Comprehensive Guide to Fibromyalgia: Causes, Effective Management Strategies, and Prevention Tips
Fibromyalgia is a chronic condition characterized by widespread pain, fatigue, and sensitivity. This comprehensive guide explores its causes, symptoms, management strategies, and prevention tips. Learn how lifestyle changes, effective stress management, and proper sleep hygiene can help control symptoms and improve quality of life. Although no cure exists, understanding fibromyalgia empowers sufferers to lead healthier, more manageable lives through proactive care and support.

Comprehensive Guide to Fibromyalgia: Causes, Effective Management Strategies, and Prevention Tips
Fibromyalgia is a complex and often misunderstood chronic health condition characterized by widespread musculoskeletal pain, persistent fatigue, and heightened sensitivity to stimuli. This disorder impacts various facets of an individual's life, including physical health, emotional stability, and social interactions. Despite its prevalence, the precise origins of fibromyalgia remain elusive, making diagnosis a challenging process that primarily relies on eliminating other possible conditions. This article aims to provide a detailed understanding of fibromyalgia, exploring its causes, symptoms, effective management methods, and practical prevention strategies to improve quality of life for those affected.
What Is Fibromyalgia?
Fibromyalgia is a long-term disorder distinguished by persistent muscle and bone pain, tenderness, sleep disturbances, and fatigue. It primarily affects soft tissues, especially muscles, ligaments, and tendons. Historically known as fibrositis, a term used to describe inflammation of fibrous tissues, the condition was renamed in 1976 to better reflect its core association with musculoskeletal pain and tissue fibrosis. Unlike injuries or inflammatory diseases, fibromyalgia does not cause visible damage or irreversible tissue destruction, which often leads to confusion and misconceptions about its severity.
Signs, Symptoms, and Impact of Fibromyalgia
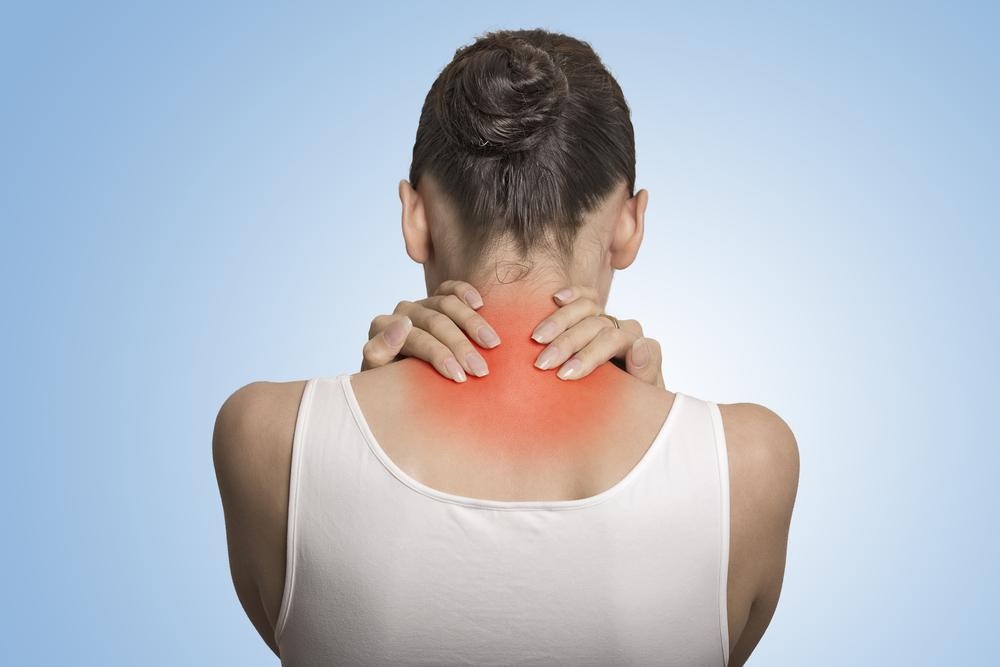
The hallmark symptoms of fibromyalgia include widespread pain affecting the entire body, often described as a constant dull ache, along with episodes of sharp or burning sensations. Patients frequently experience morning stiffness, sleep disturbances, headaches, and cognitive difficulties often referred to as “fibro fog,” which impairs concentration and memory. Fatigue is pervasive, reducing the ability to perform daily activities and participate in social or professional life. The condition also influences emotional health, leading to conditions such as anxiety and depression. Importantly, fibromyalgia does not damage joints, muscles, or tissues and is not considered life-threatening. However, its symptoms can be debilitating, and the chronic nature of the disorder requires widespread awareness, understanding, and ongoing management.
Diagnosis and Misconceptions
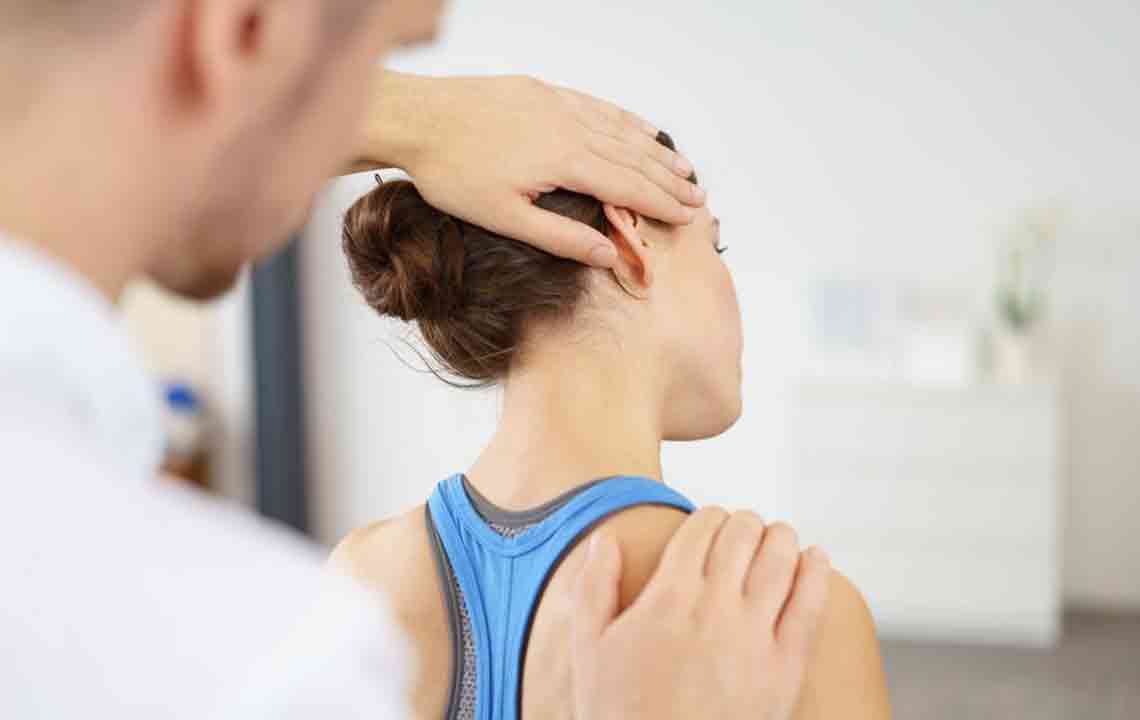
Diagnosing fibromyalgia can be complex because its symptoms overlap with many other conditions, including rheumatoid arthritis, lupus, and chronic fatigue syndrome. Healthcare providers typically rely on symptom assessment, physical examinations, and exclusion of other diseases through blood tests and imaging. The subjective nature of pain and fatigue makes objective diagnosis difficult, leading to frustration among patients. Awareness campaigns and physician education are crucial for early detection and appropriate management.
Can Fibromyalgia Be Prevented?
Although fibromyalgia itself cannot be entirely prevented, certain lifestyle practices can help reduce frequency and severity of flare-ups. The goal is to strengthen the body's resilience, manage symptoms proactively, and improve overall quality of life. Here are some evidence-based strategies:
Improve Sleep Hygiene
Sleep disturbances are both symptoms and triggers of fibromyalgia symptoms. Poor sleep quality can heighten pain sensitivity and fatigue, creating a vicious cycle. Establishing a consistent sleep schedule, avoiding screens at least an hour before bed, and engaging in relaxing activities such as reading, meditation, or gentle stretches can significantly improve sleep quality. Healthcare providers may prescribe sleep aids or recommend cognitive behavioral therapy for insomnia (CBT-I) if sleep issues persist.
Manage Stress Effectively
Stress is a common exacerbating factor in fibromyalgia. Identifying and reducing stressors—whether through resolving interpersonal issues or avoiding high-stress environments—can make a significant difference. Relaxation techniques such as mindfulness meditation, deep breathing exercises, progressive muscle relaxation, and yoga are effective tools to lower stress levels. Regular, moderate physical activity like walking, swimming, or tai chi not only eases stress but also enhances muscle strength and reduces pain sensitivity.
Adopt a Healthy, Balanced Diet
Prioritizing nutritious foods rich in antioxidants, omega-3 fatty acids, and anti-inflammatory compounds can support overall health and potentially reduce symptoms. Reducing processed foods, sugar, caffeine, and alcohol may also improve sleep and energy levels.
Engage in Regular Physical Activity
Maintaining an appropriate exercise routine tailored to individual tolerance is vital. Low-impact activities such as swimming, cycling, or guided stretching can improve muscle flexibility, decrease pain, and boost mental health. It’s important to start slowly and gradually increase activity, avoiding overexertion which can trigger flare-ups.
Seek Support and Education
Connecting with support groups and educational resources empowers individuals with fibromyalgia. Sharing experiences and strategies can foster emotional resilience and motivate adherence to management plans. Consulting healthcare professionals regularly ensures personalized adjustments to treatment strategies.
In sum, fibromyalgia remains a complex disorder with no known cure, but a comprehensive approach involving lifestyle modifications, medical management, and emotional support can significantly enhance quality of life. Awareness and understanding are key to dispelling misconceptions and ensuring affected individuals receive the care and compassion they need.