Comprehensive Guide to Managing Cholesterol for Optimal Heart Health
Learn how to effectively manage your cholesterol levels to promote heart health. This comprehensive guide covers essential dietary tips, lifestyle changes, and medical advice to help prevent cardiovascular diseases. Discover how HDL and LDL function, what the ideal blood cholesterol levels should be, and practical strategies for maintaining a healthy balance. Incorporate heart-healthy foods, exercise routines, and lifestyle modifications to protect your arteries and reduce the risk of heart-related conditions. Stay informed with expert recommendations for sustainable cholesterol management for long-term wellness.
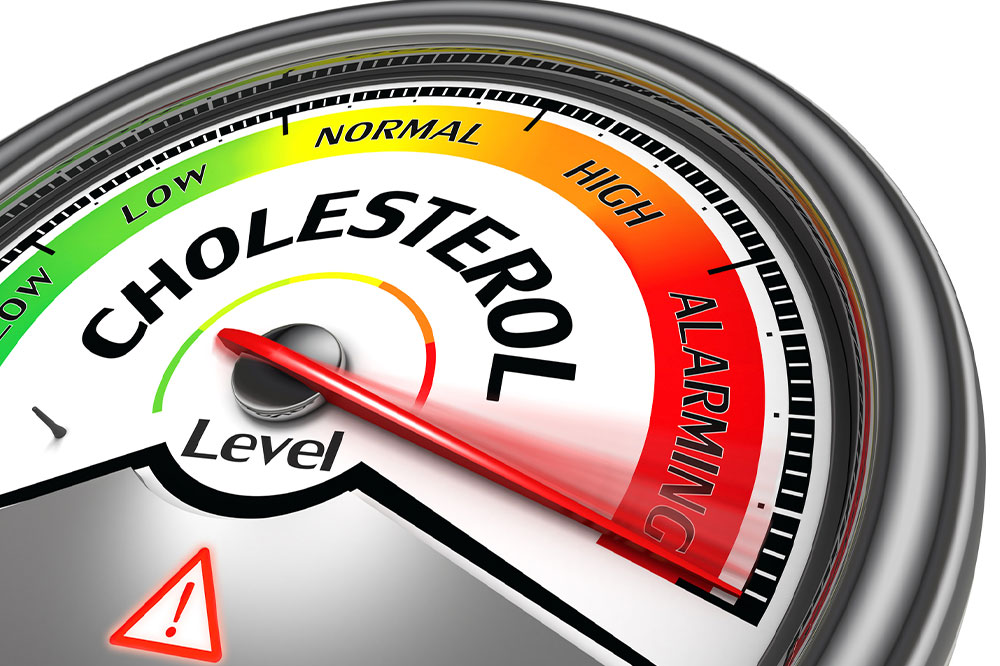

Understanding Cholesterol: Essential Knowledge for Heart Wellness
Cholesterol, a waxy, fat-like substance found in all human cells, holds a vital position in maintaining various physiological functions. Its name, originating from Greek roots meaning "bile" and "solid," highlights its structural and functional significance within the body. While often associated with negative health impacts, cholesterol is crucial for synthesizing hormones such as estrogen, testosterone, and cortisol, as well as vitamin D production and the formation of digestive bile acids. The human body predominantly produces its own cholesterol in the liver; however, dietary choices also influence blood cholesterol levels. Consuming foods high in cholesterol and saturated fats can elevate blood cholesterol, increasing the risk of cardiovascular diseases. Therefore, maintaining balanced cholesterol levels is fundamental for heart health and overall well-being.
Excessive intake of dietary cholesterol, particularly from processed foods and animal products, can lead to elevated blood cholesterol levels. Such increases heighten the risk of developing arteriosclerosis—a condition characterized by the hardening and narrowing of arteries—which can ultimately lead to heart attacks and strokes. Despite its essential role, cholesterol must be kept within healthy ranges to prevent plaque buildup within arterial walls.
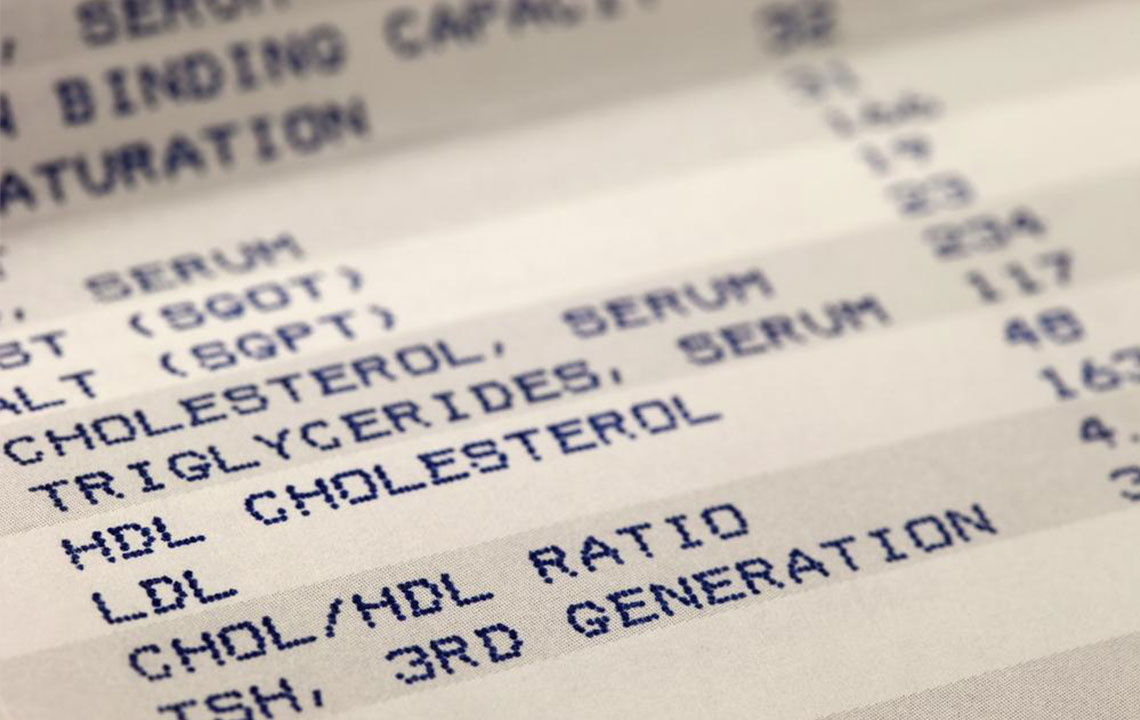
Cholesterol particles travel throughout the bloodstream via specialized carriers known as lipoproteins. These include high-density lipoproteins (HDL), often labeled as "good" cholesterol, and low-density lipoproteins (LDL), known as "bad" cholesterol. HDL helps to carry excess cholesterol away from arteries to the liver for processing and elimination, thereby protecting cardiovascular health. Conversely, LDL can deposit cholesterol in arterial walls, contributing to plaque formation and narrowing of blood vessels.
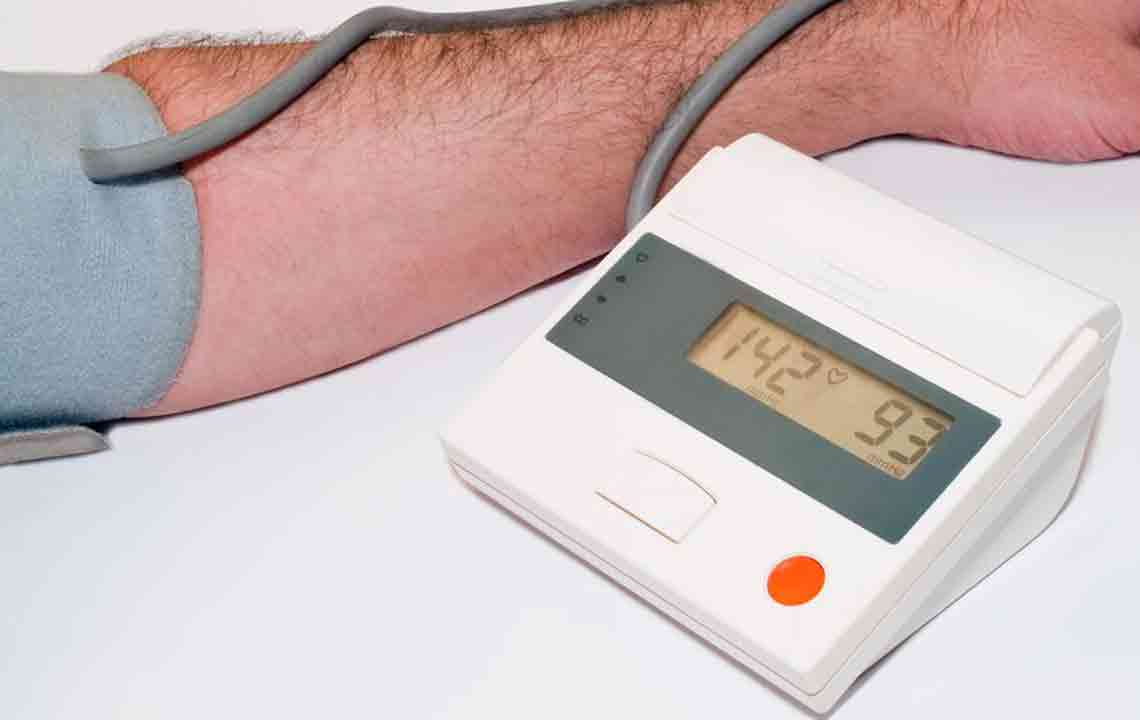
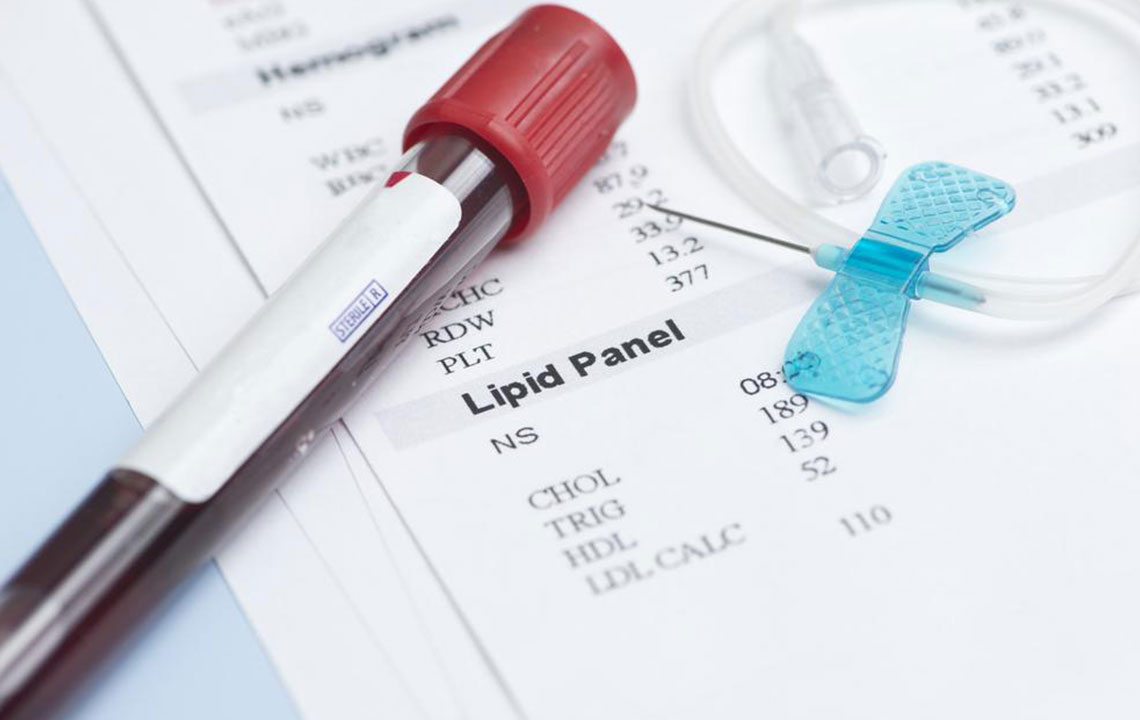
Regular blood testing to measure LDL and HDL levels provides vital insights into cardiovascular risk. Ideally, LDL cholesterol should remain below 100 mg/dL, while HDL levels should be maintained between 40 and 60 mg/dL for optimal protection. Lifestyle modifications that promote higher HDL levels and lower LDL are essential components of cholesterol management.
Effective strategies for controlling cholesterol include adopting a diet rich in soluble fiber—found in oats, legumes, fruits, and vegetables—which helps reduce LDL cholesterol. Limiting intake of trans fats, commonly present in processed snacks and fried foods, is crucial. It is also recommended to moderate saturated fat consumption from red meats, full-fat dairy, and processed meats. Incorporating heart-healthy foods such as nuts, fatty fish rich in omega-3 fatty acids, and extra-virgin olive oil can actively improve cholesterol profiles.
In addition to dietary adjustments, lifestyle approaches significantly impact cholesterol levels. Regular aerobic exercise like brisk walking, cycling, or swimming aids in raising HDL and lowering LDL. Maintaining a healthy weight through balanced nutrition prevents cholesterol imbalance. Strategies such as using spices like garlic and turmeric, enjoying moderate amounts of red wine, and consuming dark chocolates with high cocoa content are recognized for their potential cardioprotective effects. Substituting soy-based products for fatty meats and increasing fiber intake through beans and lentils further support heart health. For individuals struggling with persistently high cholesterol despite lifestyle changes, consulting healthcare professionals for medication options remains a prudent step.