Comprehensive Natural Approaches to Lower Cholesterol Levels Effectively
Discover natural and effective strategies to lower your cholesterol through dietary changes, physical activity, and lifestyle modifications. Learn about alternative medications, foods rich in heart-healthy compounds, and practical tips for managing high cholesterol naturally, supporting overall cardiovascular health and well-being.

Comprehensive Natural Approaches to Lower Cholesterol Levels Effectively
High cholesterol, especially elevated LDL cholesterol, poses significant risks to cardiovascular health, including heart attack and stroke. While statins are widely prescribed by healthcare providers to manage high cholesterol, they are not suitable for everyone due to potential side effects or genetic factors that make these medications less effective. Fortunately, there are numerous natural and lifestyle-based strategies that can help you control your cholesterol levels without solely relying on pharmaceuticals. These methods not only support heart health but also promote overall well-being.
In this comprehensive guide, we will explore a variety of proven non-statin options, dietary modifications, and lifestyle changes designed to help lower cholesterol safely and effectively. Whether you're looking for dietary approaches, supplements, or physical activity routines, this article provides detailed insights into managing cholesterol naturally.
Medical Alternatives to Statins
For individuals unable or unwilling to take statins, several alternative medications can be prescribed or considered under medical supervision. These options focus on different mechanisms to reduce LDL cholesterol, with some also enhancing HDL levels or lowering triglycerides. It's crucial to consult a healthcare professional before initiating any medication or supplement to ensure safety and proper management.
Bile Acid Sequestrants
Bile acid sequestrants are a class of drugs that bind bile acids in the digestive system, preventing their reabsorption. Bile acids are made from cholesterol, so when these drugs promote their excretion, the liver is compelled to convert more cholesterol into bile acids. This process effectively decreases LDL cholesterol levels. Common examples include colestipol, cholestyramine, and colesevelam. These medications are effective but may cause side effects like gastrointestinal discomfort, so monitoring and medical guidance are essential.
Ezetimibe
Ezetimibe is a potent medication that inhibits specific proteins responsible for absorbing cholesterol in the intestines. By blocking this absorption, ezetimibe reduces the amount of dietary and biliary cholesterol entering the bloodstream. This mechanism prompts the liver to draw more cholesterol from the blood, further lowering it. Ezetimibe is often used alone or in combination with statins when additional LDL reduction is needed.
Niacin (Vitamin B3)
Niacin, also known as vitamin B3, has been used for many years to improve lipid profiles. It raises high-density lipoprotein (HDL), the “good” cholesterol, and decreases triglycerides and LDL cholesterol. Although it is less potent than some other medications, niacin can be beneficial with fewer side effects, especially when used in controlled doses. However, high doses may lead to flushing, liver issues, or glucose intolerance, so medical oversight is necessary.
Fibrates
Fibrates are medications derived from fibric acid compounds, primarily aimed at lowering triglycerides and VLDL particles. They work by increasing the oxidation of fatty acids in the liver and muscle tissues, reducing triglyceride production. Fibrates like gemfibrozil and fenofibrate are effective for individuals with high triglyceride levels and can aid in improving overall lipid profiles.
Omega-3 Fatty Acids
Omega-3 fatty acids, primarily found in fatty fish such as salmon, mackerel, and sardines, as well as in flaxseeds and walnuts, offer powerful benefits in managing cholesterol. These essential fats help increase HDL and reduce triglycerides, supporting healthy blood lipid levels. Omega-3 supplements, available in capsule form, can be particularly useful for individuals who do not consume enough omega-3-rich foods, contributing to overall cardiovascular health.
It is important to remember that any medication or supplement should be taken under medical supervision. Potential interactions with other medications and individual health conditions must be considered carefully.
Dietary Modifications for Cholesterol Control
Diet plays a pivotal role in managing cholesterol levels naturally. Certain foods contain components that actively support healthy lipid profiles, while others may contribute to elevated cholesterol if consumed excessively. A balanced diet emphasizing natural, minimally processed foods can significantly impact your cholesterol health.
Some important dietary strategies include:
Incorporating Leafy Greens and Vegetables: Spinach, kale, and other leafy greens contain lutein, a carotenoid that prevents cholesterol particles from depositing in arteries, helping maintain clean arteries.
Adding Healthy Fats like Avocado and Olive Oil: Rich in monounsaturated fats, avocados and olive oil help reduce bad cholesterol absorption and promote heart health when used as cooking ingredients or toppings.
Consuming Dark Chocolate: High-quality dark chocolate with over 70% cocoa is packed with antioxidants that support vascular health and combat oxidative stress linked to cardiovascular disease.
Eating Fiber-Rich Foods: Beans, oats, and whole grains contain soluble fiber such as beta-glucan, which binds to cholesterol in the digestive tract and facilitates its excretion, effectively lowering LDL levels.
Incorporating Antioxidant-Rich Beverages and Foods: Green tea, black tea, and red wine contain antioxidants like catechins and resveratrol, which have been shown to support heart health by reducing oxidation of LDL cholesterol.
Using Garlic and Herbs: Garlic contains sulfur compounds that can prevent plaque formation in arteries, adding flavor and health benefits to your dishes.
Moderate Alcohol Consumption: Red wine, in moderation, can provide resveratrol—a compound linked to improved endothelial function and antioxidant properties.
Eating Whole Grains like Oats: Rich in beta-glucan, oats directly absorb LDL cholesterol, making them an excellent breakfast choice.
It is advisable to limit intake of trans fats, processed foods, and added sugars, which can raise LDL levels and contribute to inflammation and arterial damage.
Physical Activity and Lifestyle Changes
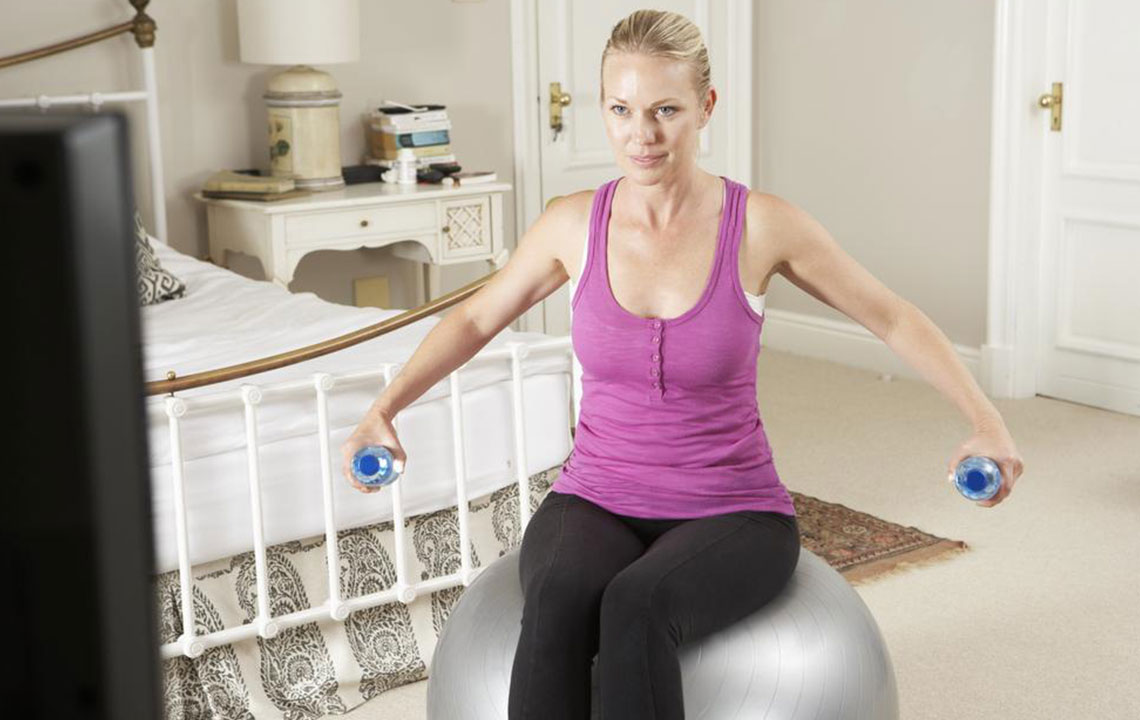
Along with diet, regular physical activity is a cornerstone of natural cholesterol management. Engaging in consistent exercise helps elevate HDL levels, decrease LDL, and reduce triglycerides. Engaging in at least 150 minutes of moderate activity per week is recommended by health authorities, including activities like brisk walking, cycling, swimming, or playing sports.
Incorporating strength training exercises, such as weightlifting or resistance workouts, can further enhance metabolic rate and improve lipid profiles. Moreover, maintaining an active lifestyle, managing stress through mindfulness or meditation, and avoiding smoking all contribute positively to cardiovascular health.
Adopting these natural approaches can help you control high cholesterol without solely relying on medications, promoting a healthier heart and a longer, more vibrant life.