Comprehensive Guide to Managing Persistent Bronchitis Coughs and Improving Lung Health
This comprehensive guide explores persistent bronchitis-related coughs, covering causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatments, home remedies, and prevention strategies. Emphasizing lifestyle modifications and medical care, it aims to improve lung health and reduce complications. Ideal for those suffering from chronic bronchitis, it provides practical advice for managing symptoms and preventing disease progression, focusing on healthy habits, dietary tips, and infection control to support overall respiratory well-being.
Comprehensive Guide to Managing Persistent Bronchitis Coughs and Improving Lung Health
Bronchitis is a common respiratory condition characterized by inflammation of the bronchial tubes—the passages that carry air to and from your lungs. This inflammation results in symptoms such as coughing, mucus production, fatigue, and breathing difficulties. Understanding the nature of bronchitis, especially the differences between acute and chronic forms, is essential for effective management and prevention. Persistent bronchitis-related coughs, often associated with chronic bronchitis, require ongoing treatment, lifestyle adjustments, and preventive measures to improve quality of life and reduce complications.
In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment options, lifestyle modifications, home remedies, and preventive strategies related to bronchitis. Whether you’re dealing with an acute episode or battling a persistent cough, gaining insight into this condition can empower you to take proactive steps toward better respiratory health.
Understanding the Types and Causes of Bronchitis
Acute bronchitis typically develops quickly and is often caused by viral infections similar to those responsible for colds and flu. It usually resolves within a few weeks with appropriate care. Bacterial infections, although less common, can also be a cause and may require antibiotics.
Chronic bronchitis is a long-term condition characterized by a productive cough lasting at least three months per year for two consecutive years. It is predominantly linked to smoking, exposure to air pollution, occupational hazards, and long-term inhalation of toxic gases. This form of bronchitis is a key component of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) and can significantly impair lung function.
Both forms share common symptoms but differ in duration, severity, and underlying causes. Recognizing these differences is fundamental for appropriate management.
Symptoms of Bronchitis
Persistent cough with mucus production
Shortness of breath, especially during physical activity
Chest discomfort or tightness
Fatigue and weakness
Mild fever or chills in some cases
Wheezing and respiratory irritation
In chronic bronchitis, these symptoms tend to persist and may worsen over time, leading to decreased lung capacity and impaired breathing.
Diagnosing Bronchitis
Initial diagnosis involves reviewing medical history and conducting a physical exam, listening to the lungs with a stethoscope for abnormal sounds like wheezing or crackles.
Imaging techniques such as chest X-rays are crucial to rule out other conditions like pneumonia or lung cancer and to evaluate lung health.
Sputum analysis can identify infectious agents or inflammatory markers.
Pulmonary function tests (spirometry) measure airflow and lung capacity, helping distinguish between bronchitis and other respiratory diseases.
Accurate diagnosis paves the way for effective treatment strategies tailored to the specific type and severity of bronchitis.
Conventional and Lifestyle Treatments for Bronchitis
Management of bronchitis typically involves medications such as bronchodilators, corticosteroids, and cough suppressants depending on severity.
For bacterial infections, antibiotics may be necessary, but they are ineffective against viral bronchitis.
Smoking cessation is critical in preventing and managing chronic bronchitis. Quitting smoking can slow disease progression and improve lung function.
Reducing exposure to irritants like fumes, dust, and pollutants is vital for symptom relief and preventing exacerbations.
Incorporating regular aerobic exercise can strengthen respiratory muscles and improve overall lung capacity.
This multifaceted approach combines medical treatment with lifestyle modifications to optimize respiratory health and reduce symptoms.
Effective Home Remedies to Ease Cough and Mucus in Chronic Bronchitis
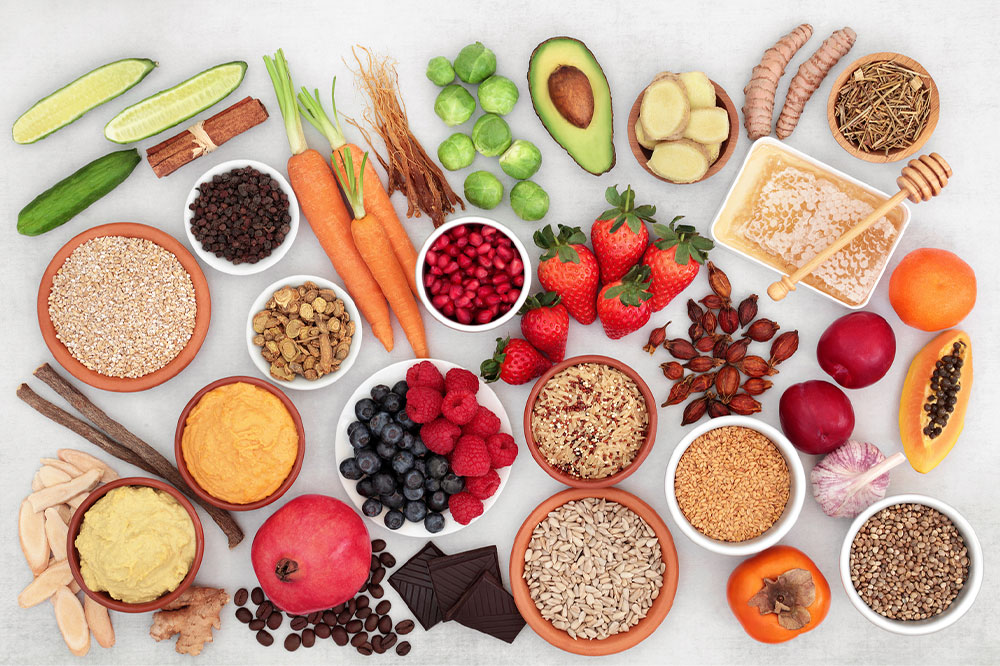
Dietary adjustments: Consuming foods high in probiotics and anti-inflammatory nutrients supports immune health and reduces mucus buildup. Incorporate fresh fruits like oranges, strawberries, kiwis, and vegetables such as kale and bell peppers into your diet.
Avoid mucus-promoting foods: Minimize intake of processed sugar, fried foods, and dairy products, which can increase mucus production.
Hydration: Drinking plenty of water, herbal teas, and warm broths helps thin mucus, making it easier to clear from the lungs.
Natural remedies: Ginger tea, honey, and steam inhalation can soothe irritated airways and reduce coughing.
Rest and stress management: Adequate rest and stress reduction techniques enhance immune function and promote faster recovery.
These home strategies complement medical treatment, relieving discomfort and supporting respiratory health.
Prevention Strategies for Chronic Bronchitis
While it may not be possible to prevent all cases of bronchitis, particularly those caused by infections, adopting healthy lifestyle habits reduces risk significantly.
Quit smoking: The most effective way to prevent chronic bronchitis is to stop smoking. Long-term abstinence can slow or halt disease progression.
Limit exposure to environmental pollutants, secondhand smoke, and occupational irritants.
Maintain good indoor air quality through proper ventilation and regular cleaning to reduce dust and allergen levels.
Engage in regular physical activity to enhance lung capacity and overall health.
Stay current with vaccines like influenza and pneumonia to prevent respiratory infections that can trigger bronchitis episodes.
By incorporating these preventive measures, individuals can lower their risk of developing chronic bronchitis and reduce the severity of symptoms if they do occur.
Preventing the Spread of Infection
Though chronic bronchitis itself is not contagious, infections causing acute bronchitis can spread easily.
Practice good hygiene: wash hands thoroughly and regularly with soap and water.
Avoid close contact with infected individuals, especially during cold and flu season.
Do not share personal items such as towels, utensils, or grooming tools.
Use masks and gloves when caring for or cleaning around someone exhibiting respiratory symptoms.
Cover mouth and nose when coughing or sneezing to prevent airborne transmission.
Disinfect surfaces regularly to kill germs and prevent crosstransmission.
Taking these precautions can help prevent the spread of infections that may worsen bronchitis symptoms or lead to other respiratory illnesses.





