Comprehensive Guide to Neuropathy: Recognizing Symptoms and Exploring Effective Treatments
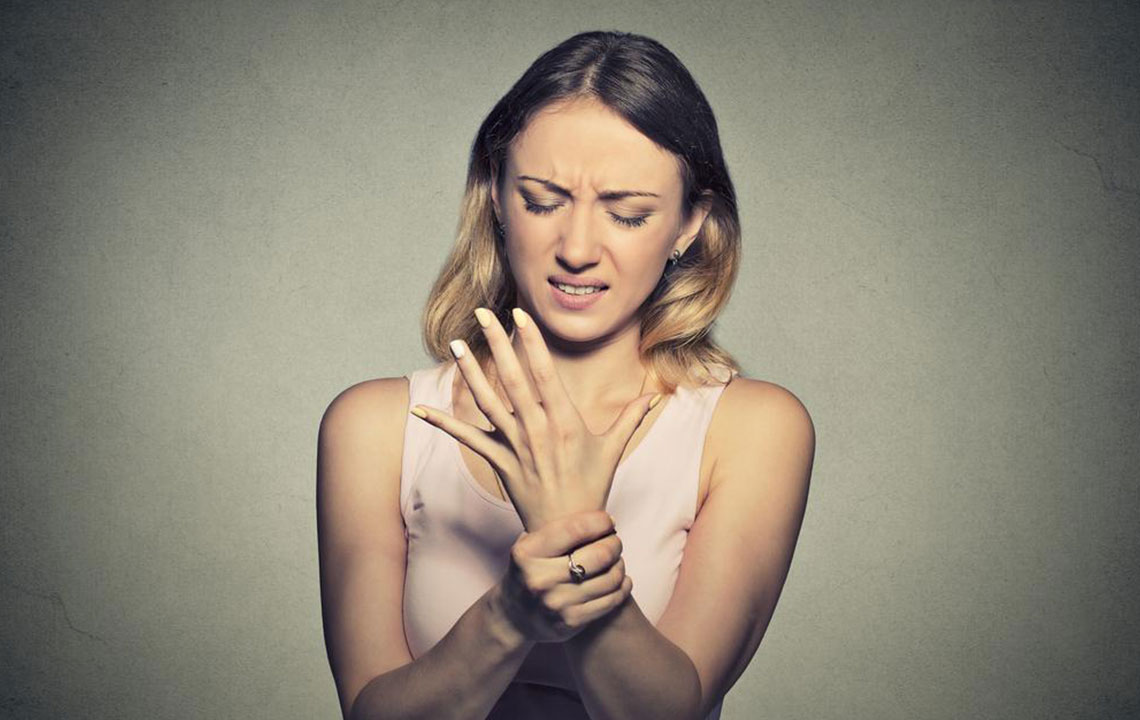
Neuropathy is a complex nerve disorder with diverse symptoms like tingling, numbness, pain, and muscle weakness. Recognizing early signs and understanding treatment options such as medication, lifestyle changes, and therapy can significantly improve quality of life. This extensive guide explores causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and tailored treatments for neuropathy, emphasizing the importance of early intervention for better outcomes. Whether caused by diabetes, injury, or other factors, timely management helps prevent further nerve damage and enhances recovery potential, making awareness vital for those at risk.
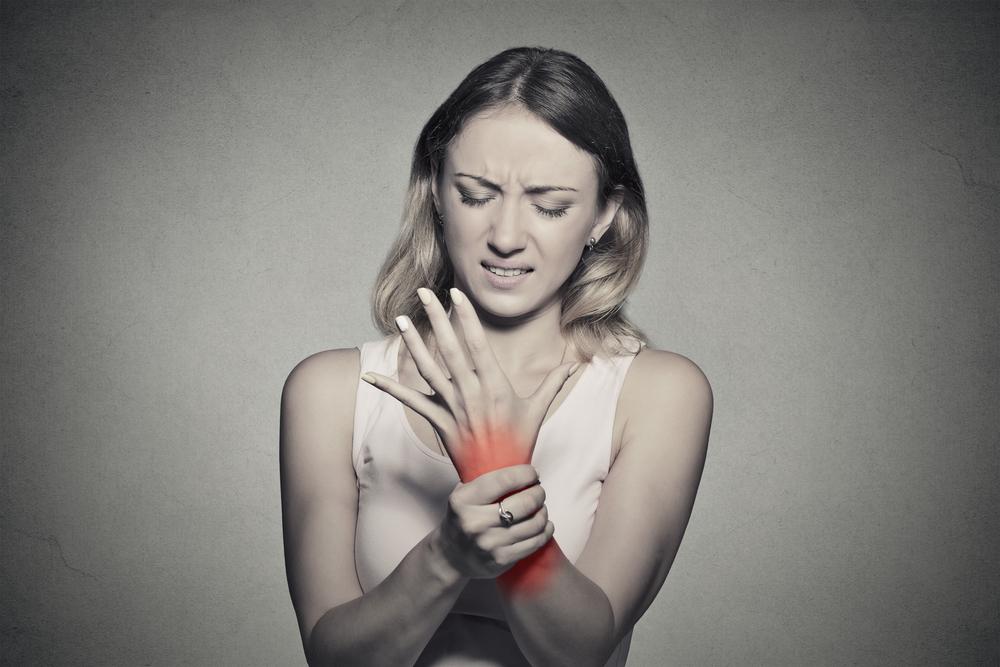

Comprehensive Guide to Neuropathy: Recognizing Symptoms and Exploring Effective Treatments
Neuropathy Explained: Symptoms, Causes, and Treatment Strategies
Our nervous system is a complex and vital network that governs many essential functions within the human body. When this network functions optimally, it ensures smooth coordination of movement, sensation, and various autonomic processes. However, when nerves become damaged or malfunction, it can lead to a range of health problems collectively known as neuropathy. This condition encompasses a spectrum of nerve disorders that can affect any part of the body, resulting in various symptoms depending on the nerves involved and the severity of the damage.
Neuropathy is not a single disease but rather a broad category of nerve impairments caused by multiple factors, including chronic illnesses like diabetes, traumatic injuries, infections, toxic exposures, and certain inherited conditions. Proper diagnosis is crucial since treatment approaches differ based on the underlying cause. Early identification of symptoms can significantly improve prognosis and quality of life. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the signs of neuropathy, its possible causes, diagnostic procedures, and the most effective treatment options available today.
Neuropathy symptoms can vary greatly, making early recognition challenging but essential. Common manifestations include sensory disturbances such as tingling, numbness, burning sensations, and pain, typically starting in the feet and lower legs before ascending to other parts of the body. Patients often report difficulty sensing temperature changes or recognizing limb positions, leading to increased risk of injuries and falls. Additional symptoms may involve muscle weakness, cramps, and decreased reflexes. In cases where motor nerves are affected, muscle wasting and weakness become apparent. When autonomic nerves are involved, symptoms like dizziness, abnormal sweating, nausea, urinary difficulties, erectile dysfunction, and vision disturbances can occur. Recognizing these signs early is instrumental in preventing further nerve deterioration and managing the condition effectively.
Managing neuropathy requires a multidisciplinary approach, often involving neurologists, endocrinologists, physical therapists, and other healthcare professionals. Accurate diagnosis relies on a detailed medical history, physical examination, and specialized tests such as nerve conduction studies, electromyography (EMG), blood tests, and sometimes nerve biopsies. Once the underlying cause is identified, tailored treatment plans can be developed. For example, vitamin deficiencies are addressed with appropriate supplementation, and dietary modifications that emphasize nutrient-rich, anti-inflammatory foods can support nerve repair. Medications prescribed may include pain relievers, anticonvulsants, antidepressants, or topical agents to alleviate nerve pain. Avoiding exposure to neurotoxins, controlling chronic illnesses like diabetes, and lifestyle modifications such as exercise and quitting smoking are critical in minimizing nerve damage progression. In some cases, physical therapy enhances muscle strength and coordination, while surgical interventions may be necessary for nerve compression or injury repair. The goal of treatment is to reduce symptoms, slow disease progression, and improve overall nerve function and quality of life.
Early detection of neuropathy symptoms and timely intervention are key to better outcomes. If you or someone close to you experiences signs of nerve damage, seeking immediate medical attention is crucial. Proper management not only alleviates discomfort but can also prevent irreversible nerve damage. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options, individuals can take proactive steps toward nerve health and overall well-being. Remember, advancements in medical science continue to offer new hope for those affected by this potentially debilitating condition.