Comprehensive Overview of Ozempic: A Breakthrough Treatment for Type 2 Diabetes Management
Ozempic is a pioneering injectable medication for type 2 diabetes that effectively controls blood sugar levels by mimicking natural hormones. This comprehensive guide covers dosing, injection techniques, precautions, and best practices, helping patients manage their condition safely and efficiently. Proper use of Ozempic® can lead to improved health outcomes, weight management, and better quality of life. Always consult your healthcare provider for personalized advice to ensure optimal results with this innovative treatment.
Understanding Ozempic: A Crucial Medication for Controlling Type 2 Diabetes
Managing type 2 diabetes effectively requires a combination of lifestyle modifications and medication. For many patients, traditional oral medications may not achieve optimal blood sugar control. In such cases, healthcare providers often turn to innovative injectable treatments like Ozempic® (semaglutide). This medication has revolutionized the approach to managing blood glucose levels, offering a potent solution for patients struggling with conventional therapies. Ozempic® is part of the GLP-1 receptor agonist class of drugs, which work by mimicking the body's natural incretin hormones to enhance insulin secretion and suppress glucagon release, thereby stabilizing blood sugar and aiding weight management.
Learn about the recommended dosing regimen for Ozempic® in managing type 2 diabetes and how to administer it safely and effectively for optimal outcomes.
Effective Ozempic® Dosing for Optimal Blood Sugar Control
**Starting Dose:** Typically, patients begin with an initial dose of 0.25 mg administered once weekly via subcutaneous injection. This initial dose is primarily designed to familiarize the body with the medication and reduce potential gastrointestinal side effects. The first four weeks allow for gradual titration, helping patients to adapt to the treatment.
**Dose Escalation:** After the initial period, if blood glucose levels remain inadequately controlled, healthcare providers usually increase the dose to 0.5 mg per week. This dose is often sufficient for many patients to achieve meaningful improvements in blood sugar management.
**Maximum Dose:** For some patients, further dose escalation to 1 mg per week may be necessary, especially if blood sugar targets are not met with lower doses. This is generally considered the highest recommended dose of Ozempic® and should only be prescribed under medical supervision.
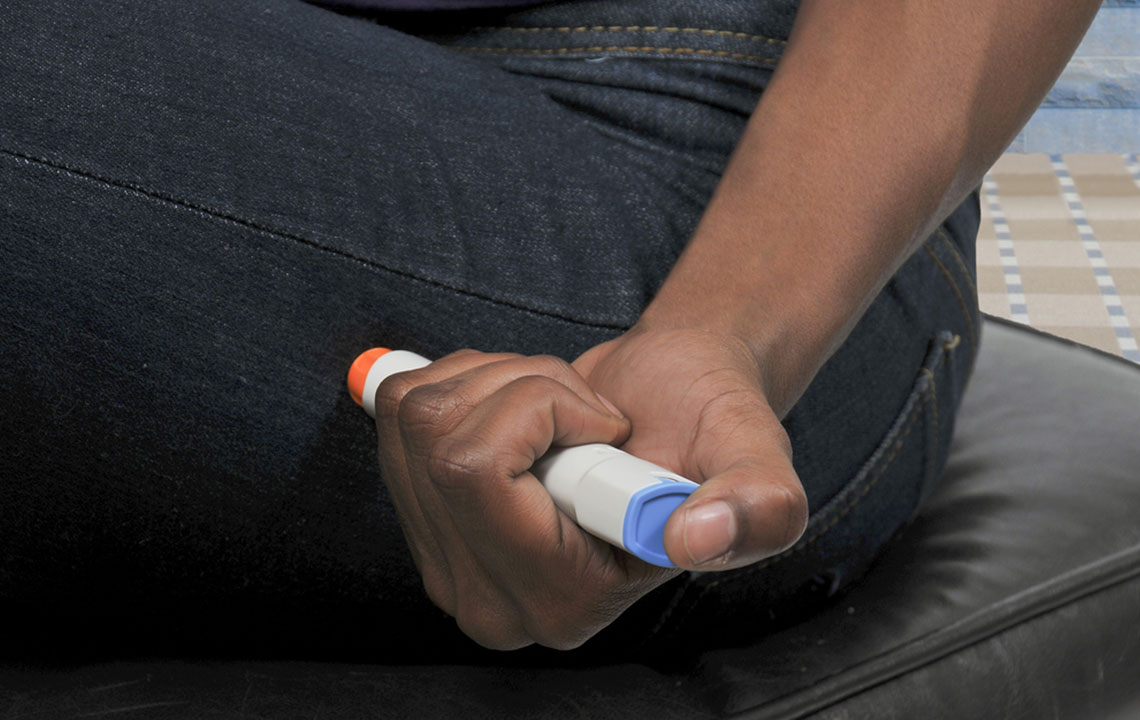
**Consistency is Key:** To maximize efficacy, administer your weekly injection on the same day each week. While the timing can be flexible—either with or without meals—maintaining a routine helps ensure steady medication levels in the body.
**Adjusting Injection Days:** If needed, you can change your injection day, provided there is at least a 48-hour gap between doses. This flexibility helps accommodate your daily schedule without compromising treatment efficacy.
**Missed Dose Protocol:** If you miss a dose within five days of the scheduled time, you can take it as soon as possible. However, if more than five days have passed, skip the missed dose and resume your regular schedule. Do not double doses to make up for missed injections.
**Precautions for Safe Use:** Never share your Ozempic® pen with others, as this can increase the risk of infections. Also, reuse of needles is strongly discouraged to prevent contamination and injury.
Pre-Treatment Considerations and Precautions with Ozempic®
Before initiating therapy with Ozempic®, discuss your full medical history with your healthcare provider, especially regarding pancreatic health, kidney function, and any history of diabetic retinopathy, a diabetic eye condition that can affect treatment choices.
Women who are pregnant, planning pregnancy, or breastfeeding should seek medical advice before starting Ozempic®. Since the medication is not recommended during these periods, your doctor may suggest alternative treatments or strategies.
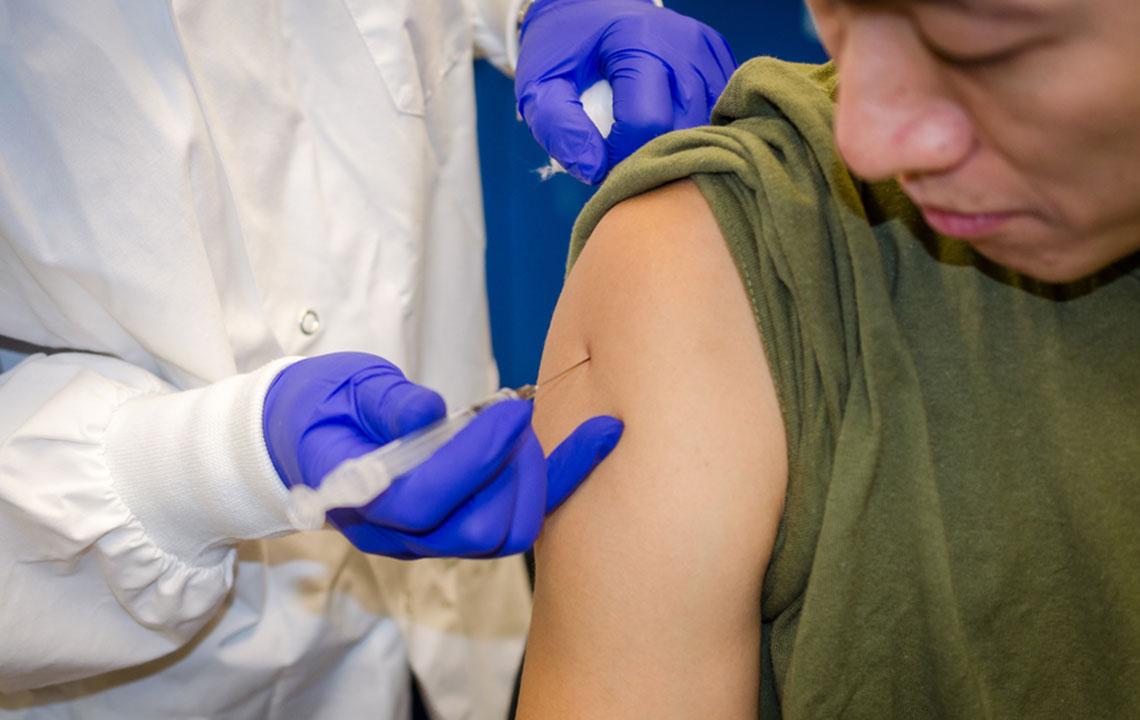
Proper Technique for Ozempic® Injections
Injection sites should be rotated weekly among the abdomen, upper arm, or thigh to prevent skin irritation and tissue damage. Consistent site rotation avoids localized side effects and ensures comfort.
Prior to injection, inspect the medication to ensure it is clear, colorless, and free from particles. Discard any contaminated or unusual medication.
If you are also using other injectable medications like insulin, keep the injections separate and ensure they are administered at different sites or with adequate spacing, even if in the same area, to reduce the risk of adverse reactions.
The primary purpose of Ozempic® is to assist in managing blood glucose levels in type 2 diabetes patients. It is not a replacement for insulin therapy nor suitable for treating type 1 diabetes. When used correctly alongside a proper diet and regular exercise, Ozempic® can significantly improve glycemic control and support weight loss efforts. Always consult your healthcare provider for guidance on the right dosage and administration techniques, and never hesitate to ask questions about your treatment plan to ensure safe and effective diabetes management.