Comprehensive Guide to Preventing and Managing Rheumatoid Arthritis Effectively
This comprehensive guide explores effective strategies to prevent and manage rheumatoid arthritis through lifestyle changes, diet, relaxation, and environmental awareness. It emphasizes the importance of tailored exercise routines, anti-inflammatory diets, stress relief techniques, and minimizing exposure to environmental toxins to improve joint health and reduce symptoms. Empowering individuals with knowledge and practical steps, this article provides valuable insights into maintaining a better quality of life despite RA challenges.
Comprehensive Strategies for Rheumatoid Arthritis Prevention and Management
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic autoimmune disease that seriously impacts joint health and overall well-being. It is characterized by persistent joint pain, swelling, stiffness, and decreased mobility, affecting millions globally. Although the exact cause of RA remains elusive, scientific research identifies a combination of genetic predispositions, environmental factors, and hormonal influences as key contributors to its development. Some individuals may experience fleeting symptoms, while others face long-term joint degeneration and disability. Hence, understanding effective methods to prevent or manage this condition is vital for maintaining a good quality of life.
In this extensive guide, we delve into proven strategies designed to help reduce the risk, alleviate symptoms, and improve joint health in those affected by RA. From lifestyle modifications such as regular exercise and diet changes to relaxation methods and environmental awareness, these comprehensive approaches are aimed at empowering individuals to take control of their health.
Adopt a Consistent Physical Activity Routine to Support Joint Health
Engaging in regular, gentle exercise is one of the most pivotal steps in managing rheumatoid arthritis. Physical activity strengthens the muscles surrounding the joints, providing better support and reducing undue strain that can exacerbate symptoms. Exercise also enhances flexibility, improves circulation, and promotes joint lubrication, which collectively contribute to decreased stiffness and pain.
Before initiating a new exercise program, consult with your healthcare provider or a physical therapist to develop a tailored plan suitable for your condition. Recommended activities include walking, swimming, and cycling, all of which are low-impact and joint-friendly. Incorporate stretching exercises to improve mobility and reduce stiffness, performing these routines consistently to achieve optimal benefits. Remember, gradual progression is key; avoid overexertion that might cause flare-ups or injuries.
The Power of Relaxation Techniques in Managing RA Symptoms
Stress is a well-known trigger that can amplify inflammation and intensify joint discomfort in rheumatoid arthritis sufferers. Incorporating relaxation practices into your daily routine can significantly alleviate these effects. Techniques such as guided imagery, progressive muscle relaxation, deep breathing exercises, and meditation help calm the nervous system and lower cortisol levels, which are associated with reduced inflammation.
Specific practices like yoga and tai chi are particularly advantageous as they combine gentle movement, stretching, and mindfulness. Yoga improves flexibility and reduces stress, while tai chi’s slow, flowing movements enhance balance, coordination, and mental health. Ensure to learn these techniques from qualified instructors to maximize their benefits and avoid movements that may trigger pain.
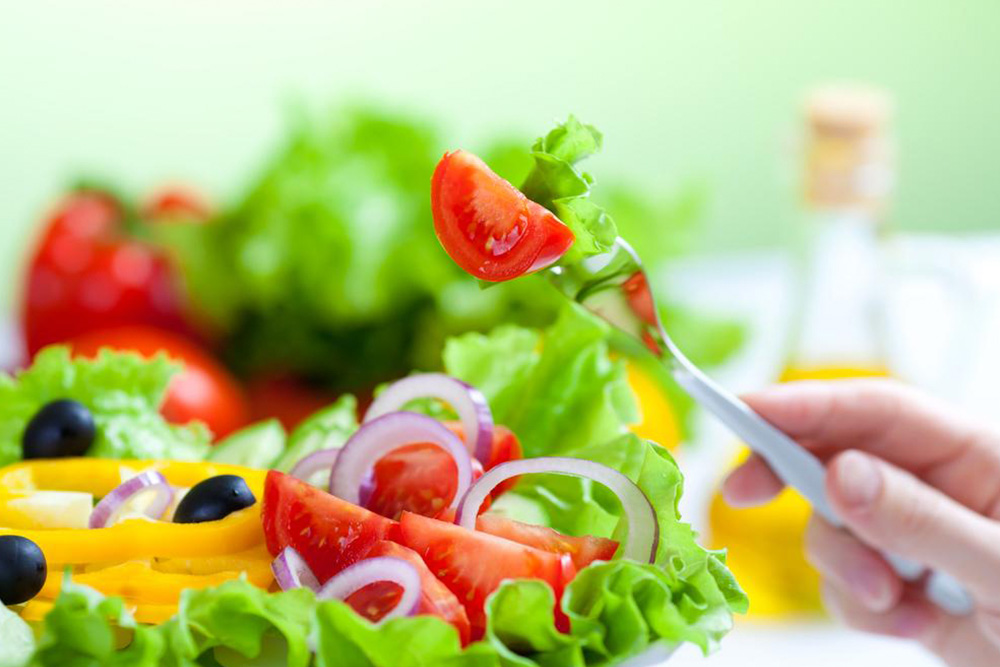
Implement an Anti-Inflammatory Diet to Reduce Joint Inflammation
Diet plays a crucial role in managing rheumatoid arthritis. Consuming foods rich in anti-inflammatory properties can help diminish joint inflammation and pain. Omega-3 fatty acids, found abundantly in fatty fish such as salmon, mackerel, and sardines, are especially effective in reducing inflammatory markers.
In addition to omega-3s, incorporate a variety of fruits and vegetables like walnuts, strawberries, oranges, kale, and spinach, which are high in antioxidants and phytochemicals that combat oxidative stress and inflammation. Low-fat dairy products such as yogurt and milk are also beneficial for joint health by providing essential nutrients without adding excess saturated fats.
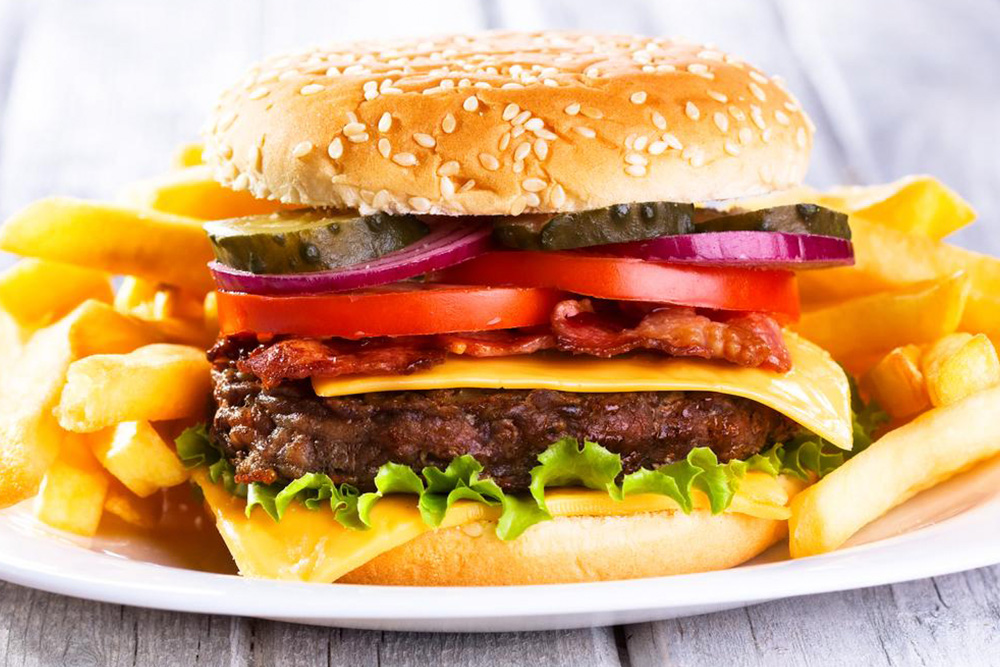
Finally, avoid foods that could worsen inflammation, such as processed foods, fried foods, and red meats, which tend to promote inflammatory responses and metabolic disturbances.
Minimize Exposure to Environmental Pollutants and Toxins
Environmental toxins are increasingly recognized as potential triggers or accelerators of rheumatoid arthritis in genetically susceptible individuals. Industrial chemicals, cleaning agents, pesticides, and airborne pollutants can provoke immune responses that worsen RA symptoms.
To mitigate these risks, it is advisable to minimize exposure by choosing organic and chemical-free products when possible, ensuring proper ventilation in indoor environments, and using protective gear during activities involving chemicals. Healthcare professionals recommend reducing contact with such toxins in daily life to help manage and prevent disease progression.
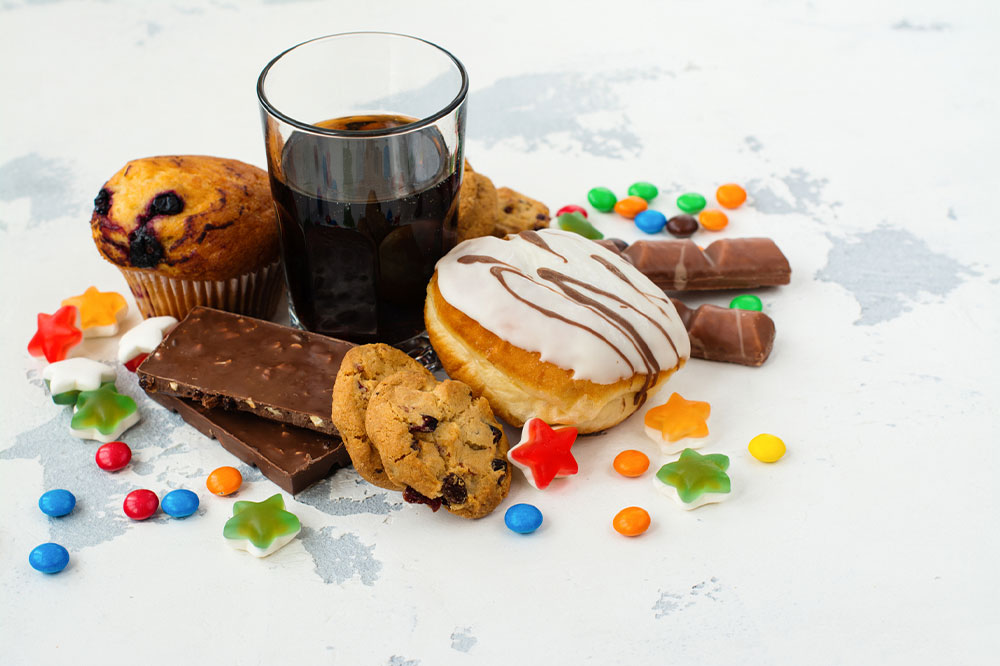
Foods and Substances That Can Exacerbate RA Symptoms
Dietary choices significantly influence the severity of rheumatoid arthritis symptoms. Certain foods have been linked to heightened inflammation and discomfort in affected individuals, and limiting or avoiding these can lead to noticeable improvements.
Red Meat: Rich in saturated fats and omega-6 fatty acids, which can promote inflammatory pathways in the body. Reducing intake may alleviate joint swelling and pain.
Fried and Fast Foods: Contain trans fats and unhealthy oils that exacerbate inflammation and contribute to weight gain, placing additional stress on joints.
Processed Foods and Sugars: Often loaded with refined carbs, artificial additives, and preservatives, these foods can trigger inflammatory reactions.
Gluten: For some individuals, wheat, barley, and rye might increase systemic inflammation, especially in those with celiac disease or gluten sensitivity.
Adopting a diet that emphasizes whole, unprocessed foods and minimizes these inflammatory foods can substantially improve symptom control and overall health in people with RA.
In summary, effective management of rheumatoid arthritis hinges on a multifaceted approach that combines physical activity, dietary modifications, relaxation techniques, and environmental awareness. Staying informed and proactive allows those affected to regain control over their health and potentially slow disease progression, leading to a more comfortable and active life.





