Comprehensive Guide to Arthritis: Types, Symptoms, and Effective Management Strategies
This comprehensive article explores the main types of arthritis, including rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis. It offers insights into symptoms and effective management strategies such as medication, physical therapy, and surgery. Understanding these aspects helps patients make informed decisions for better joint health and quality of life. Recognizing early signs and seeking timely treatment are key components to managing this widespread condition effectively.
Comprehensive Guide to Arthritis: Types, Symptoms, and Effective Management Strategies
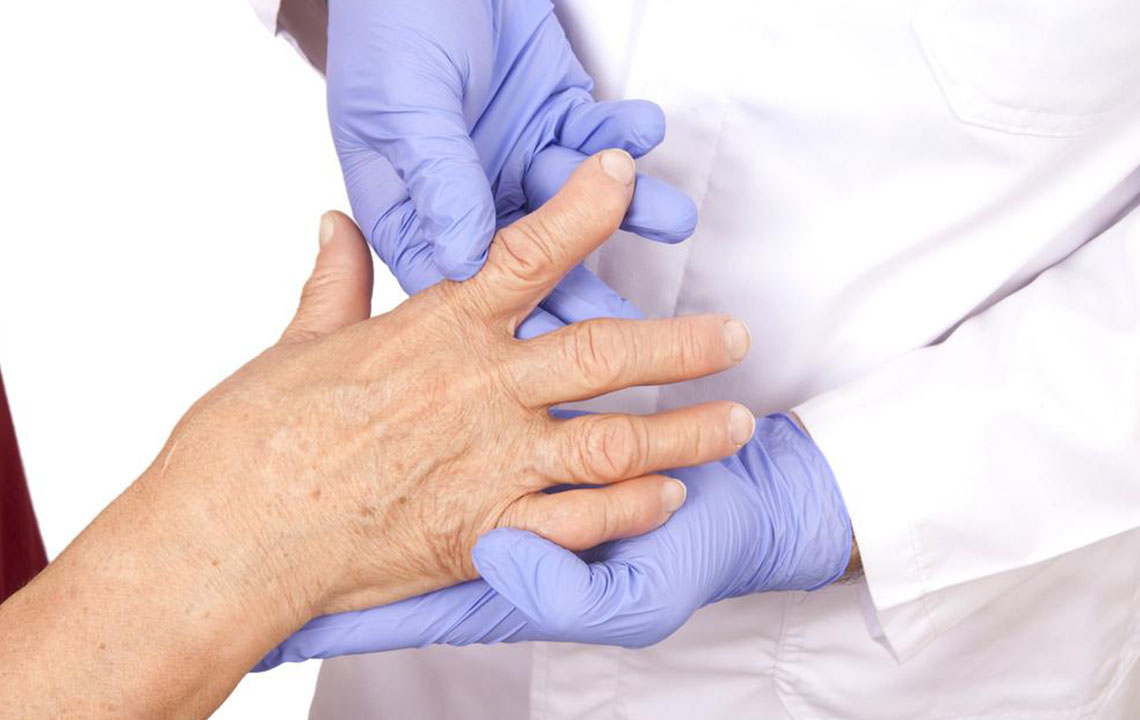
Arthritis is a common joint disorder characterized by inflammation that affects millions of people worldwide. It predominantly targets the joints, especially the knees, but can also impact other areas such as the hips, hands, and spine. This condition is a significant cause of disability and discomfort, often impairing daily activities and reducing quality of life. Understanding the various types of arthritis, their symptoms, and the available management options is crucial for those affected by this condition.
Arthritis can arise from multiple factors, including genetics, lifestyle choices, injury, and aging. Recognizing the specific type of arthritis you have is essential because it influences treatment strategies and long-term management plans. Among the most common forms are rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis, each with distinct characteristics, causes, and progression patterns.
Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA)
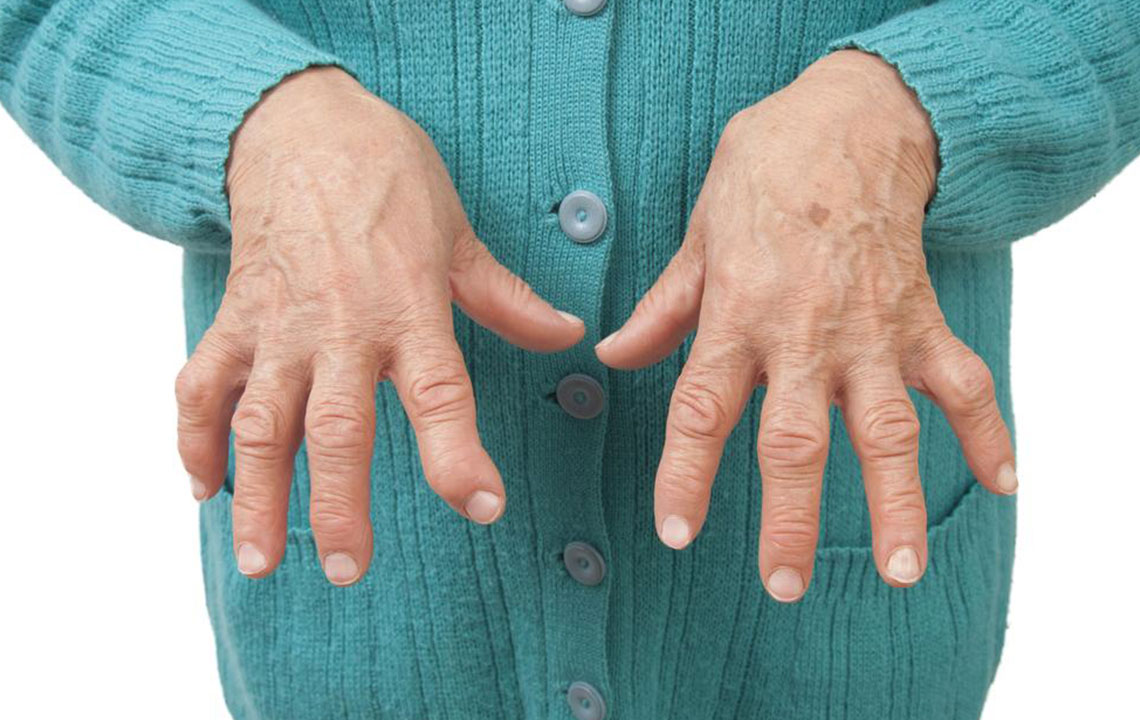
This autoimmune disease occurs when the immune system mistakenly attacks the synovial lining of the joints, leading to inflammation, swelling, and pain. RA often affects joints symmetrically, meaning if one knee is affected, the other likely is too. Over time, chronic inflammation can cause joint deformity, erosion of cartilage and bone, and loss of function. Initially, joint stiffness and pain may be subtle but tend to worsen with time, especially after periods of inactivity such as overnight or prolonged sitting.
Symptoms and Progression of RA
Patients may experience joint redness, warmth, swelling, and tenderness. Morning stiffness lasting more than an hour is typical. The disease often impacts other organs and can cause systemic symptoms such as fatigue, fever, and weight loss. Early diagnosis and treatment are vital to prevent irreversible joint damage and improve outcomes.
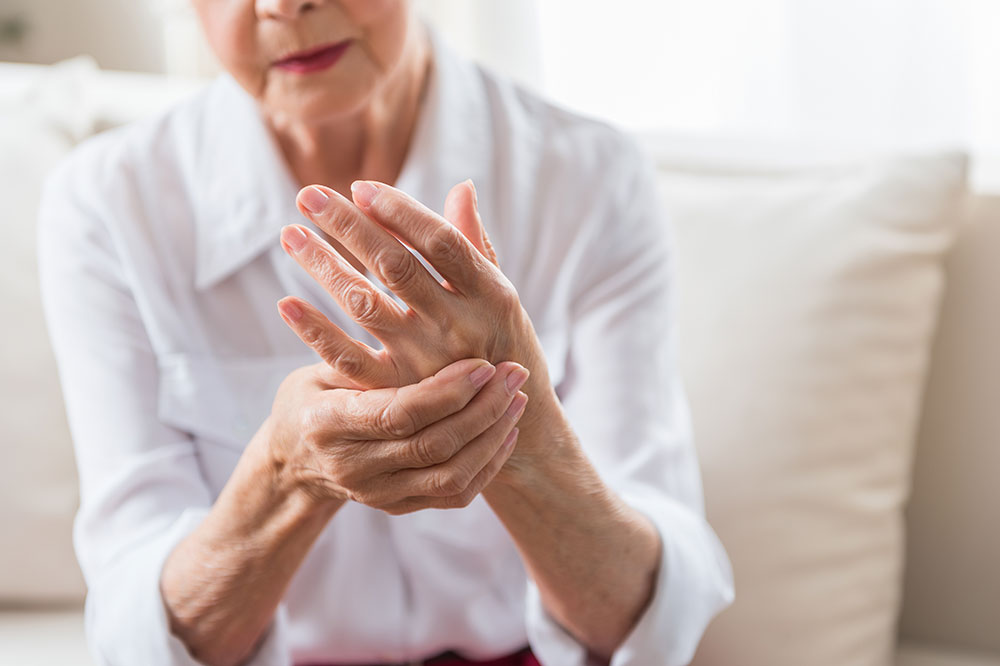
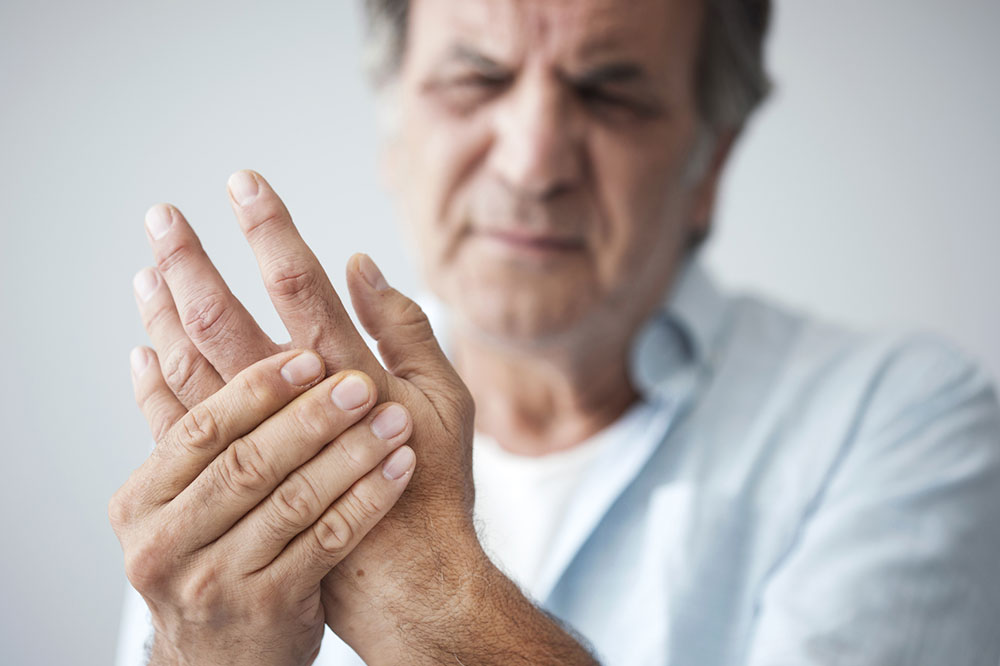
Another prevalent form of arthritis is osteoarthritis (OA), which mainly results from mechanical wear and tear of the joints over time. It is often associated with aging, injury, or repetitive stress, leading to cartilage deterioration—the smooth tissue that cushions the ends of bones within joints. As cartilage breaks down, bones may rub against each other, causing pain and stiffness.
Osteoarthritis primarily affects weight-bearing joints such as knees, hips, feet, and the spine. Its symptoms include joint pain, stiffness, reduced flexibility, and sometimes swelling. The pain tends to worsen with activity and improve with rest, but in advanced stages, even minimal movement can be painful.
Managing osteoarthritis involves multiple strategies aimed at reducing inflammation, alleviating pain, and improving joint function. Non-pharmacological approaches like physical therapy, weight management, and exercise play a vital role. Medications such as NSAIDs (Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs) can help control symptoms. In severe cases or when conservative treatments fail, surgical options like joint replacement therapy are considered.
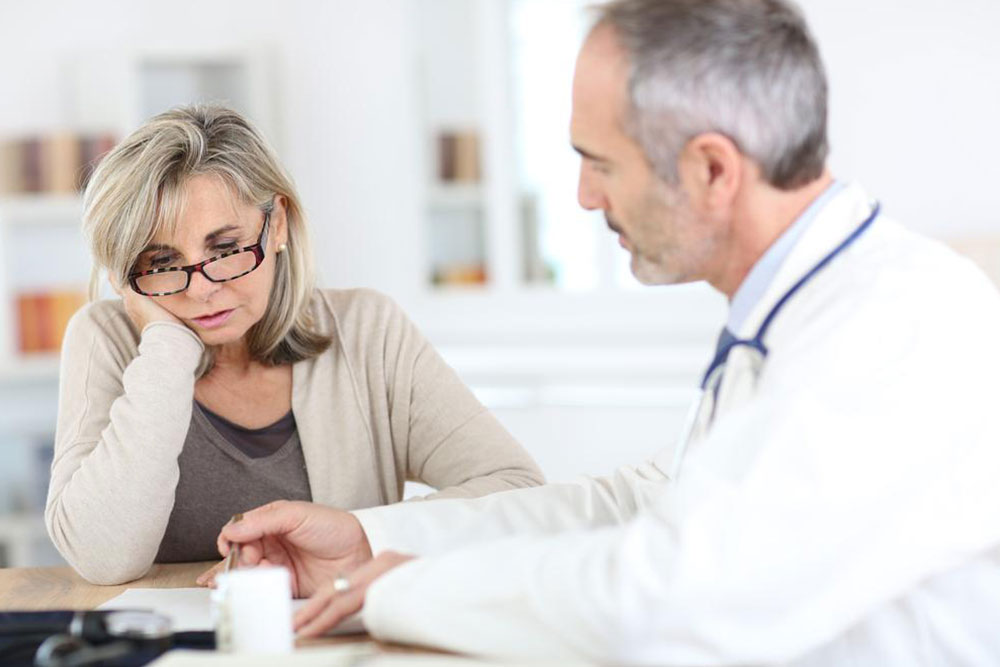
It is essential for individuals with arthritis to work closely with healthcare providers to tailor treatment plans that suit their specific needs and lifestyle. Early intervention and an integrated approach can significantly improve quality of life and slow disease progression.