, leading to conditions such as tendinitis or bursitis. Additionally, degenerative diseases like osteoarthritis cause gradual deterioration of cartilage, resulting in persistent pain and stiffness. Nerve or blood vessel damage can complicate the condition, requiring comprehensive evaluation. Because knees support our entire body weight during movement and activity, any compromise to their structure or function can significantly impair mobility and quality of life.
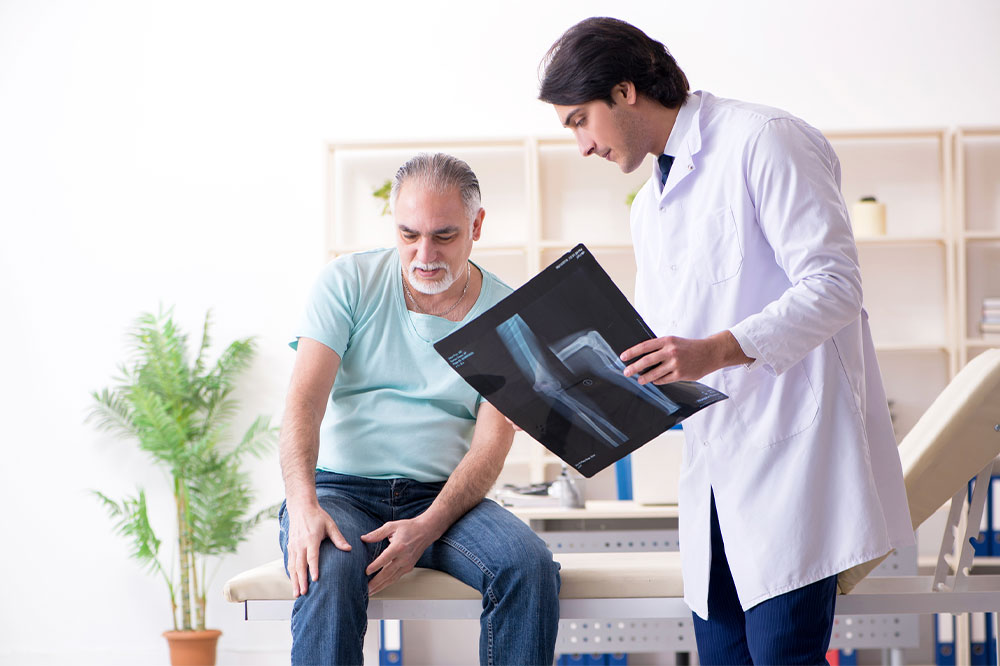
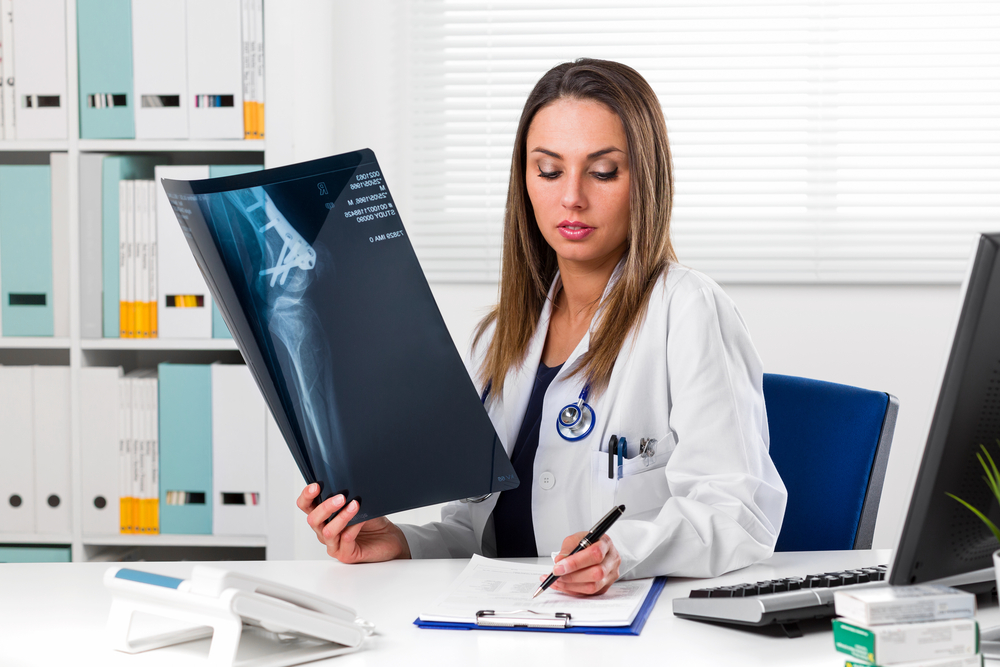
Proper diagnosis is crucial for effective treatment. Medical assessments often include physical exams to evaluate strength, stability, and range of motion, complemented by imaging tests like X-rays, MRI scans, or ultrasound to visualize internal structures. Functional assessments help determine the extent of impairment and plan appropriate interventions. Treatment options vary based on the specific diagnosis, injury severity, and patient health status. Treatment strategies encompass conservative methods, minimally invasive procedures, and surgical options, tailored to target the root cause of knee discomfort and restore joint function effectively.
Conservative treatments are typically the first line of defense and include:
Exercise and Physical Therapy: Strengthening exercises for surrounding muscles, such as quadriceps and hamstrings, improve joint stability and reduce pain. Therapists may suggest stretching routines and low-impact activities like swimming or cycling to enhance mobility and prevent stiffness.
Ice and Heat Therapy: Applying ice packs helps reduce inflammation and numb pain, especially post-injury or after activity. Heat pads promote relaxation of muscles and can ease chronic stiffness.
Medications: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), analgesics, and corticosteroid injections are often used to control pain and swelling in the short term.
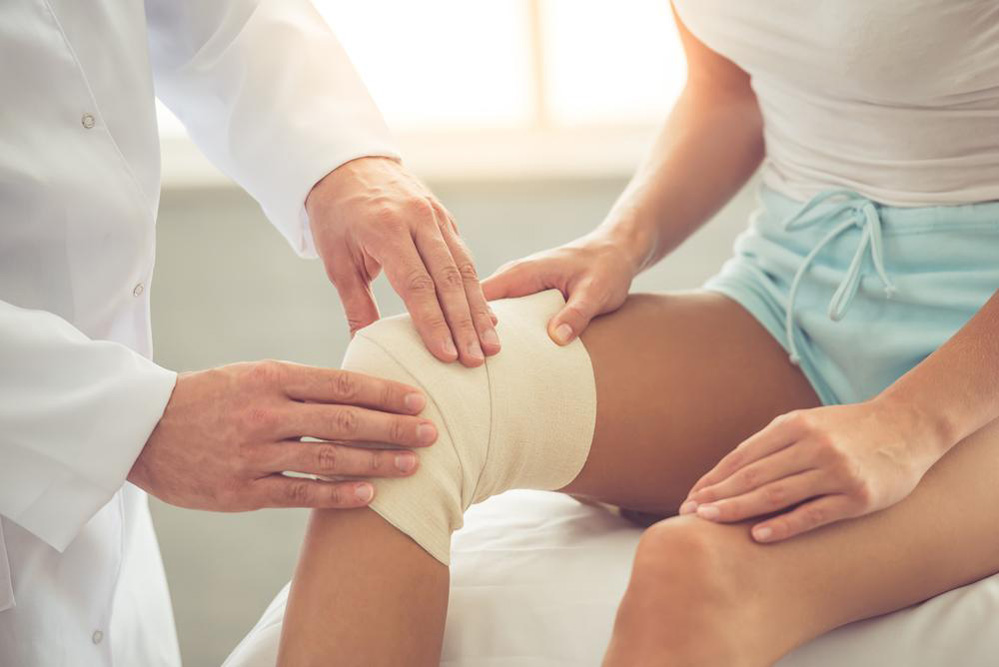
Assistive Devices: Braces, orthotic inserts, and walking aids can alleviate pressure on the knee, improve alignment, and support recovery.
For cases where conservative measures are insufficient, additional interventions may be necessary. These include:
Injections: Corticosteroid injections provide rapid relief from inflammation. Hyaluronic acid injections can lubricate the joint, easing movement.
Surgical Procedures: When pain persists or structural damage is severe, surgical options are considered. Arthroscopy—a minimally invasive procedure—allows surgeons to remove or repair damaged tissue, cartilage, or menisci. Osteotomy involves altering bone alignment to decrease pressure on damaged areas, improving joint function.
Joint Replacement: For end-stage osteoarthritis or irreparable damage, total or partial knee replacement surgery may be recommended. This involves replacing damaged joint surfaces with prosthetic components designed to restore mobility and alleviate pain.
Advances in orthopedic technology have revolutionized knee injury treatment. Innovations like cartilage regeneration therapies aim to delay or prevent the need for joint replacement by stimulating the growth of new cartilage tissues. Stem cell therapies and platelet-rich plasma (PRP) injections are gaining popularity for their potential to promote healing and reduce inflammation. Moreover, minimally invasive surgeries today offer quicker recoveries and fewer complications compared to traditional open surgeries.
In conclusion, managing knee discomfort requires an accurate diagnosis and a personalized treatment plan. From conservative measures like physical therapy and medications to surgical interventions and regenerative medicine, numerous options exist to address the root causes of knee pain. As research progresses, emerging therapies promise to improve patient outcomes, reduce recovery times, and enhance joint longevity. If you experience persistent knee pain or swelling, consulting a healthcare professional promptly ensures timely management and a return to active, pain-free living.