Smart Ways to Save Money When Buying Hearing Aids: Your Complete Guide
This comprehensive guide offers practical tips and strategies to help individuals find affordable hearing aids. By reviewing insurance options, comparing prices online and in-store, choosing basic models, and exploring assistance programs, users can significantly reduce costs while securing effective hearing solutions. Emphasizing the importance of professional consultation and careful selection, the article aims to make hearing health accessible to all, highlighting how smart planning can make quality devices more affordable and less intimidating financially.

Hearing loss can significantly impact your quality of life, but the high cost of hearing aids often acts as a barrier for many people needing these essential devices. With prices sometimes reaching several thousand dollars, individuals are frequently reluctant or delayed in seeking assistance for their hearing health. However, by understanding the various options available and employing strategic purchasing approaches, you can find affordable hearing aid solutions that meet both your needs and your budget. This comprehensive guide covers practical tips, financial assistance programs, and strategies to help you secure cost-effective hearing aids without compromising quality or functionality.
Understanding the True Cost of Hearing Aids
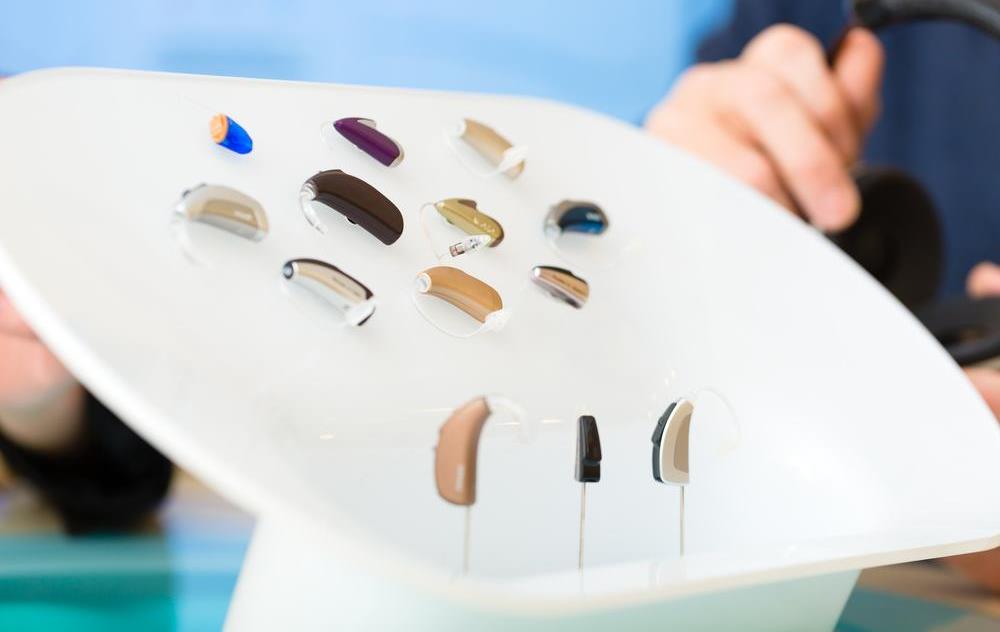
Before diving into specific savings strategies, it's essential to grasp why hearing aids are often expensive. The costs encompass various factors, such as advanced technology, custom fitting, professional consultations, ongoing maintenance, and batteries. Premium models with sophisticated features like Bluetooth connectivity, noise reduction, and rechargeable batteries tend to be pricier, but they may not always be necessary for every user.
Typically, basic hearing aids start at around $1,000 per device, with high-end models exceeding $5,000. The average price most consumers encounter hovers between $2,000 and $4,000 for a pair. The expense can be daunting, especially since Medicare and most private insurance plans offer limited coverage for these devices, if any. This financial challenge is why exploring cost-effective options and leveraging available resources is vital for many in need of hearing assistance.
Analyzing Your Insurance Coverage and Benefits
One of the first steps to reducing the financial burden is to review your insurance policies thoroughly. While traditional Medicare generally does not cover hearing aids, some private insurance plans, Medicaid programs, or specific employer-sponsored health plans may provide partial or full coverage. Families with federal employees, military personnel, or state-specific programs may also find tailored benefits for hearing health services.
If you have a health insurance plan that covers hearing aids, make sure to understand the coverage details, including the maximum amount covered, co-payments, and the list of approved vendors or providers. Often, insurance companies collaborate with particular audiologists or hearing aid stores, offering discounts or lower co-pays for services purchased through designated providers.
For those with flexible spending accounts (FSAs) or health savings accounts (HSAs), the good news is you can use pre-tax dollars to purchase hearing aids and related accessories like batteries and maintenance supplies. This approach effectively reduces the after-tax cost and makes acquiring hearing aids more affordable. Be sure to retain proper documentation and receipts, as these may be required for reimbursement or tax purposes.
Shopping for the Best Price: In-Person and Online Options
Price comparison is crucial when seeking budget-friendly hearing aids. Visiting multiple brick-and-mortar clinics allows you to experience different device styles, undergo professional hearing evaluations, and receive personalized recommendations. Many clinics provide free hearing tests, which can help identify the severity of your hearing loss and guide you toward suitable options.
In addition to physical stores, the online marketplace presents a significant opportunity for savings. Digital retailers often offer lower prices due to reduced overhead costs. Some reputable online vendors sell pre-programmed devices or hearing amplifiers starting as low as $100 to $500, making them accessible alternatives for mild hearing difficulties.
However, it's essential to exercise caution when purchasing from online sources. Many devices sold online are over-the-counter (OTC) hearing amplifiers rather than medical-grade hearing aids. Although cheaper, they may lack the advanced features or calibration necessary for effective hearing improvement. Consulting with an audiologist before purchasing online ensures you select devices suited to your specific hearing profile, which may sometimes involve additional costs for adjustments and fittings.
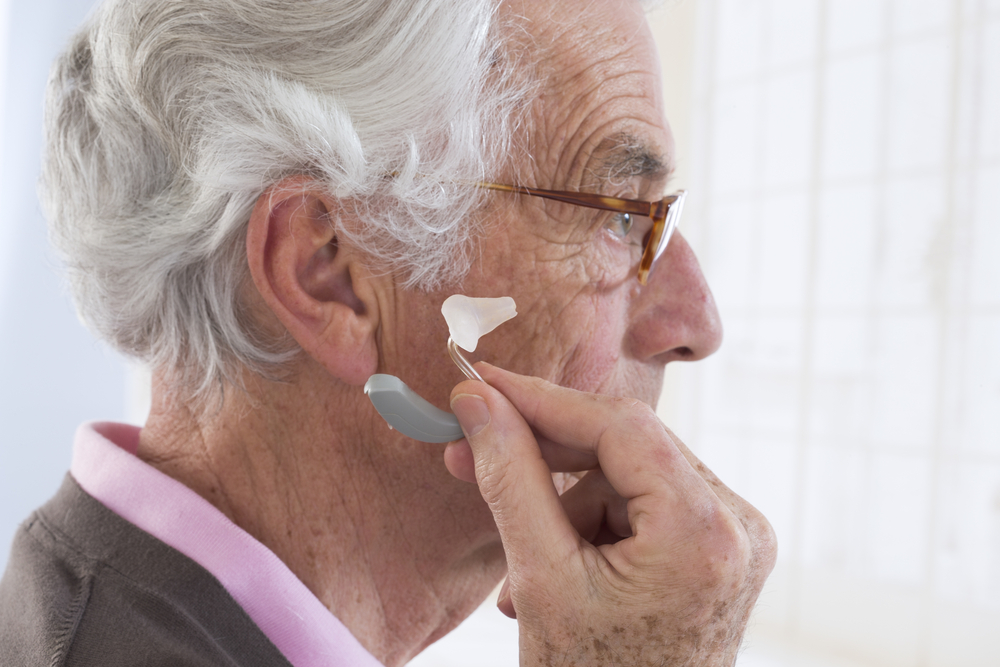
Furthermore, consider the possibility of secondhand or refurbished hearing aids. Some clinics or specialty stores might offer pre-owned devices that are fully functional and reprogrammed. Ensure these are inspected by professionals to verify their integrity and compatibility with your needs. Remember, while saving money is important, ensuring device reliability is crucial for effective hearing support and preventing further auditory health issues.
Choosing Basic Models and Avoiding Unnecessary Features
Hearing aids come with a variety of features that influence their price point. Many advanced features—such as Bluetooth connectivity, AI-powered noise reduction, rechargeable batteries, or smartphone app controls—are appealing but can significantly raise the cost. For many users, especially those with mild to moderate hearing loss, these extras might be unnecessary.
Consult your audiologist to determine which features are truly beneficial for your lifestyle. Opting for a basic, straightforward device that fulfills your hearing needs without added bells and whistles can lead to substantial savings. For instance, a simple behind-the-ear model without Bluetooth may suffice for basic amplification and clarity, providing excellent value for money.
Moreover, consider non-digital or analog models if your hearing loss is mild. Over-the-counter hearing amplifiers or personal sound amplification products (PSAPs) can be effective and affordable options, ranging from $50 to $300. These devices are often available without a prescription and can serve as interim solutions, but they are not a substitute for professionally fitted hearing aids when significant hearing issues are present.
Negotiation, Warranties, and Trial Periods
When purchasing hearing aids, always ask for detailed quotes that itemize the costs of the device, fitting, programming, and follow-up services. Negotiating directly with providers can sometimes result in reduced prices or the inclusion of free adjustments or extended warranties. Many clinics offer trial periods ranging from 30 to 60 days, allowing you to test the device and ensure it meets your expectations before committing fully.
Warranties are also an essential consideration. Reputable manufacturers typically provide coverage for repairs and replacements within a specified period, often 1-3 years. Prioritize models that come with comprehensive warranties and accessible customer support, as this can save you money on repairs and maintenance in the long run.
Exploring Financial Aid and Assistance Programs
Numerous government programs, nonprofit organizations, and charitable foundations aim to provide financial assistance for individuals needing hearing aids. For example, programs like the Federal Medicare Savings Program or state-specific Medicaid waivers may offer coverage or discounts based on income levels. Local agencies, community health centers, or veteran affairs offices might also have programs to subsidize costs for qualifying applicants.
Applying for these assistance programs typically requires proof of income and medical necessity. Demonstrating genuine financial hardship or disability can increase your chances of obtaining support. Keep in mind that eligibility criteria vary widely, so it's worth researching local resources and non-profit initiatives dedicated to hearing health.
The National Institute on Deafness and Other Communication Disorders (NIDCD) and other organizations frequently publish lists of resources and grants available for low-income individuals or seniors. These programs are vital avenues for reducing the financial burden and ensuring access to necessary hearing care.
Summary: Making Hearing Aids Affordable and Accessible
Although the high costs of hearing aids can pose significant challenges, proactive strategies can significantly reduce expenses. By thoroughly reviewing your insurance coverage, leveraging government and nonprofit aid, comparing prices at multiple vendors, and choosing suitable models without unnecessary features, you can secure quality hearing devices at a more affordable price. Remember to prioritize professional consultations to ensure the device matches your hearing needs, and explore options for secondhand or refurbished devices when appropriate.
Ultimately, the goal is to make hearing health accessible without financial stress. With careful planning and informed choices, everyone can enjoy better hearing without overspending.