Comprehensive Guide to Ozempic: Proper Dosage, Usage Tips, and Safety Considerations
This comprehensive guide covers essential information about Ozempic, including proper dosing regimens, administration tips, safety precautions, and when to consult your doctor. Designed for individuals managing type 2 diabetes, it emphasizes the importance of adherence to medical advice to optimize blood sugar control and minimize risks, offering clear instructions on injection techniques, timing, and dosage adjustments for safe, effective treatment with Ozempic.
Comprehensive Guide to Ozempic: Proper Dosage, Usage Tips, and Safety Considerations
Ozempic® has become a vital medication in managing type 2 diabetes, especially for patients who have not achieved satisfactory blood sugar control through traditional treatments. As a non-insulin injectable drug, Ozempic works by mimicking the body's natural hormones, specifically targeting pathways that influence blood glucose levels. Its ability to stimulate insulin production while suppressing glucagon makes it an effective choice for many patients. The medication is delivered via easy-to-use injection pens, and adhering to recommended dosage guidelines is essential for safety and effectiveness. This detailed guide aims to walk you through the proper use, dosing schedules, administration techniques, and precautions associated with Ozempic®, ensuring you maximize its benefits while minimizing potential risks.
Ozempic® is classified as a GLP-1 receptor agonist, a medication designed to enhance the body's natural regulation of blood sugar. Understanding its dosing regimen is crucial for optimal results. Typically, treatment begins with a conservative dose of 0.25 mg administered once weekly for the first four weeks. This initial dose helps to gently stimulate insulin release and reduce glucagon secretion, aiding in blood sugar control without overwhelming the system. After this period, your healthcare provider may recommend increasing the dose to 0.5 mg weekly, based on your blood glucose response. If additional control is necessary, dosing can be further increased to 1 mg weekly, although doses exceeding this are rarely prescribed due to potential side effects and diminishing returns.
The timing of Ozempic® injections offers flexibility; patients can choose a consistent day each week for administration. It is advisable to select a specific day and stick to it to establish a routine. The timing in relation to meals is not critical, giving you the freedom to inject at any convenient time. If you miss a weekly dose, you can take it within five days of the scheduled day; otherwise, it is recommended to skip the missed dose and resume the regular schedule to maintain consistent blood levels of the medication. Proper planning and adherence are essential to avoid fluctuations in blood glucose levels.
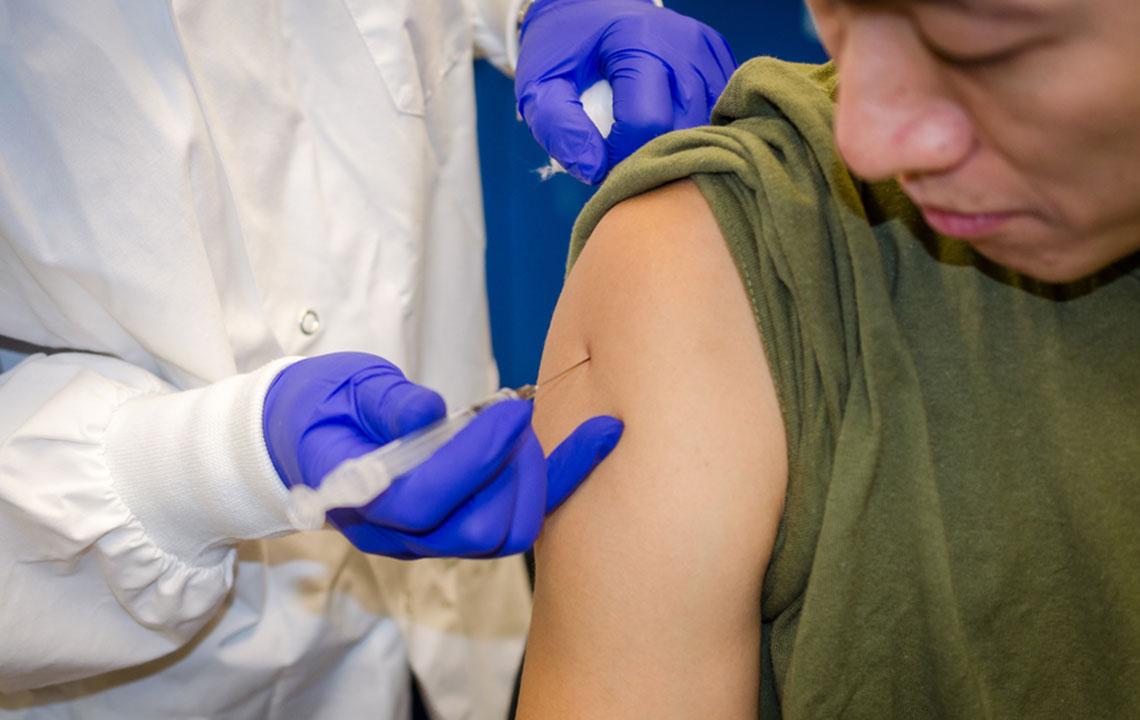
Proper injection technique is vital to ensure safe and effective therapy. Always use a new needle with each injection and avoid sharing your injection pen or needles with others. Inject into specified areas such as the upper arm, abdomen, or thigh, and rotate injection sites weekly to prevent skin irritation or lipodystrophy. Before injecting, inspect the solution; it should be clear and colorless. Do not use the medication if it appears cloudy, discolored, or contains particles. When administering insulin, it is safe to inject into the same area as Ozempic®, provided different needles are used, and injections are spaced adequately apart to avoid tissue damage.
Understanding precautions and contraindications is equally important for safe usage. Patients with a history of diabetic retinopathy, kidney disease, or pancreatic issues should discuss these with their healthcare provider before starting Ozempic®. Pregnant or breastfeeding women, or those planning pregnancy, should seek medical advice prior to use. While no conclusive evidence links Ozempic® directly to harm in pregnancy or lactation, caution is advised, and many providers recommend discontinuing the medication at least two months before conception. Additionally, discuss any other medications you are taking to avoid potential interactions.
It is important to recognize that Ozempic® is specifically approved for managing type 2 diabetes and is not a substitute for insulin therapy in type 1 diabetes. When used appropriately alongside diet and exercise, it can significantly improve glycemic control. Always follow your healthcare provider's instructions regarding dosage adjustments and treatment plans. Do not alter your medication regimen without consultation, and report any adverse effects or concerns promptly. With proper use and monitoring, Ozempic® can be an effective part of comprehensive diabetes management, helping patients achieve better control over their condition and improve their overall quality of life.