Comprehensive Guide to Managing Gout: Natural Remedies and Effective Strategies
This comprehensive guide explores effective strategies and natural remedies for managing gout. It emphasizes the importance of medication, lifestyle adjustments, and dietary modifications to reduce uric acid levels, prevent flare-ups, and promote joint and kidney health. The article provides practical tips for controlling gout, highlights the role of natural supplements, and underscores the need for professional medical advice for persistent cases. Whether you're experiencing an acute attack or seeking long-term management, this in-depth resource offers valuable insights to help you maintain better gout control and improve overall health.

Comprehensive Guide to Managing Gout: Natural Remedies and Effective Strategies
Essential insights into the management and treatment options for gout
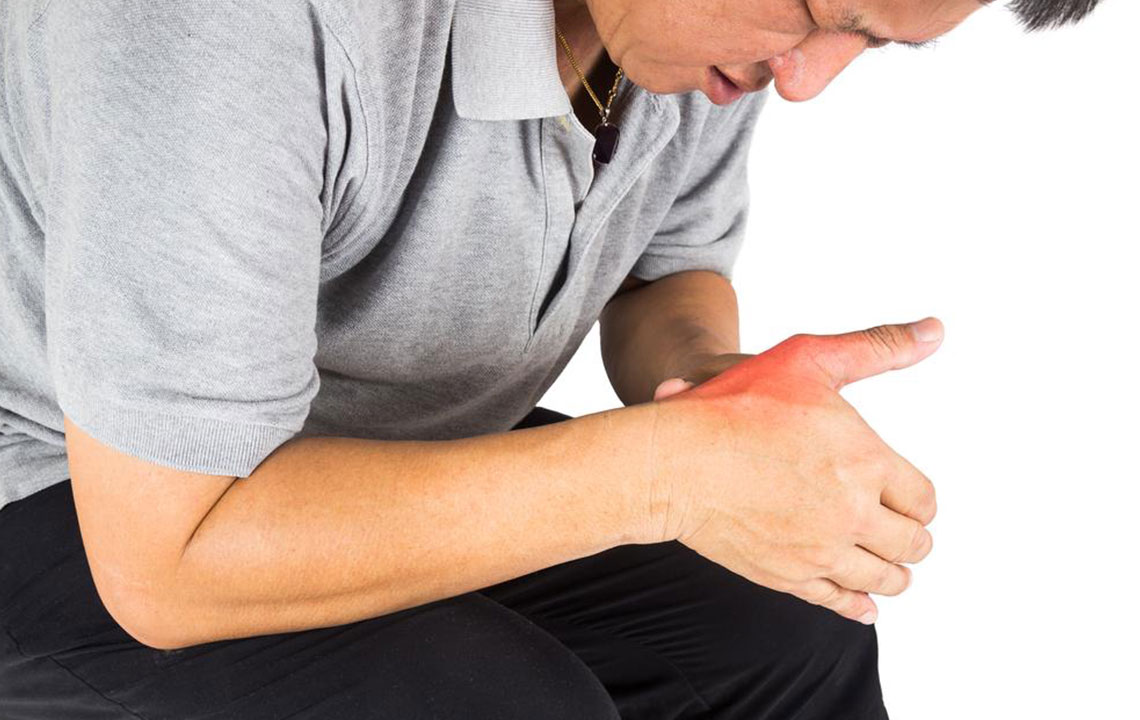
Gout is one of the most common forms of inflammatory arthritis affecting millions worldwide. Characterized by sudden, intense pain, swelling, redness, and warmth in a joint—most frequently the big toe—gout occurs due to the accumulation of uric acid crystals in the joint space. These needle-like crystals trigger rapid inflammation, leading to episodes that can be debilitating. Typically, a gout attack lasts between 36 hours and ten days, often resolving spontaneously or with appropriate treatment. Proper diagnosis often involves extracting synovial fluid from the affected joint and examining it under a microscope to identify uric acid crystals, which confirms the condition.
Effective management of gout hinges on reducing uric acid levels in the body, primarily through a combination of medication and lifestyle modifications. Failing to control uric acid levels can lead to persistent joint damage, formation of tophi (hard uric acid crystal deposits under the skin), kidney stones, and impaired kidney function. To prevent recurring attacks and long-term complications, it is crucial to understand and implement both pharmacologic and natural strategies. These approaches focus on targeting the underlying causes, minimizing flare-ups, and promoting overall joint and kidney health.
Medications play a vital role in gout management. Commonly prescribed drugs include NSAIDs such as ibuprofen or naproxen, which provide quick pain relief during acute episodes. Corticosteroids, either taken orally or injected directly into the joint, are also effective for reducing inflammation. Colchicine remains a mainstay for both acute and preventive therapy. For long-term management, healthcare providers may recommend urate-lowering medications like allopurinol, febuxostat, and probenecid. These drugs aim to decrease uric acid production or increase its excretion via the kidneys. In resistant or severe cases, newer options like lesinurad and pegloticase can be employed to control uric acid levels more effectively.
Aside from medication, lifestyle modification is paramount. Maintaining a healthy weight through regular exercise and balanced nutrition reduces the risk of flare-ups. Dietary adjustments include limiting foods rich in purines—such as red meat, organ meats, and certain seafood—while increasing intake of vegetables, low-sugar fruits, and whole grains. Staying well-hydrated by drinking plenty of water helps flush out excess uric acid. Avoiding alcohol, especially beer and spirits, is essential, as alcohol can inhibit uric acid excretion. Additionally, managing comorbid conditions like hypertension, diabetes, and kidney disease is critical, as they are linked to higher uric acid levels and gout risk.
Natural remedies and supplementary approaches can complement conventional treatments. For example, cherry extract and cherry juice have anti-inflammatory properties and are believed to reduce gout attacks. Incorporating herbs like turmeric and ginger, known for their anti-inflammatory effects, can also be beneficial. Regular consumption of omega-3 fatty acids from fish oil may help decrease joint inflammation. Furthermore, ensuring adequate hydration and reducing intake of processed foods high in sugar and trans fats support overall health and gout prevention. Patients with chronic gout should also consider adopting stress management techniques, as stress can trigger flare-ups.
In cases of persistent or recurrent gout, collaboration with a healthcare professional or specialist is essential for tailoring a comprehensive management plan. Monitoring uric acid levels periodically allows for adjustments in medication dosage and lifestyle strategies. Patient education on recognizing early signs of a flare-up can enable prompt treatment, reducing severity and duration. Ultimately, a combination of prescribed medications, dietary modifications, natural remedies, and lifestyle changes can lead to effective long-term control of gout, improving quality of life and preventing serious complications.