Comprehensive Guide to Identifying and Treating Yeast Infection Sites
This comprehensive article explores common sites of yeast infections, such as skin folds, feet, and internal areas, explaining their causes, symptoms, prevention, and treatment options. It emphasizes the importance of hygiene and timely medical intervention, especially for vulnerable populations like infants, breastfeeding mothers, and immunocompromised individuals. Readers will learn practical advice for managing and preventing yeast infections, ensuring better health and comfort. The guide covers various infection types, highlighting effective over-the-counter remedies and when to seek medical help for more complex cases.

Comprehensive Guide to Identifying and Treating Yeast Infection Sites
Yeast infections, also known as candidiasis, are common fungal infections that can affect various parts of the body. One of the primary reasons these infections occur is due to excess moisture on the skin, which creates an ideal environment for fungal overgrowth. When the immune system becomes weakened—whether due to illness, stress, or underlying health conditions—the body’s ability to combat these fungi diminishes, increasing the likelihood of infection. Those with compromised immunity, such as individuals with diabetes, are especially vulnerable to these infections. Recognizing the specific sites affected and understanding appropriate treatment strategies are crucial steps toward effective management and relief.
Understanding Different Types of Yeast Infections and Prevention Methods
Yeast infections can manifest in a variety of body parts, each presenting unique symptoms and requiring tailored approaches for management. Here, we explore the most common infection sites, preventive measures, and treatment options for each.
Skin Folds and Intertriginous Areas: Skin folds—such as underarms, groin, or neck—are common spots where yeast thrives due to trapped moisture and warmth. Persistent dampness can lead to redness, itching, and skin breakdown. Applying antifungal creams like miconazole or clotrimazole helps resolve these infections. For extensive cases, a healthcare provider may prescribe oral antifungal medications to speed up recovery. To prevent recurrence, keeping these areas dry, clean, and well-ventilated is essential. Wearing loose, breathable clothing and using powders designed to absorb moisture can significantly reduce the risk.
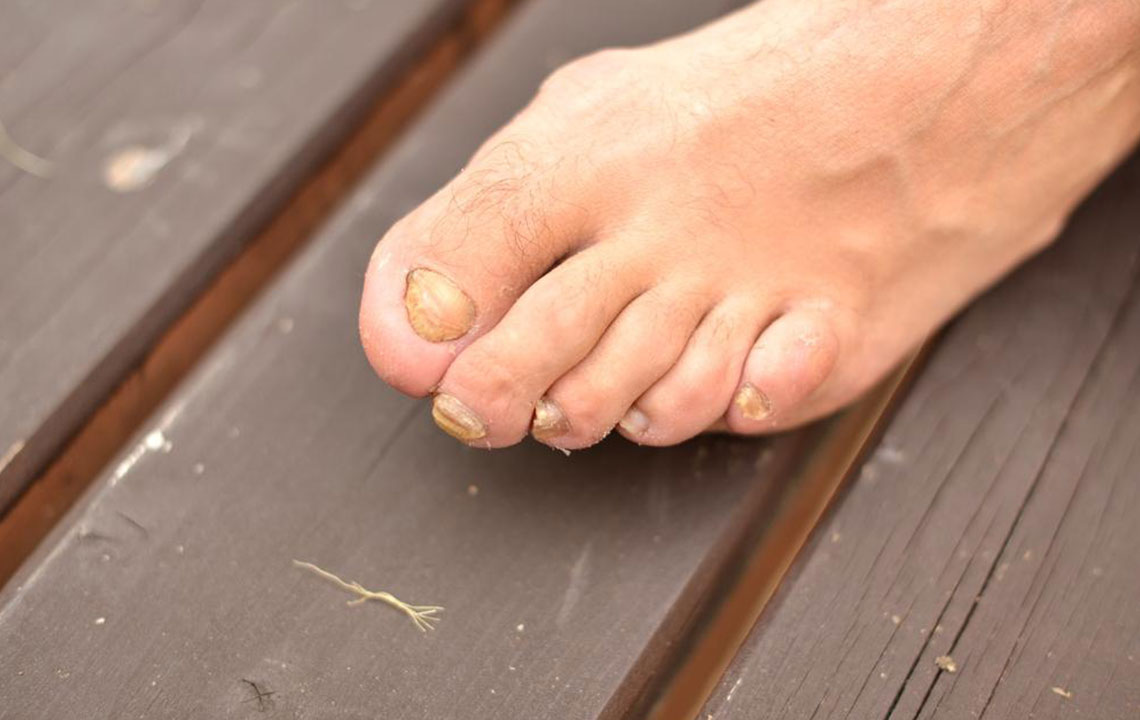
Fungal Infections on Feet (Athlete’s Foot): Feet, particularly between the toes, are prone to fungal infections due to sweating and inadequate drying. Athlete’s foot presents with scaling, redness, and itching, which can be managed with over-the-counter antifungal creams, powders, or sprays. Maintaining good foot hygiene, regularly changing socks, and wearing moisture-wicking footwear are vital preventive tips.
Oral Thrush in Infants: Young children, especially those bottle-fed, can develop oral thrush caused by Candida fungi, often from milk residues remaining in the mouth. Symptoms include white patches on the tongue and inside of the cheeks. Pediatricians typically prescribe oral antifungal medications, which should be used until the infection clears completely. Ensuring proper sterilization of feeding bottles and maintaining good oral hygiene are key preventive measures.
Yeast Infections in Breastfeeding Women: Due to increased moisture and alteration in pH levels, breastfeeding mothers are susceptible to yeast infections under the breasts and other fold areas. Symptoms include redness, itching, and discomfort. Benefits of maintaining hygiene, wearing breathable nursing bras, and ensuring proper drying after feeds cannot be overstated. Mild cases can be treated with topical antifungal creams, while severe or recurrent infections may require medical consultation for additional treatment options.
Yeast Infections in Immunocompromised Individuals: People undergoing chemotherapy, living with autoimmune diseases, or on immunosuppressive drugs face a higher risk. These individuals may develop yeast infections in the throat, esophagus, or other internal sites. Recognizing early symptoms and seeking prompt medical attention are crucial, as infections can be more severe and complex to treat in these patients.
Vaginal Candidiasis: This common yeast infection among women often stems from poor hygiene, contaminated environments, or imbalance of natural flora. Symptoms include itching, burning, abnormal discharge, and soreness. Treatment typically involves topical antifungal creams like Monistat or suppositories, used consistently over 3-7 days to ensure complete eradication. Proper hygiene practices, avoiding scented products, and wearing breathable cotton underwear help reduce incidence. Antibiotics, when necessary, should be taken under medical supervision, and taking fluconazole at the start and end of antibiotic therapy can prevent overgrowth.
Impact of Antibiotics and Self-Care: Antibiotics, while essential for bacterial infections, can disturb the balance of healthy bacteria in the body, creating opportunities for yeast to proliferate. To mitigate this, healthcare providers often recommend completing courses of antifungal medication concurrently with antibiotics if necessary. Maintaining good hygiene, avoiding unnecessary antibiotic use, and dietary adjustments can further support balance. Importantly, yeast infections are not classified as sexually transmitted diseases and can occur independently of sexual activity.
In conclusion, yeast infections are widespread and can affect many areas of the body. Recognizing the signs early and understanding the differences in natural defenses across body sites are vital for effective prevention and treatment. If symptoms persist or worsen, consulting a healthcare professional is advisable to determine the best course of action. With proper hygiene practices, timely intervention, and appropriate medications, most yeast infections can be swiftly and successfully managed, restoring comfort and health.