Comprehensive Guide to Uterine Cancer: Causes, Symptoms, and Modern Treatment Approaches
This comprehensive guide offers detailed insights into uterine cancer, covering its causes, symptoms, risk factors, diagnostic procedures, and modern treatment options such as surgery, radiation, chemotherapy, and immunotherapy. It emphasizes early detection, preventive measures, and lifestyle choices to reduce risk and improve prognosis. Designed for women and healthcare providers, this article aims to enhance awareness and understanding of uterine cancer for better health outcomes.

Comprehensive Guide to Uterine Cancer: Causes, Symptoms, and Modern Treatment Approaches
Uterine cancer, also known as endometrial cancer, arises from the lining of the uterus and is one of the most common gynecologic cancers worldwide. It affects women predominantly in their postmenopausal years but can occur at younger ages. Understanding the intricate details about its causes, symptoms, risk factors, and evolving treatment options is essential for early detection and effective management. This comprehensive guide aims to provide in-depth information on uterine cancer to empower women and healthcare providers alike.
Globally, uterine cancer accounts for a significant number of cancer-related deaths among women, with approximately 97,370 fatalities recorded in 2020 alone. Despite its seriousness, the prognosis for early-stage uterine cancer is relatively favorable, with a five-year survival rate reaching approximately 81%. This highlights the importance of recognizing early signs and seeking prompt medical attention. Advances in medical research and treatment modalities continue to improve survival rates and quality of life for patients diagnosed with this disease.
Understanding the root causes of uterine cancer involves examining genetic, hormonal, and lifestyle factors. Elevated exposure to estrogen without adequate progesterone regulation plays a crucial role in the development of endometrial cancer. Other contributing factors include obesity, high blood pressure (hypertension), diabetes, a history of personal or family cancer, and conditions like polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS). Additionally, certain lifestyle choices like a sedentary lifestyle and poor diet can increase the risk.
Recognizing symptoms early can significantly influence treatment outcomes. Common signs include abnormal uterine bleeding, especially in postmenopausal women, irregular bleeding between periods, pelvic discomfort, unusual vaginal discharge, and heavy menstrual bleeding. Women over 40 should remain vigilant and report any abnormal symptoms to their healthcare provider promptly. Noticing these early warning signs can facilitate timely diagnosis and intervention, improving long-term prognosis.
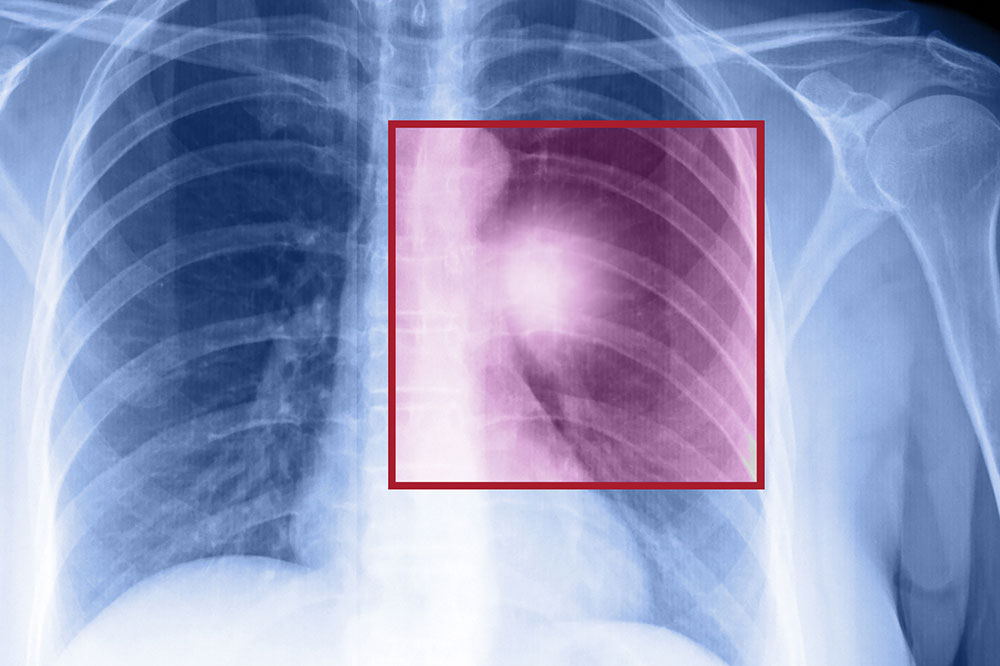
Staging of uterine cancer is vital to determine the extent of disease spread and inform treatment decisions. The staging system ranges from Stage 1, where cancer is confined to the lining of the uterus, to Stage 4, indicating spread to distant organs such as the lungs or liver. Specifically, Stage 1 is further divided into sub-stages based on the depth of invasion, while Stage 2 involves the cervix. Advanced stages often require more aggressive treatment approaches, including combined therapies.
Modern treatment options for uterine cancer are diverse and tailored to each patient's specific stage and overall health. Surgical interventions form the cornerstone of treatment, with procedures such as abdominal hysterectomy—removal of the uterus through a traditional open approach—and minimally invasive options like laparoscopic or robotic-assisted hysterectomy. When the cancer affects adjacent structures, a radical hysterectomy may be performed, which involves removing the uterus, cervix, part of the vagina, and surrounding tissues.
Beyond surgery, non-surgical therapies have evolved considerably. Radiation therapy, including external beam radiation and brachytherapy, targets residual cancer cells within the pelvis. Chemotherapy, often involving drugs like paclitaxel and carboplatin, is employed especially in advanced or recurrent cases. Hormone therapy can be effective for tumors that express hormone receptors, while immunotherapy is emerging as a promising treatment in certain subtypes, harnessing the immune system to attack cancer cells.
Preventative strategies are crucial in reducing uterine cancer risk. Maintaining a healthy weight through balanced diet and regular physical activity can decrease estrogen levels associated with obesity. Managing comorbid conditions such as hypertension and diabetes further lowers risk. Regular screening, particularly for women with a family history of gynecologic cancers or other risk factors, enables early detection and improves outcomes. Women should also discuss preventive options like hormonal therapies with their healthcare providers.
In conclusion, uterine cancer remains a significant health concern, but advances in understanding its causes, symptoms, and treatments provide hope for improved management. Women are encouraged to stay informed, adopt healthy lifestyles, and seek prompt medical attention for any abnormal uterine symptoms. Through early detection and personalized treatment strategies, the prospects for women diagnosed with uterine cancer continue to improve, ensuring better health and quality of life.